Space news stories
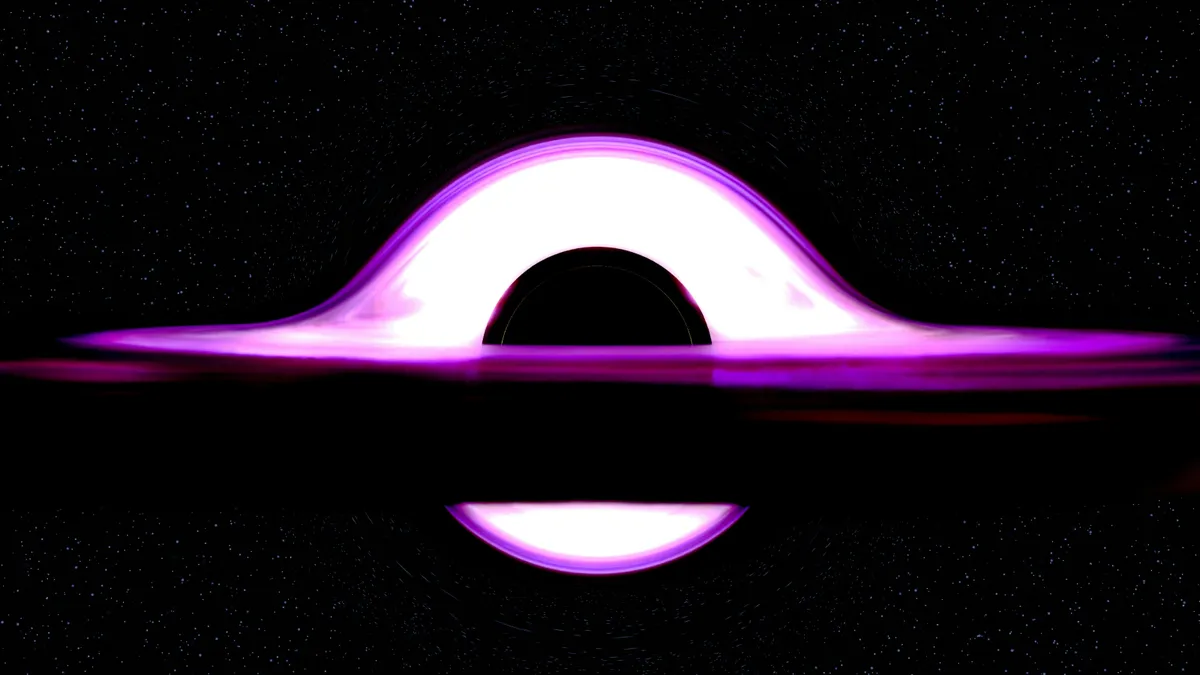

New research suggests that black holes may actually be “frozen stars,” bizarre quantum objects that lack a singularity and an event horizon, potentially solving some of the biggest paradoxes in black hole physics.

Remember to look skyward to see the moon when it will be about 27000km closer to Earth than usual

The largest moon in the solar system was struck by an ancient asteroid 20 times bigger than the rock that clattered into Earth and ended the reign of the dinosaurs 66m years ago, research suggests. See the study here.

Yet the scars of our past aren’t always easy to distinguish from more mundane tides that advance cosmic evolution, leaving researchers to speculate which patterns are evidence of cataclysmic events and which are typical signs of ageing. This research was submitted to Astronomy & Astrophysics and is available on the preprint server arXiv.

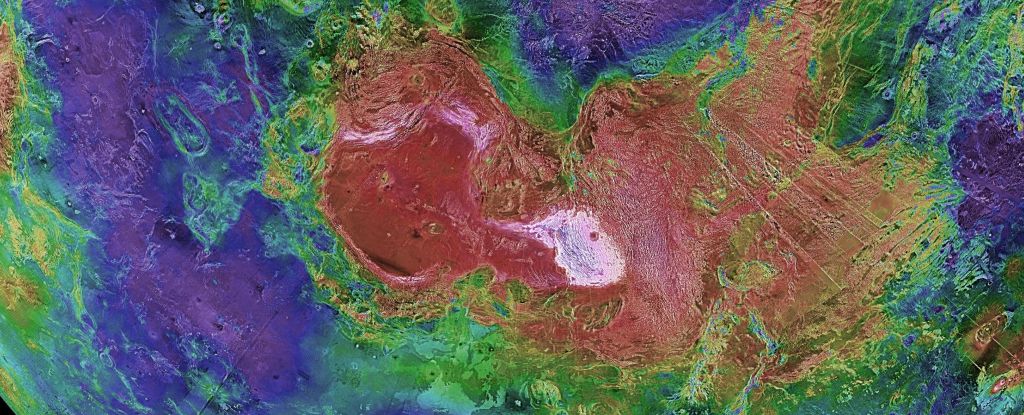
Astronomers have traced the origins of 200 meteorites to five impact craters in two volcanic regions on Mars, known as Tharsis and Elysium.
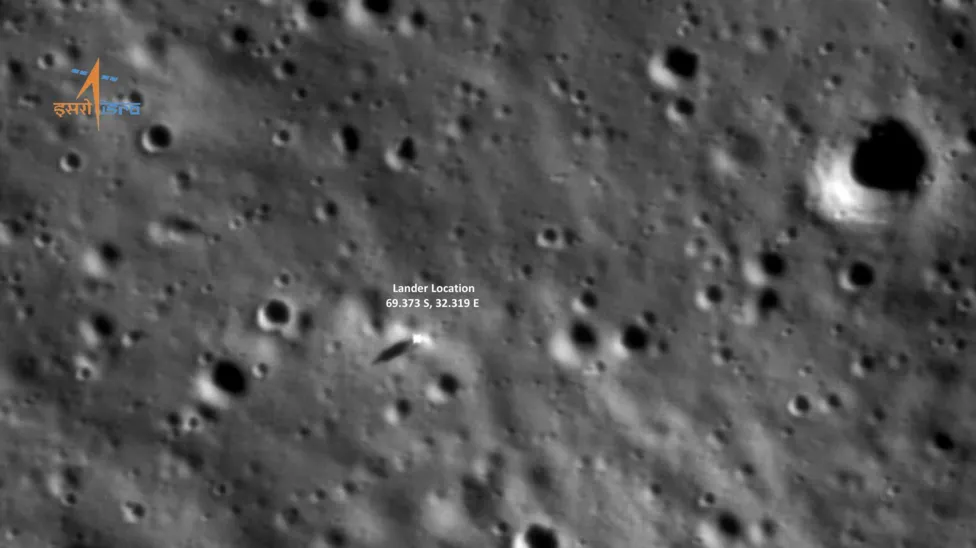

The Moon’s south pole was once covered in an ocean of liquid molten rock, according to scientists. The findings back up a theory that magma formed the Moon’s surface around 4.5 billion years ago.
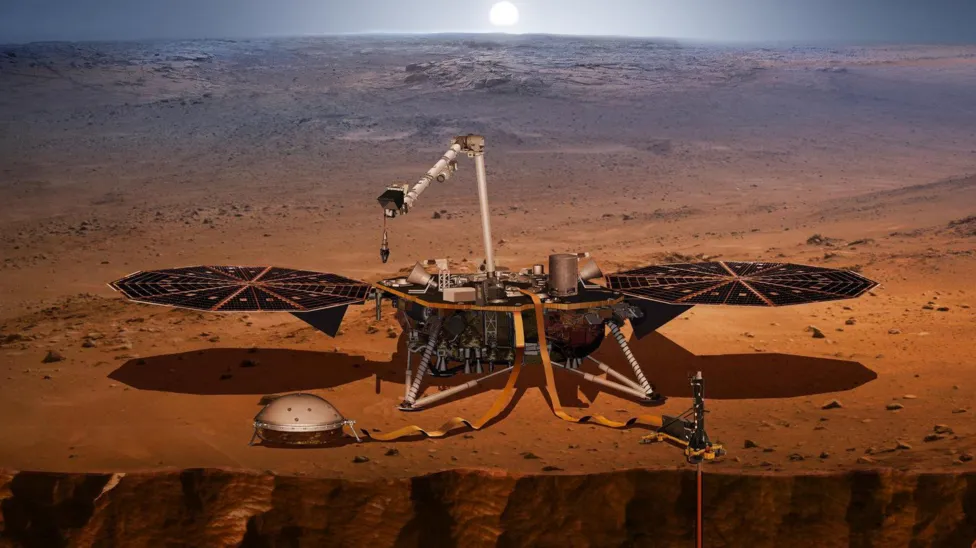

Scientists have discovered a reservoir of liquid water on Mars – deep in the rocky outer crust of the planet. The findings come from a new analysis of data from NASA’s Mars Insight Lander, which touched down on the planet back in 2018.
Venus and Earth seem like twins who, through dramatically different circumstances and choices, ended up leading dramatically different lives. The research has been published in Nature Geoscience.
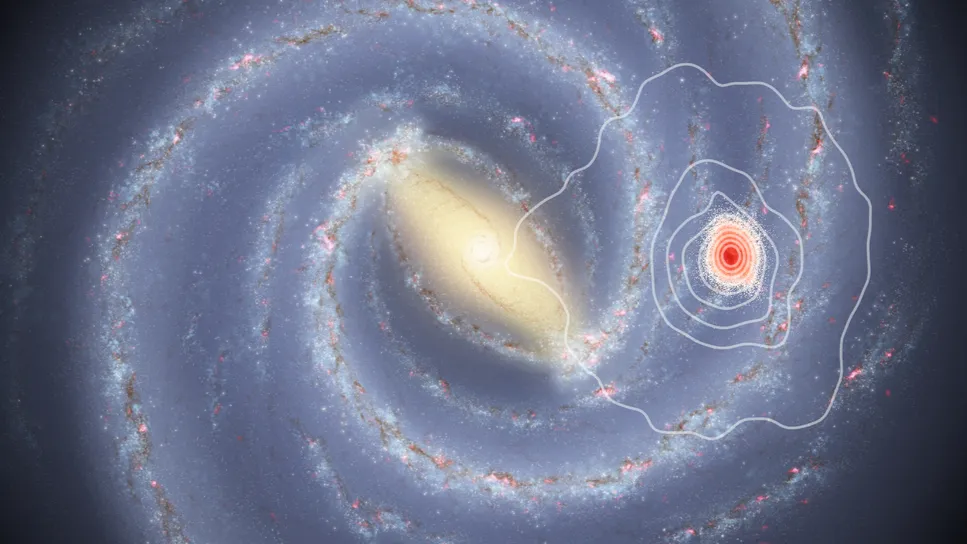
Researchers using the Gaia space telescope studied some ancient stars near the sun, revealing that our corner of the Milky Way may be billions of years older than once thought. See their findings in the pre-print arXiv server earlier this year.

In 2029, an asteroid larger than the Eiffel Tower will skim past Earth in an event that until recently scientists had feared could foreshadow a catastrophic collision. Now, researchers hope to scrutinise 99942 Apophis as it makes its close encounter in an effort to bolster our defences against other space rocks

The hunt for alien civilisations may be entering a new era, researchers believe. Scientists with Breakthrough Listen, the world’s largest scientific research programme dedicated to finding alien civilisations, say a host of technological developments are about to transform the search for intelligent life in the cosmos.
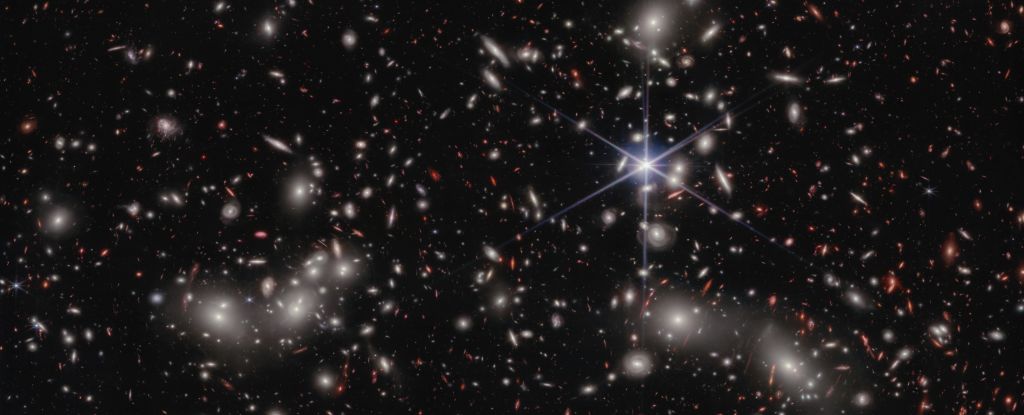

According to data from the Hubble and James Webb Space Telescopes, the origins of the free-flying photons in the early cosmic dawn were small dwarf galaxies that flared to life, clearing the fog of murky hydrogen that filled intergalactic space. A new paper about the research was published in February.

T Coronae Borealis, or the Blaze star, was last seen in 1946 and will be visible again some time between now and September.
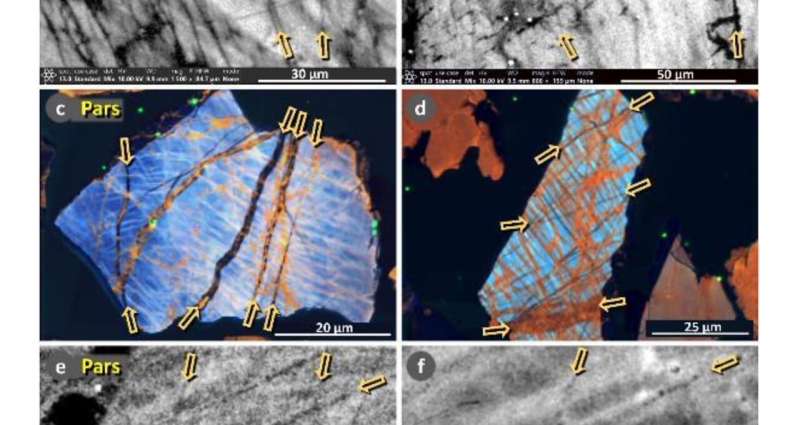
Researchers continue to expand the case for the Younger Dryas Impact hypothesis. The idea proposes that a fragmented comet smashed into the Earth’s atmosphere 12,800 years ago, causing a widespread climatic shift that, among other things, led to the abrupt reversal of the Earth’s warming trend and into an anomalous near-glacial period called the Younger Dryas. See the study here.
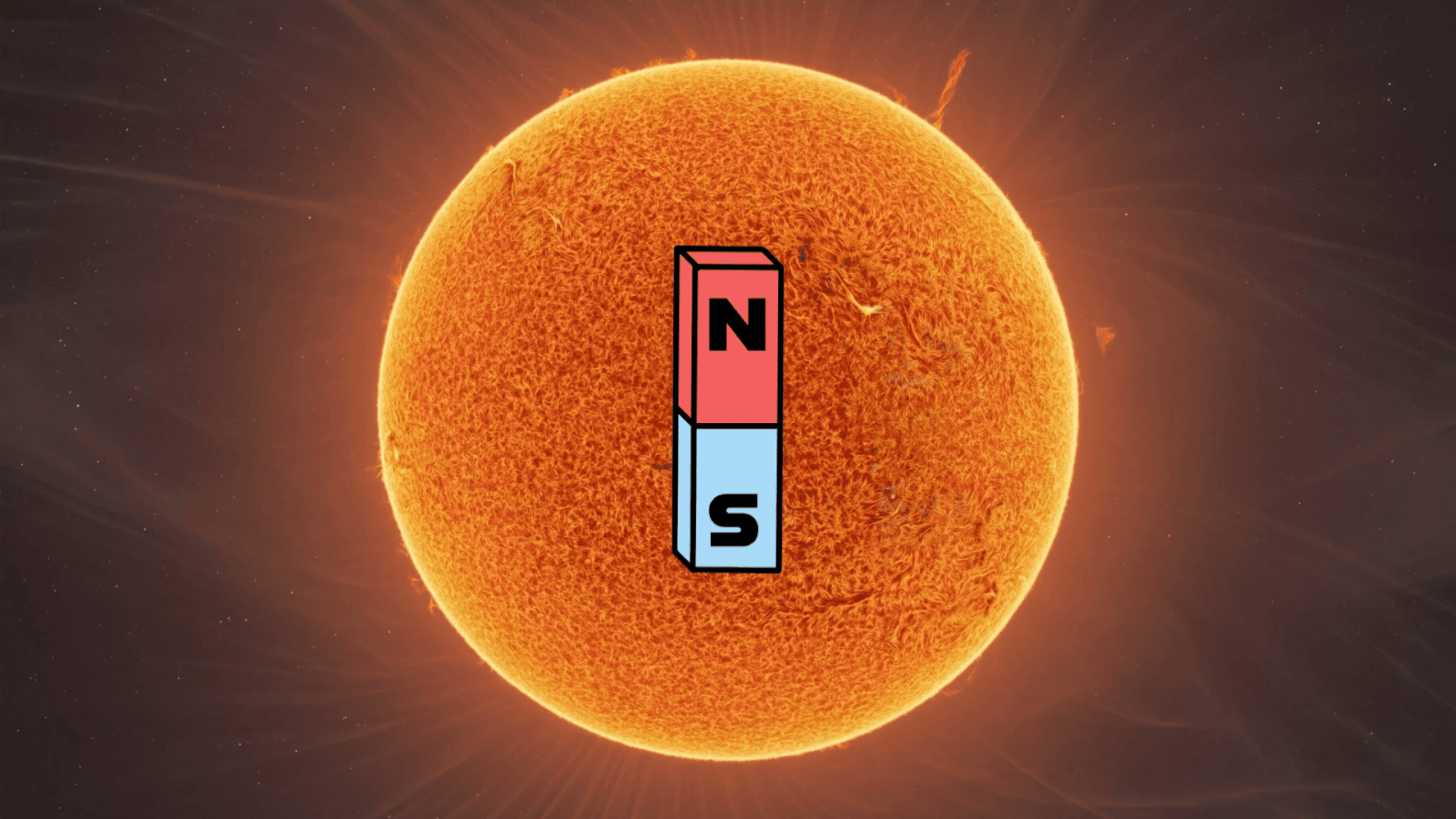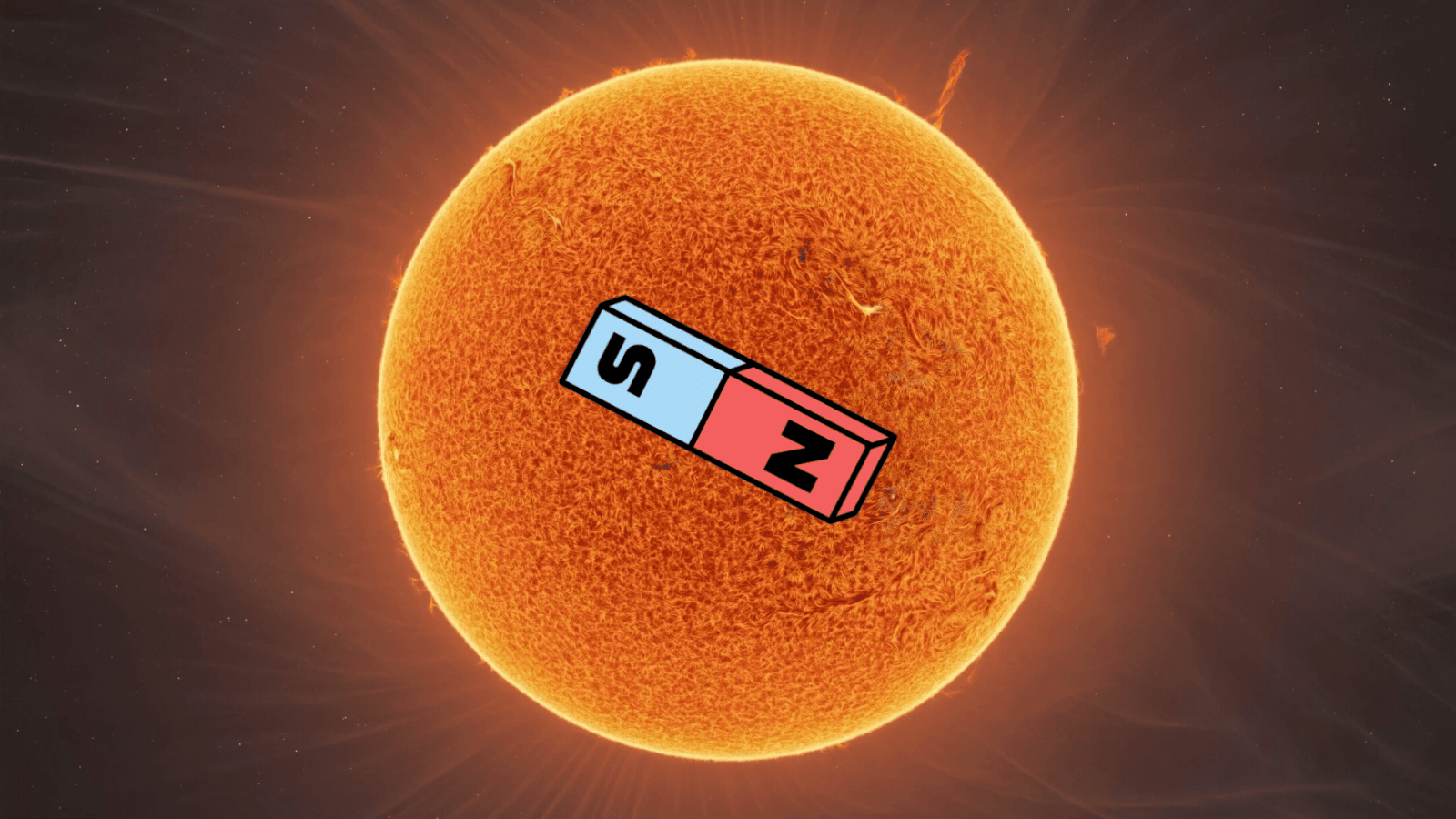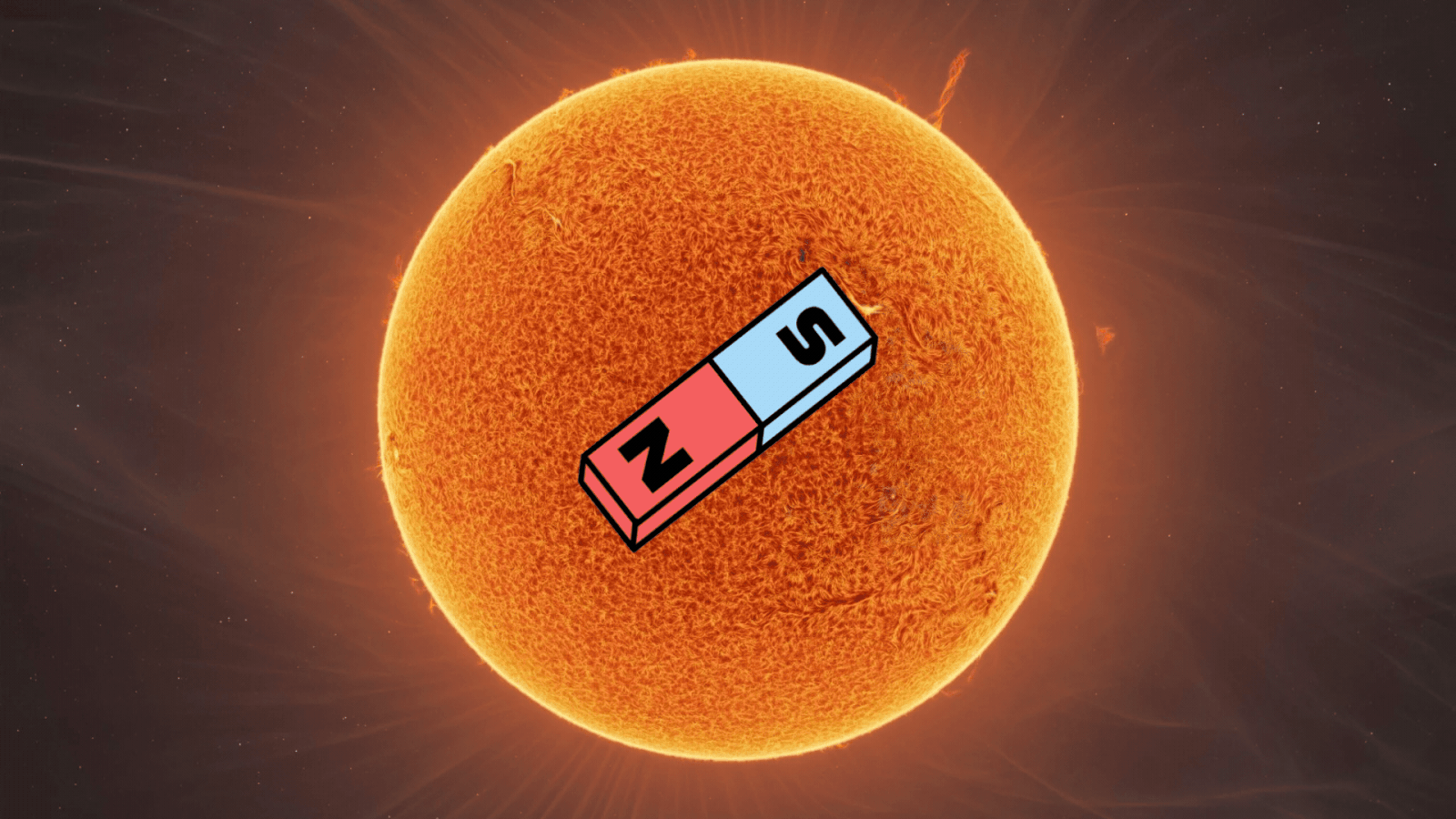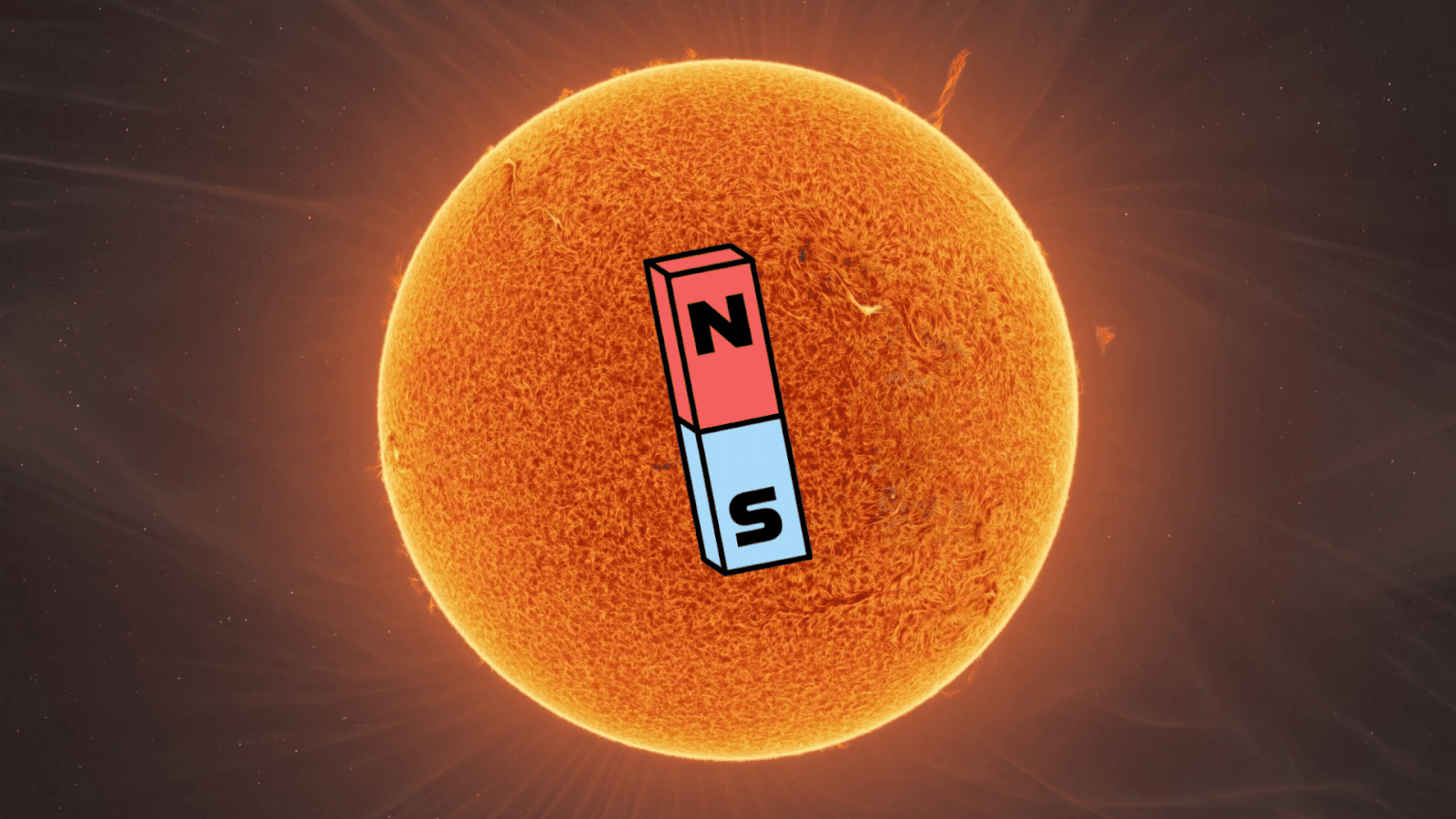
This phenomenon happens roughly every 11 years and marks an important stage in the solar cycle. The shift in polarity indicates the halfway point of solar maximum, the height of solar activity, and the beginning of the shift toward solar minimum.

Thin dusting of water ice appears to form overnight in summit craters and evaporate after sunrise, scientists say








