Space news stories

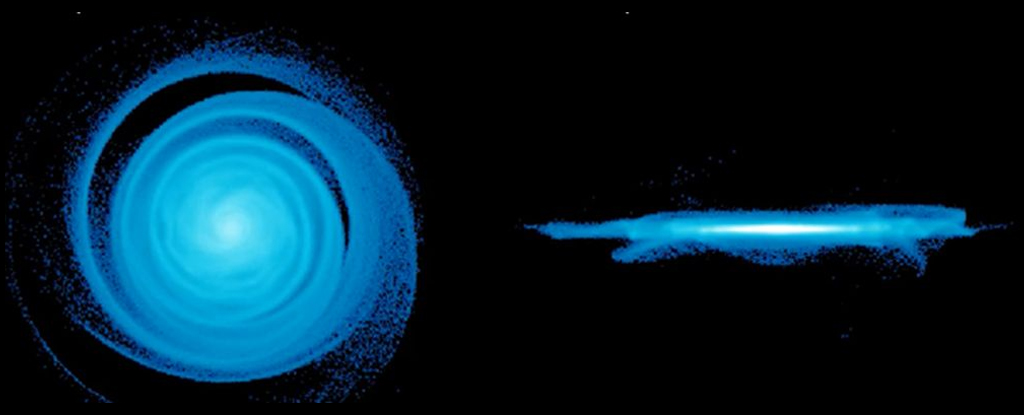
Astronomers have discovered a mysterious group of giant elderly stars at the heart of the Milky Way that are emitting solar system-sized clouds of dust and gas. The findings are published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
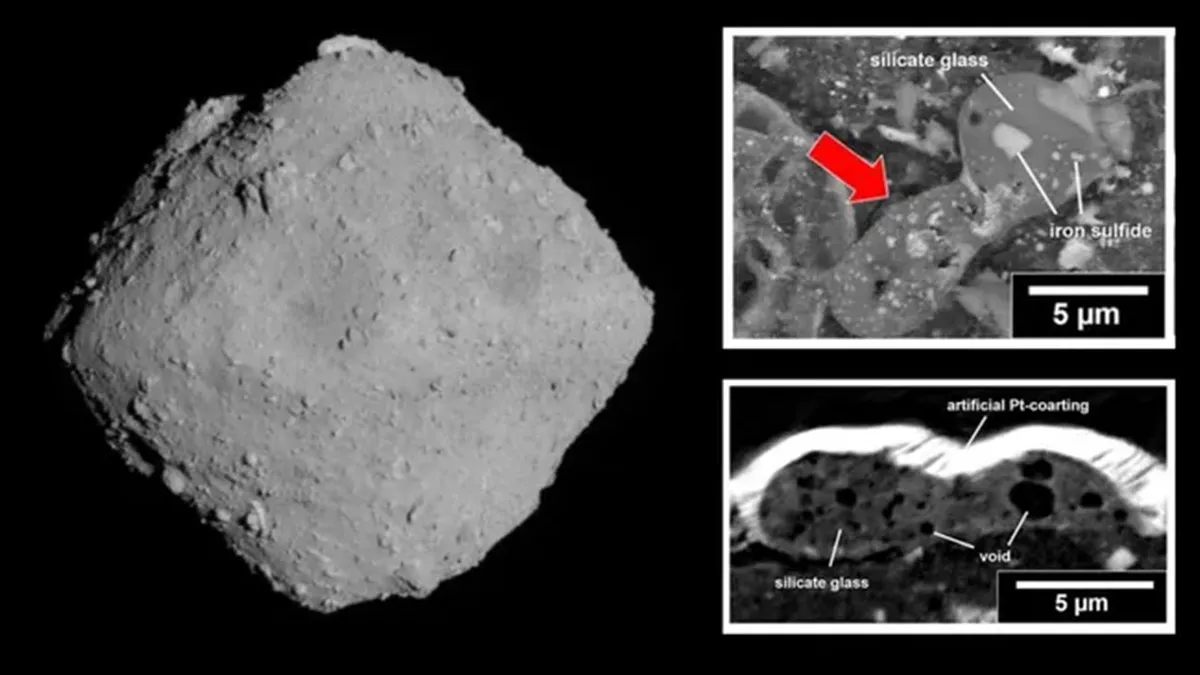

A detailed investigation of asteroid Ryugu samples has provided further evidence that the organic molecules which gave rise to life to our planet were brought here by ancient comets.

Windswept piles of dust, or layers of ice? ESA’s Mars Express has revisited one of Mars’s most mysterious features to clarify its composition. Its findings suggest layers of water ice stretching several kilometers below ground—the most water ever found in this part of the planet.
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/73062155/stsci_01gqqfcdz3j7arc9f8qdxe0f7z__1_.0.jpg)
Monsters lurk in the background of James Webb Space Telescope images. Scientists are scrambling to make sense of them.
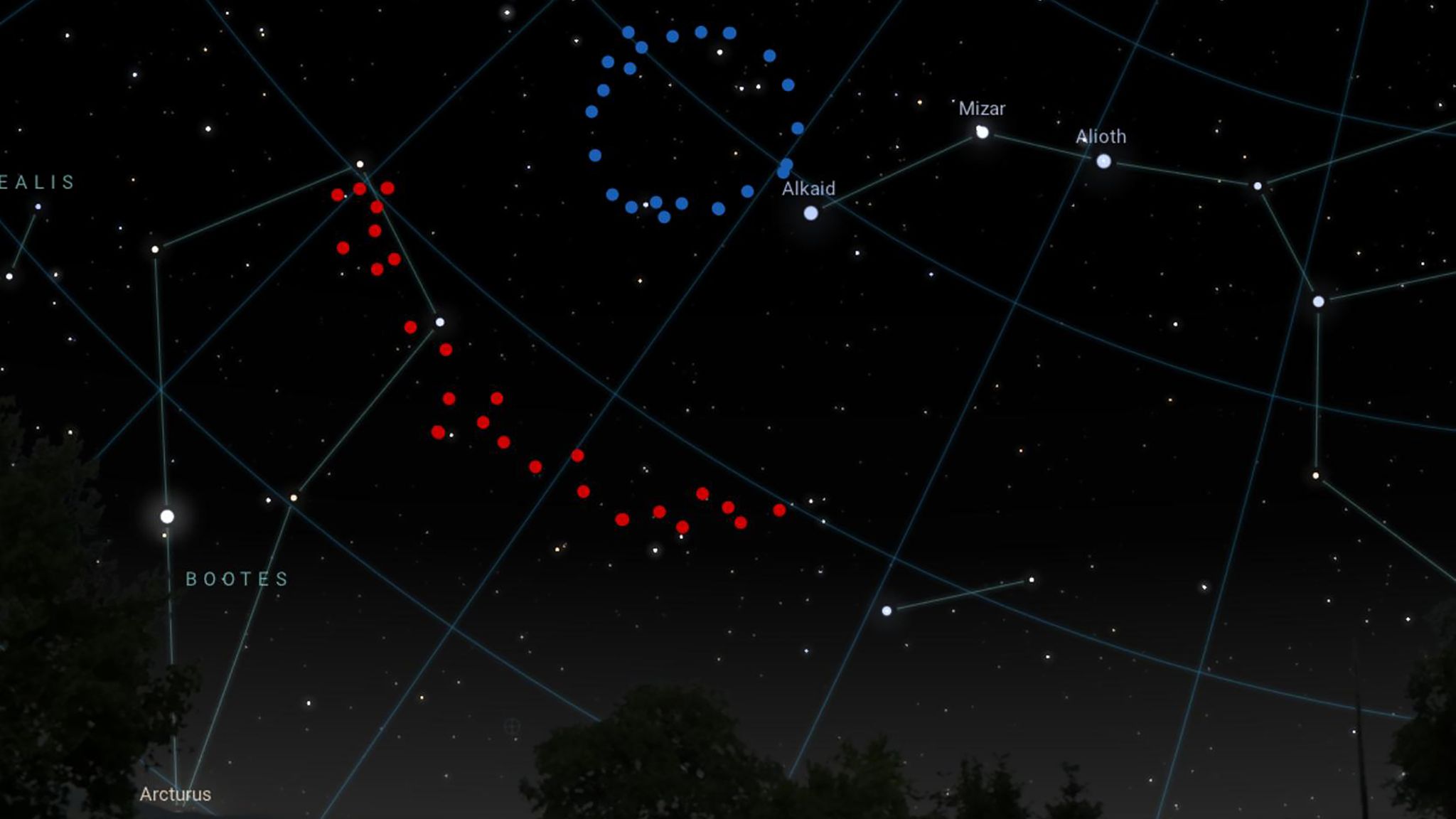
Scientists have discovered a huge ring-shaped structure in outer space – and it’s so big that it challenges our current understanding of the universe.

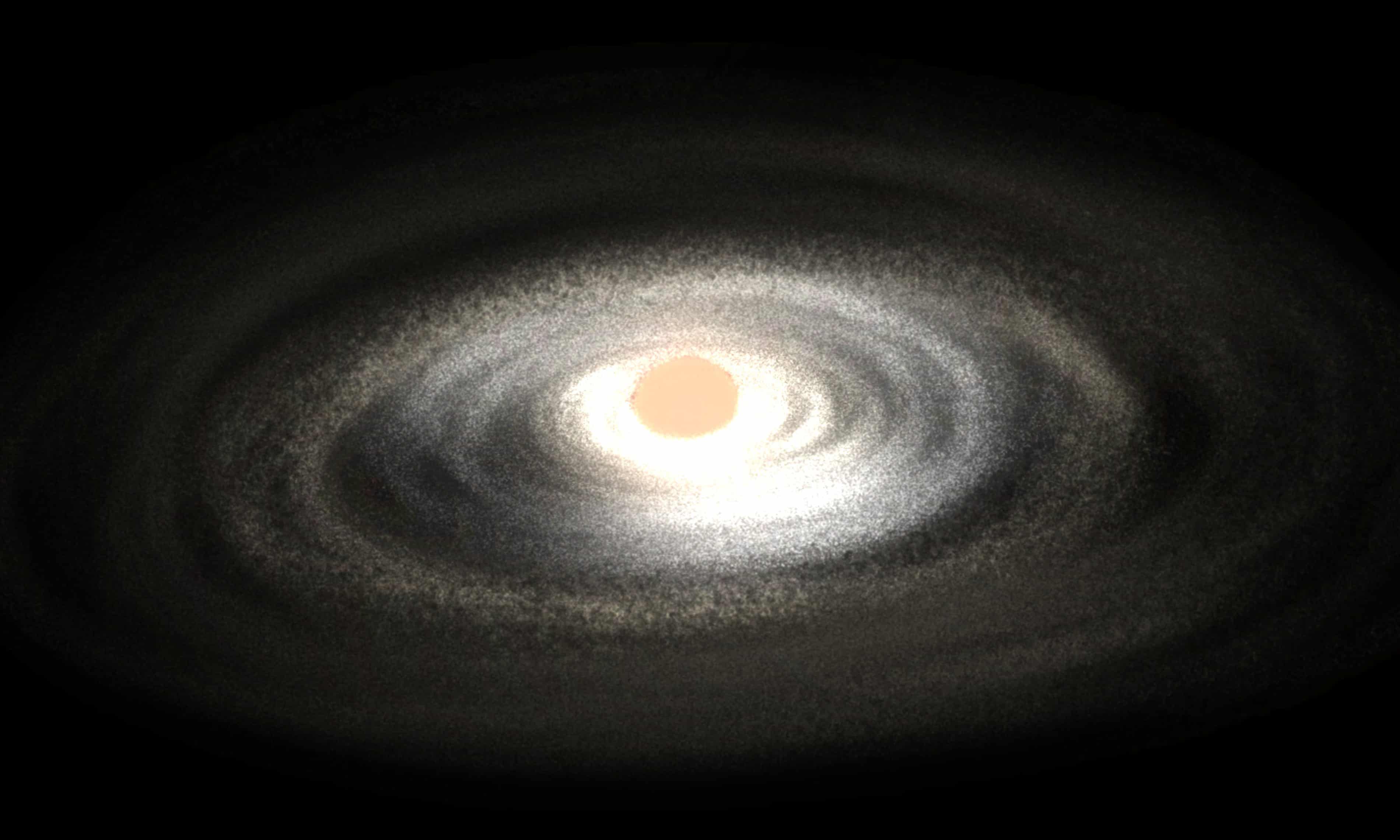
Astronomers have detected pond-like ripples across the gaseous disk of an ancient galaxy. What caused the ripples, and what do they tell us about the distant galaxy’s formation and evolution? And whatever happened, how has it affected the galaxy and its main job: forming stars? See the research here.
In a new study published in Nature Astronomy, University of Rochester astrophysicist Adam Frank explores the links between atmospheric oxygen and detecting extraterrestrial technology on distant planets.

The Quadrantids is due to peak at 12:53 UTC on 4 January 2024, with up to 110 to 120 meteors streaking through the atmosphere per hour. It’s one of the most intense meteor showers to grace our skies per year…
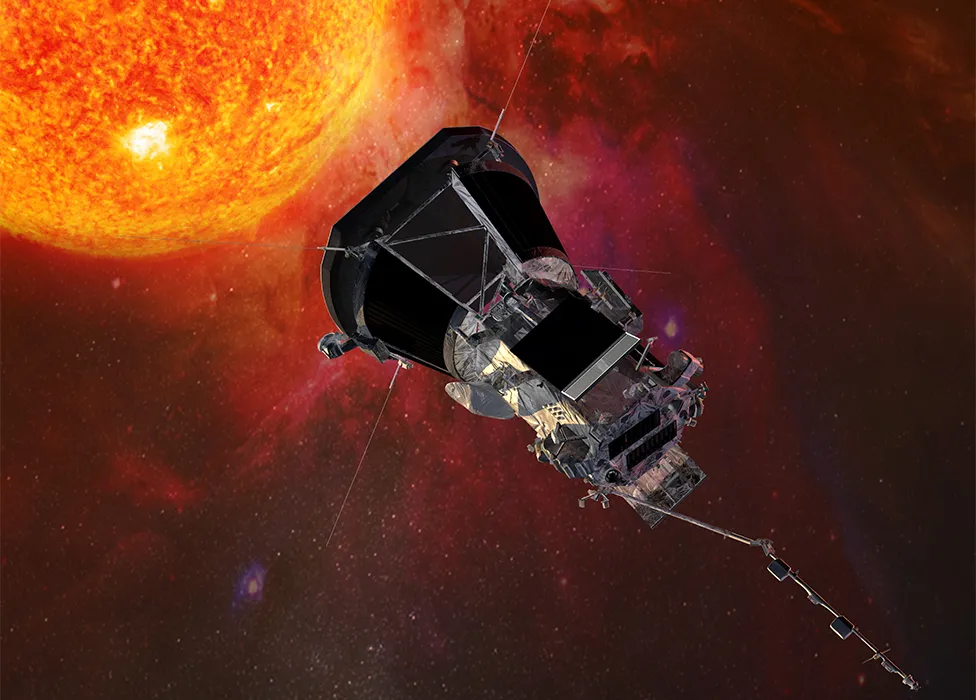

A year from now, on 24 December, Nasa’s Parker Solar Probe will race past the Sun at the astonishing speed of 195 km/s, or 435,000 mph. No human-made object will have moved so fast nor, indeed, got so close to our star – just 6.1 million km, or 3.8 million miles from the Sun’s “surface”.
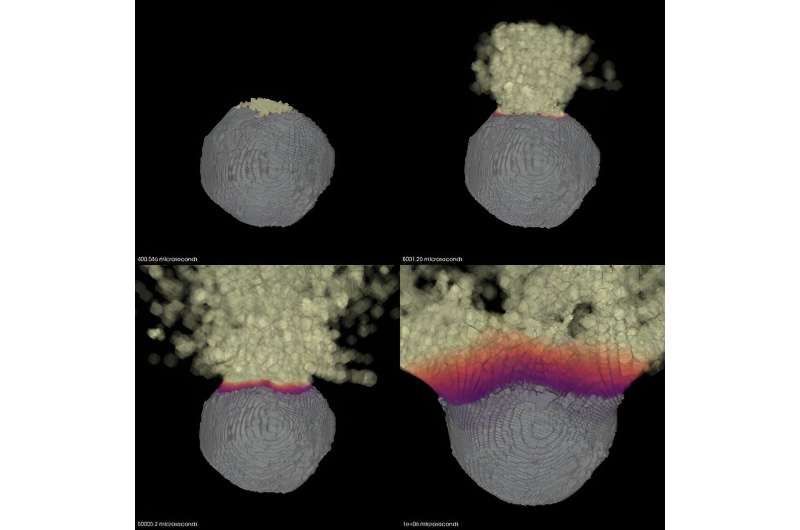
The research, published in the Planetary Science Journal, introduces a novel approach to simulating the energy deposition from a nuclear device on an asteroid’s surface.
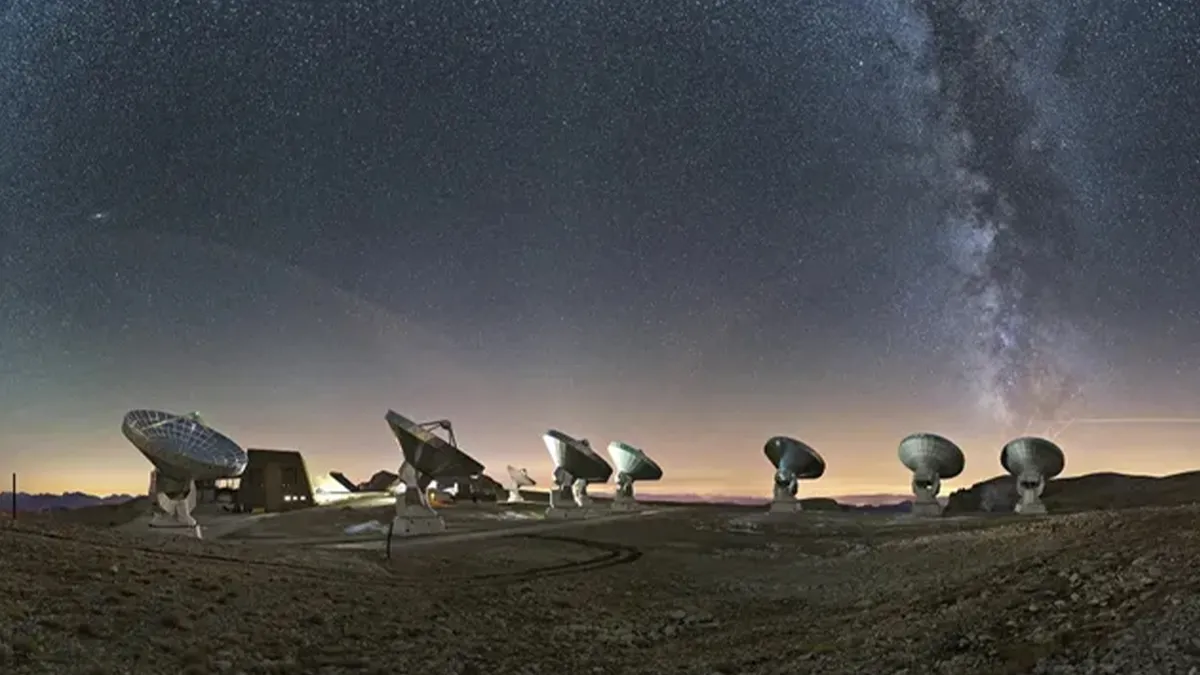

Scientists find ultra-rare collection of molecules in 2 ancient galaxies from the early universe. The findings were published on December 14th in the journal Astronomy and Astrophysics.
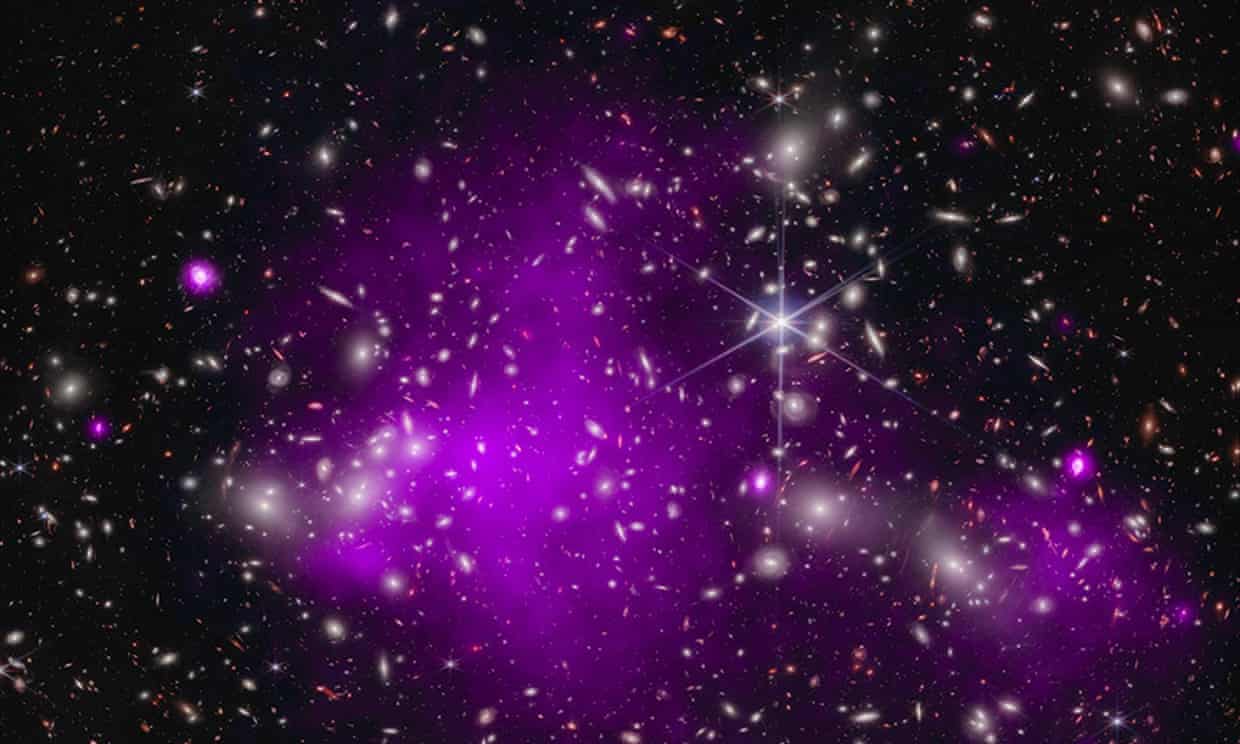

Exclusive: astronomers surprised at size of 13bn-year-old object, which raises new questions about where black holes came from.

One of the biggest and brightest stars in the night sky will momentarily vanish as an asteroid passes in front of it to produce a one-of-a-kind eclipse. The rare and fleeting spectacle, late on Monday into early Tuesday, should be visible to millions of people…

Similar patterns develop on the surface of Earth’s polar regions when icy sediments cool and contract. A comparable process long ago may have created the shapes on Mars, found near the planet’s dry equator, researchers reported recently in Nature Astronomy.
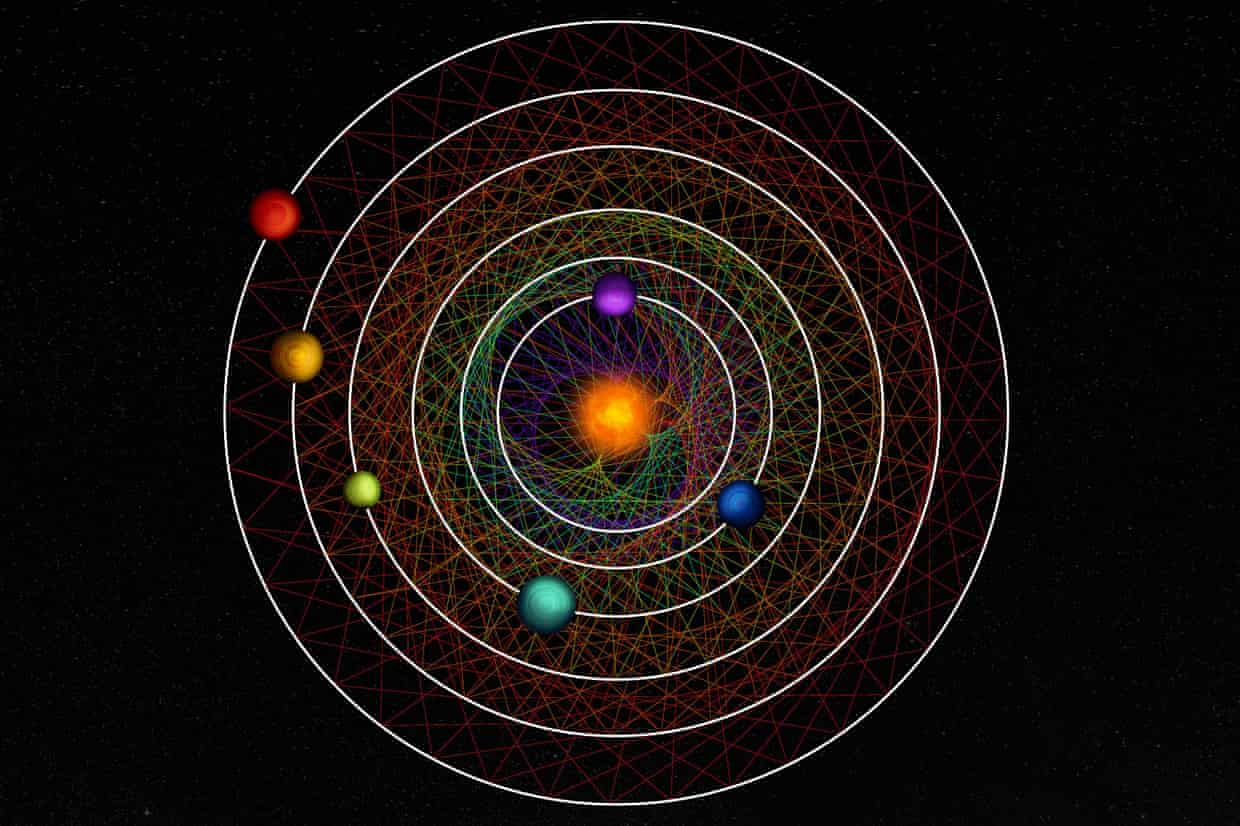
Six planets that orbit their star in a coordinated dance have been discovered by scientists, who say the finding could help shed light on why planets in our own solar system move to their own beat.
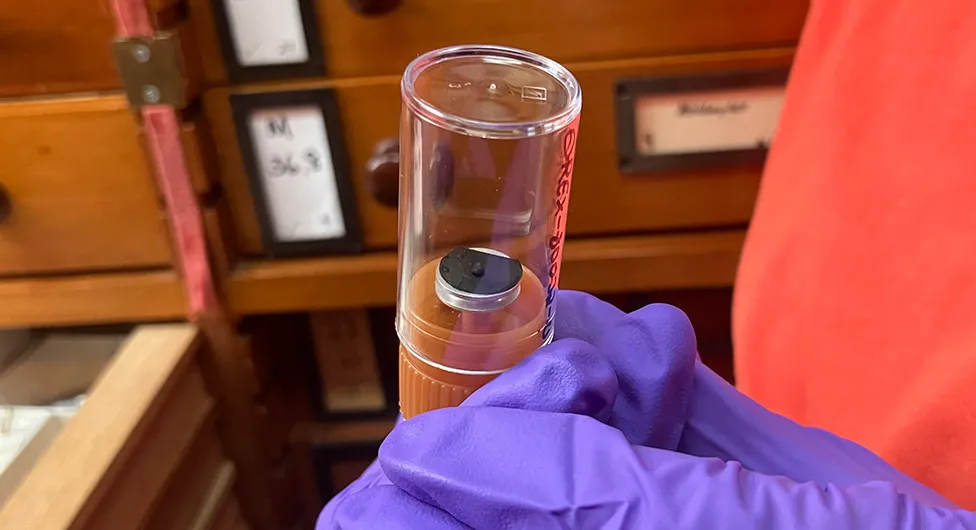

Fragments from the asteroid US space agency Nasa has described as the most dangerous rock in the Solar System have arrived in the UK for study.








