Space news stories

Earth and Mars are the only two rocky planets in the Solar System to have moons. Based on lunar rock samples and computer simulations, we are fairly certain that our Moon is the result of an early collision between Earth and a Mars-sized protoplanet called Theia.

Evidence is growing that Mars was once sloshy and wet, draped with lakes and oceans, which lapped at shorelines and deposited sediments that are, even as you read these words, being scrutinized by robots rolling across the now dry and dusty surface.

The analysis, which looked at nearly 6 million galaxies and quasars spanning 11 billion years of cosmic time, found that even at colossal scales, the force of gravity behaves as predicted by Albert Einstein’s theory of general relativity.
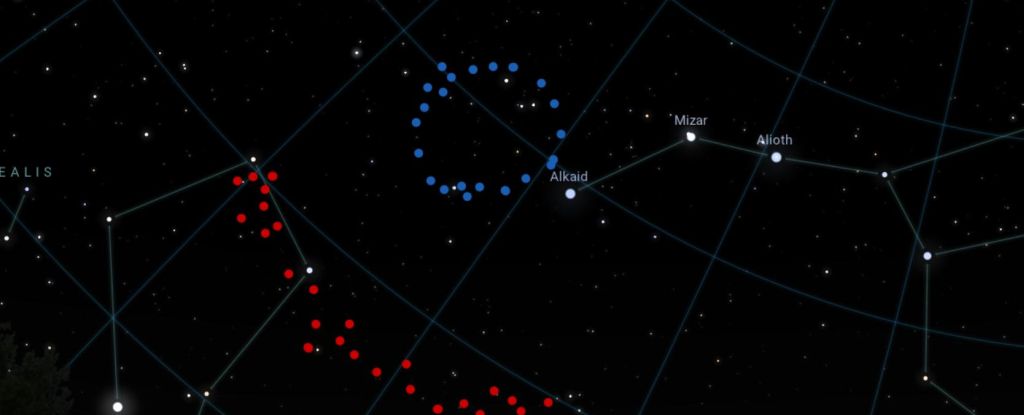
The discovery, led by astronomer Alexia Lopez of the University of Central Lancashire, was presented at the 243rd meeting of the American Astronomical Society in January, and has been published in the Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics.
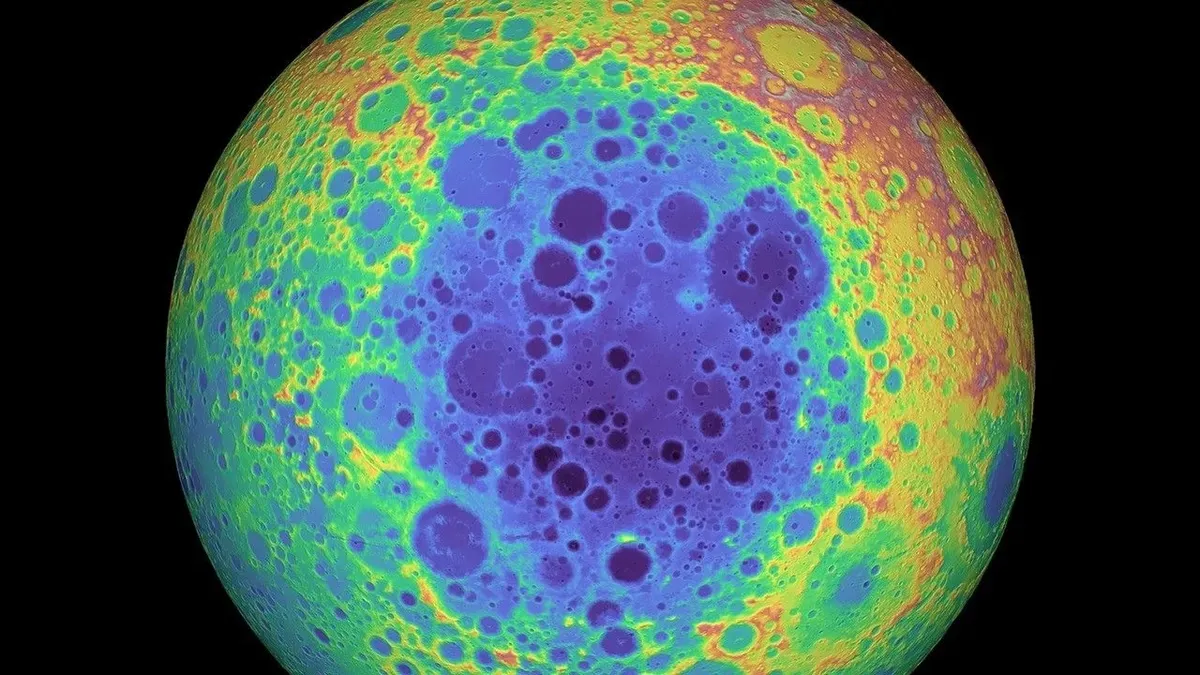
The largest and oldest-known impact site on the moon is the South Pole-Aitken basin. Thanks to new research, scientists have dated the basin to the period between 4.32 and 4.33 billion years ago.
For the first time, a black hole has been discovered with two orbiting stars, leading astrophysicists to suggest a surprising way such systems could form. The first triple system is described in a paper published in Nature…

One of the brightest stars in the night sky, Betelgeuse, may not be on the brink of exploding as a supernova, according to a new study of the star’s brightening and dimming. Instead, recent research shows that the observed pulsing of the starlight is probably caused by an unseen companion star orbiting Betelgeuse.
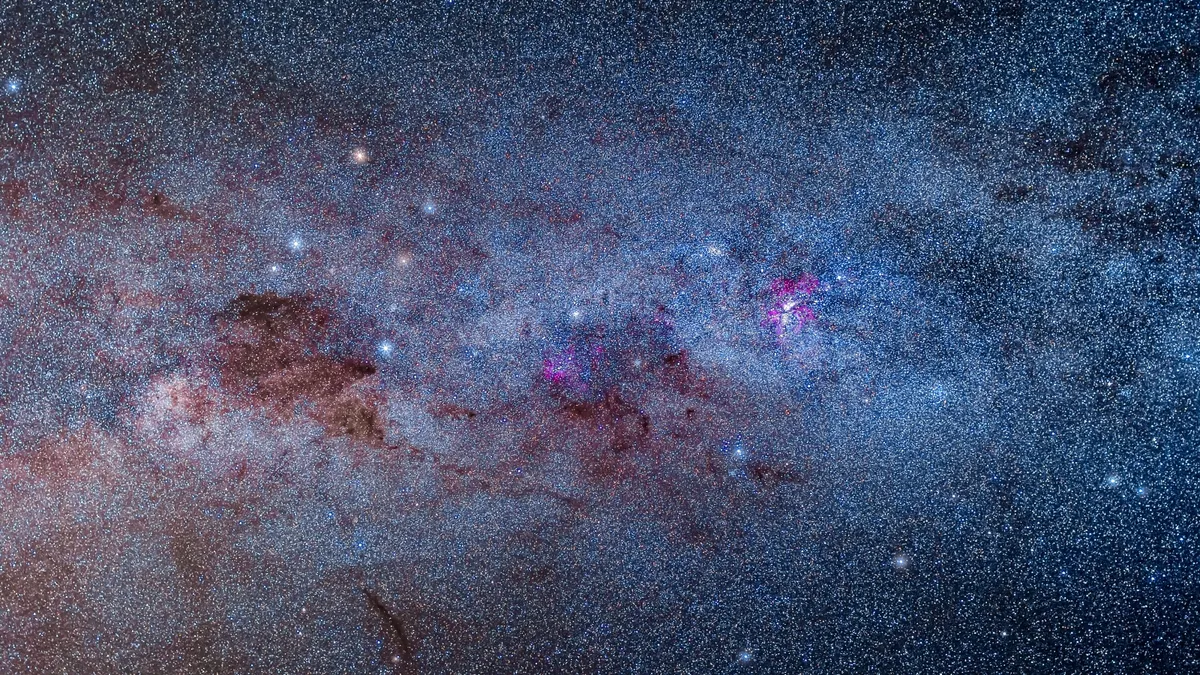

A probabilistic new map of the universe surrounding the Milky Way reveals that our galaxy is likely part of an even larger “basin of attraction” than we previously assumed. See the study here.
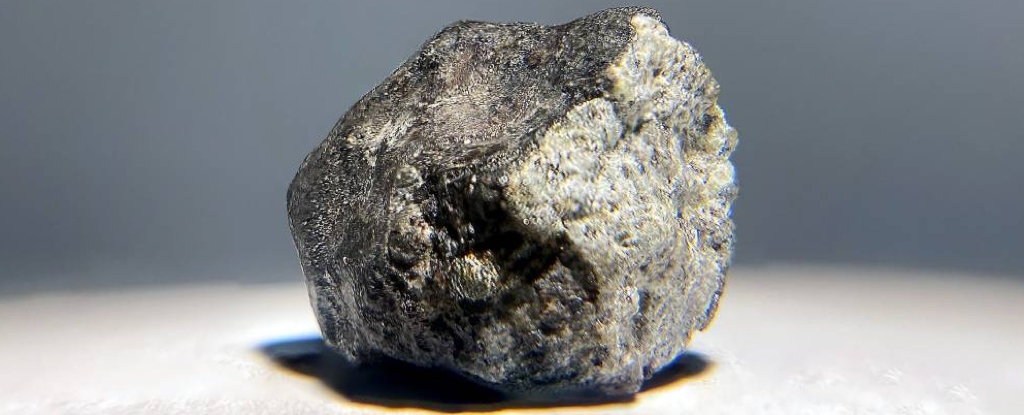

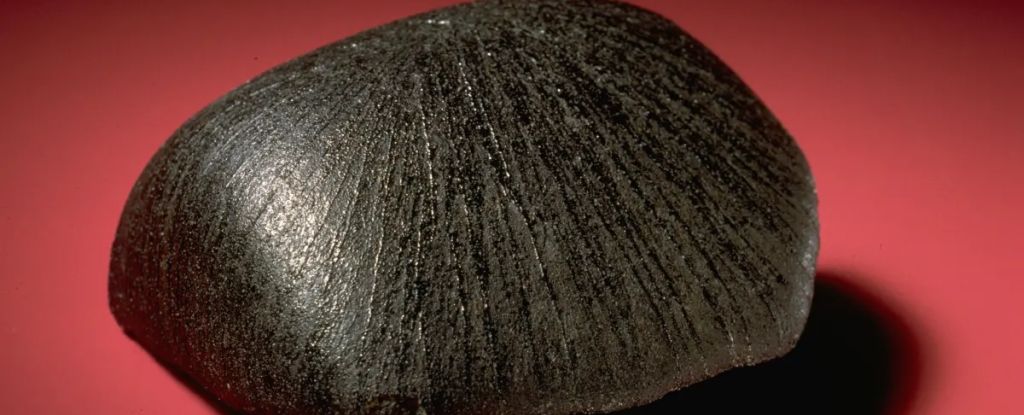
Until now, only a small fraction of meteorites that land on Earth had been firmly linked back to their parent body out in space – but a set of new studies has just given us compelling origin stories for more than 90 percent of meteorites today. The research has been published in Nature, here and here, and Astronomy and Astrophysics.
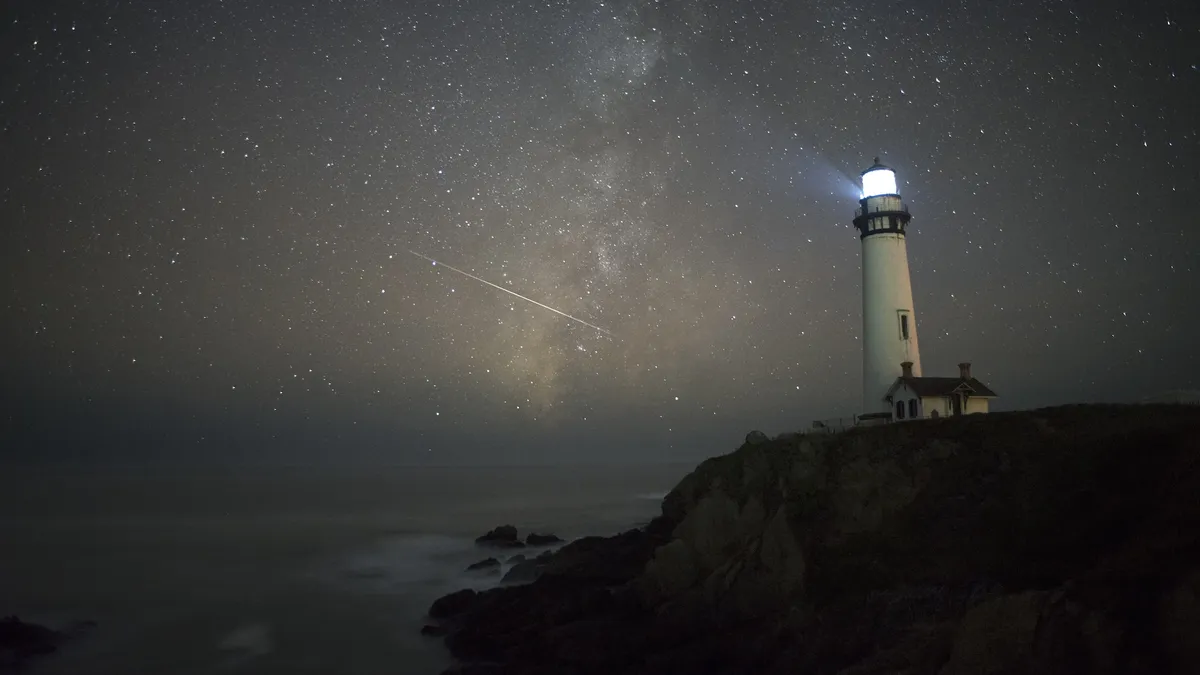

Active from Sept. 26 through Nov. 22, the Orionids will peak in the early hours of Monday, Oct. 21, when around 23 “shooting stars” are expected per hour, according to the American Meteor Society. The precise peak is predicted to occur at 1 a.m. EDT (0500 GMT).

Using the Zwicky Transient Facility (ZTF) telescope to survey large expanses of sky, a team of researchers led by the University of Maryland investigated a stream of space debris known to drift near Earth called the Taurid swarm.
If you want to pinpoint your place in the Universe, start with your cosmic address. You live on Earth->Solar System->Milky Way Galaxy->Local Cluster->Virgo Cluster->Virgo Supercluster->Laniakea.

The huge asteroid that hit Earth and wiped out the dinosaurs 66 million years ago was not alone, scientists have confirmed. A second, smaller space rock smashed into the sea off the coast of West Africa creating a large crater during the same era.

A comet that has not been seen from Earth since Neanderthals were alive and kicking has reappeared in the sky, with astronomers saying it might be visible to the naked eye.

The existential threat from a large meteor is real, but two next-generation telescopes are about to make us safer.

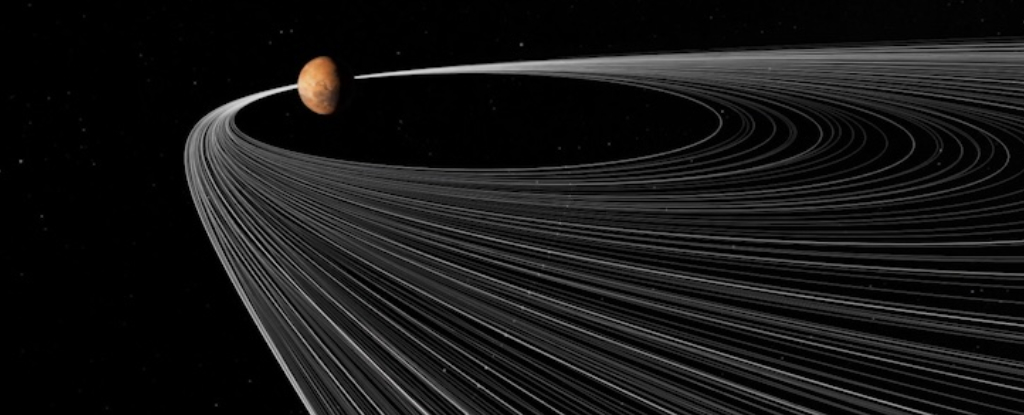
New research published in The Planetary Science Journal suggests that the moon was captured during a close encounter between a young Earth and a terrestrial binary—the moon and another rocky object.








