Earth news stories
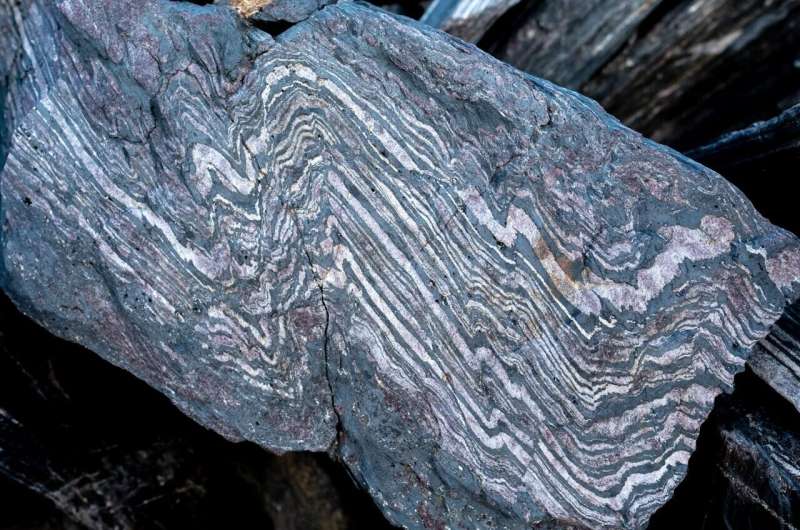

A new study, led by the University of Oxford and MIT, has recovered a 3.7-billion-year-old record of Earth’s magnetic field and found that it appears remarkably similar to the field surrounding Earth today. The findings have been published in the Journal of Geophysical Research. Without its magnetic field, life on Earth would not be possible…
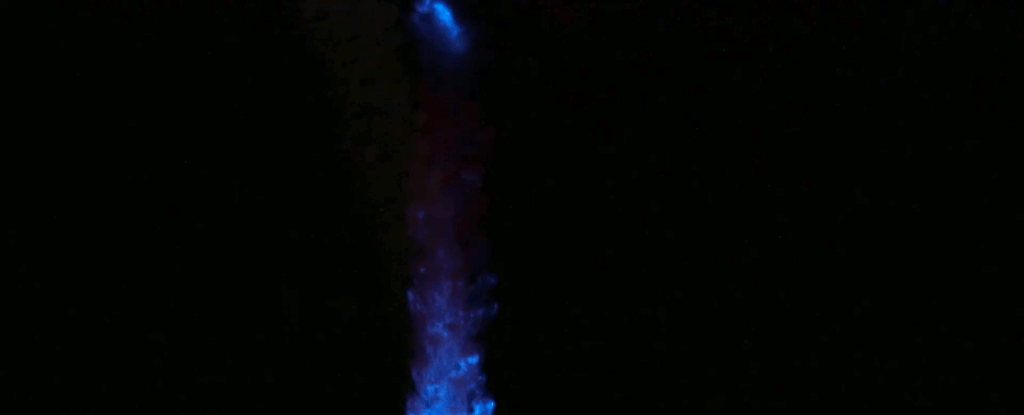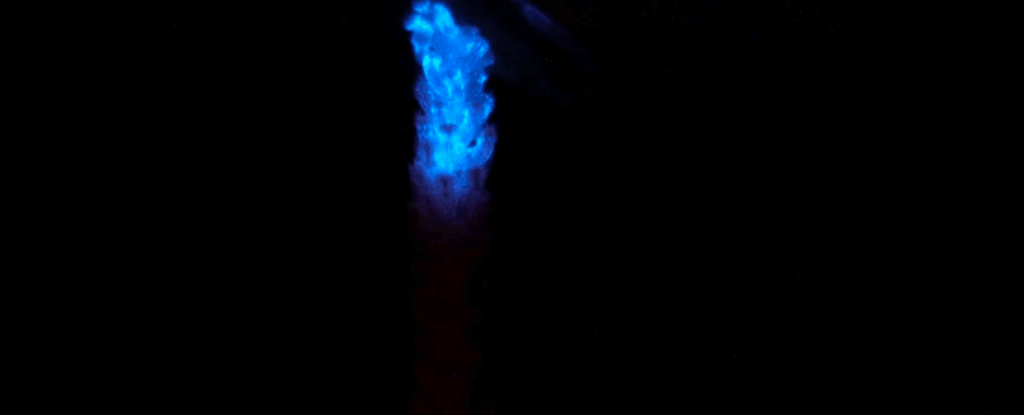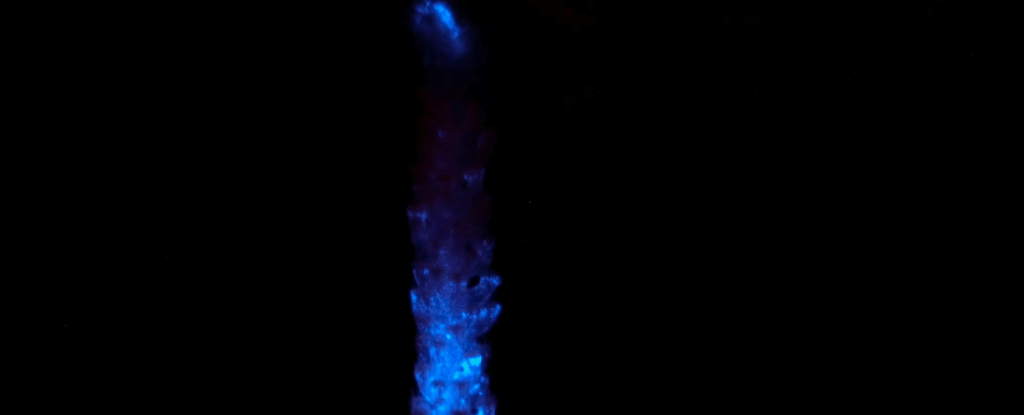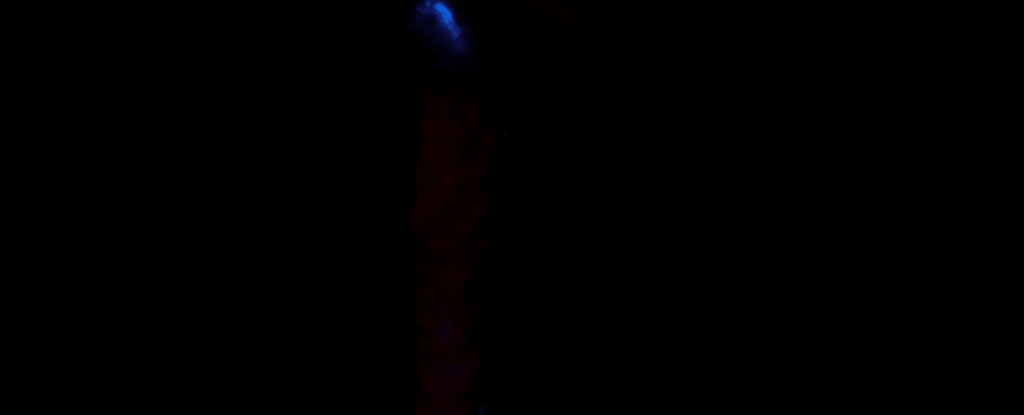
In the darkest corners of the planet, where the light of the Sun never touches, eerie glows can yet be found, illuminating the shadows. This is bioluminescence, a remarkable ability that has evolved separately at least 94 times throughout the history of life on Earth. See the study here.

Since the first Earth Day in 1970, the world has experienced profound ecological changes. Wildlife populations have decreased by 69 percent, the result of habitat loss caused by rapid industrialization and changing temperatures. 2023 was the hottest year on record.

From house plants and gardens to fields and forests, green is the color we most associate with surface life on Earth…But an Earth-like planet orbiting another star might look very different, potentially covered by bacteria that receive little or no visible light or oxygen…Instead of green, many such bacteria on Earth contain purple pigments…Cornell scientists report in new research.
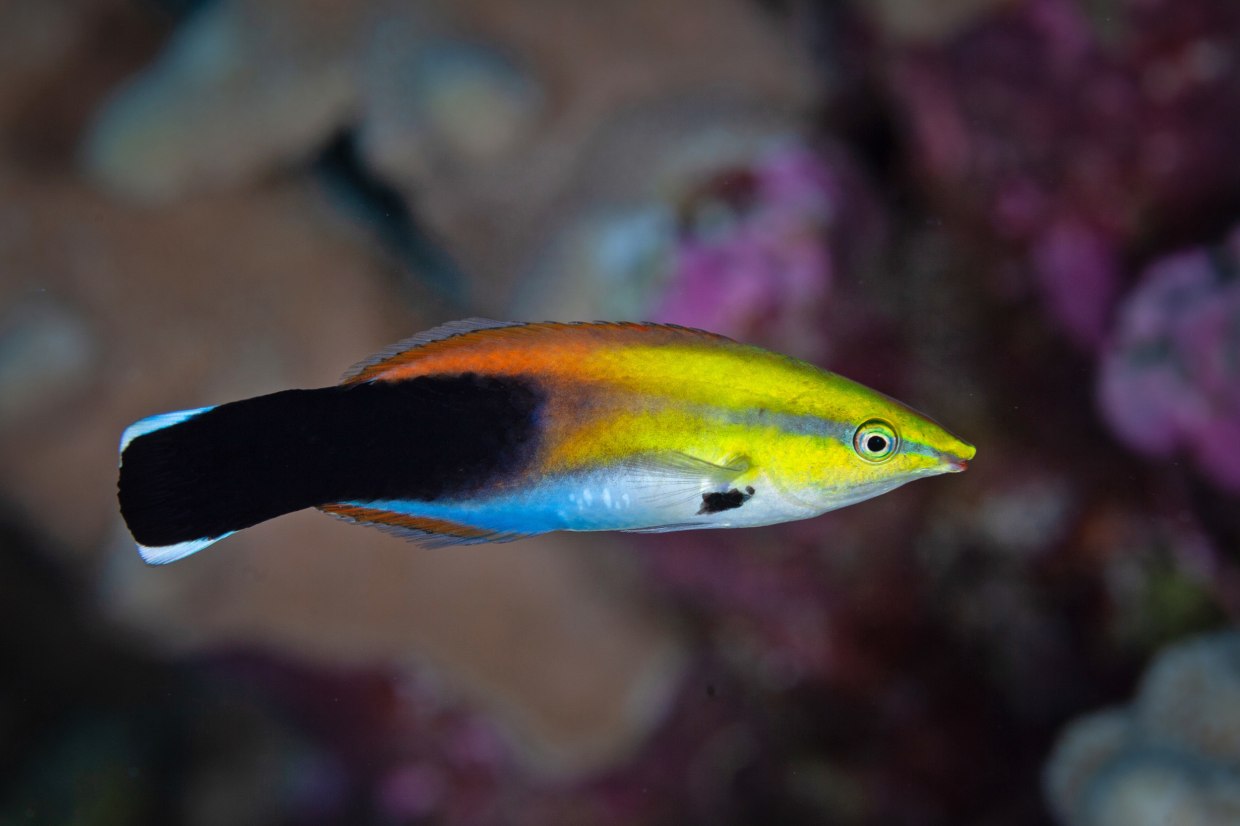

Bees play by rolling wooden balls — apparently for fun. The cleaner wrasse fish appears to recognize its own visage in an underwater mirror. Octopuses seem to react to anesthetic drugs and will avoid settings where they likely experienced past pain. Nearly 40 researchers signed “The New York Declaration on Animal Consciousness,” which marks a pivotal moment, as a flood of research on animal cognition collides with debates over how various species ought to be treated.
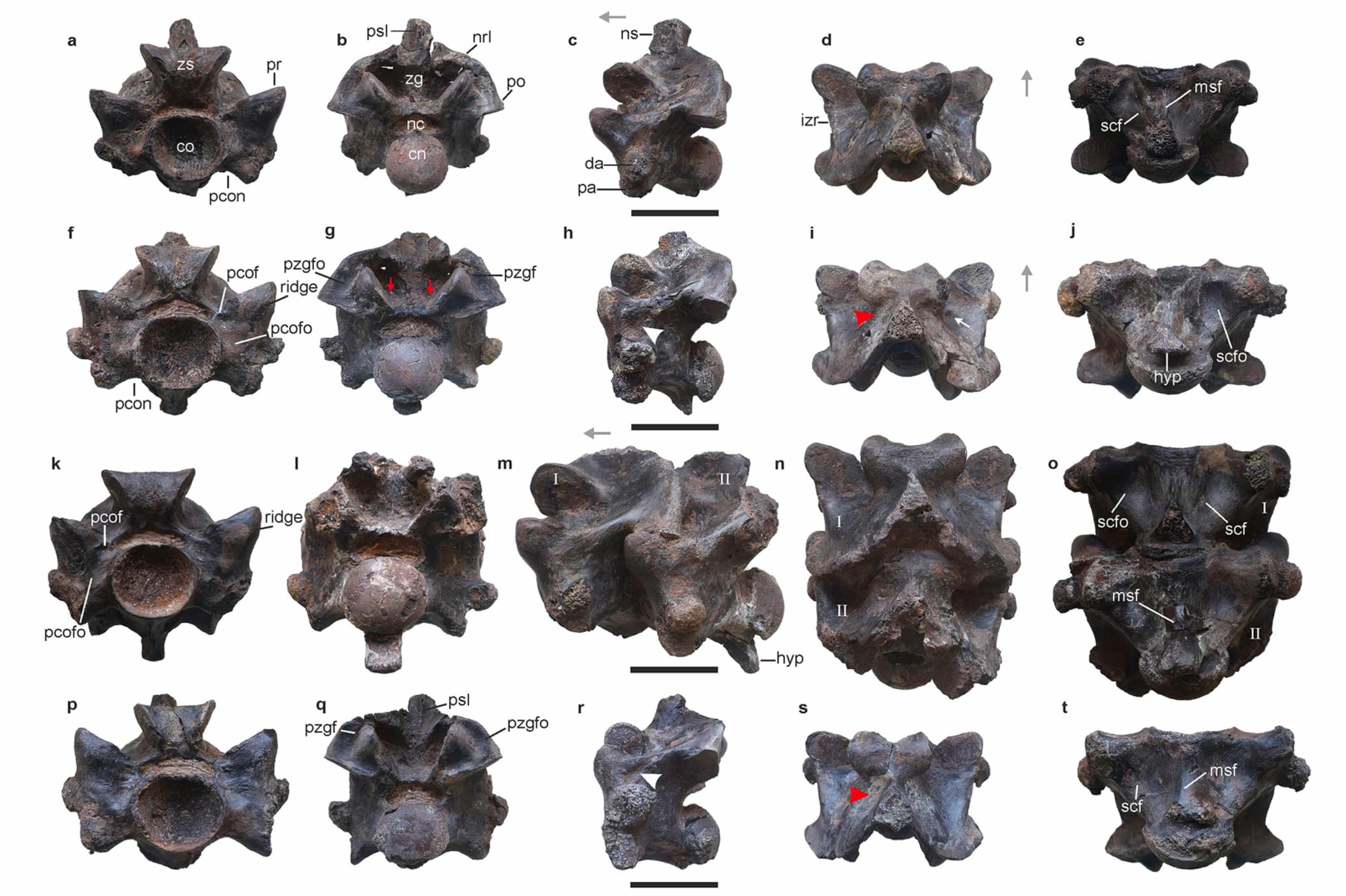

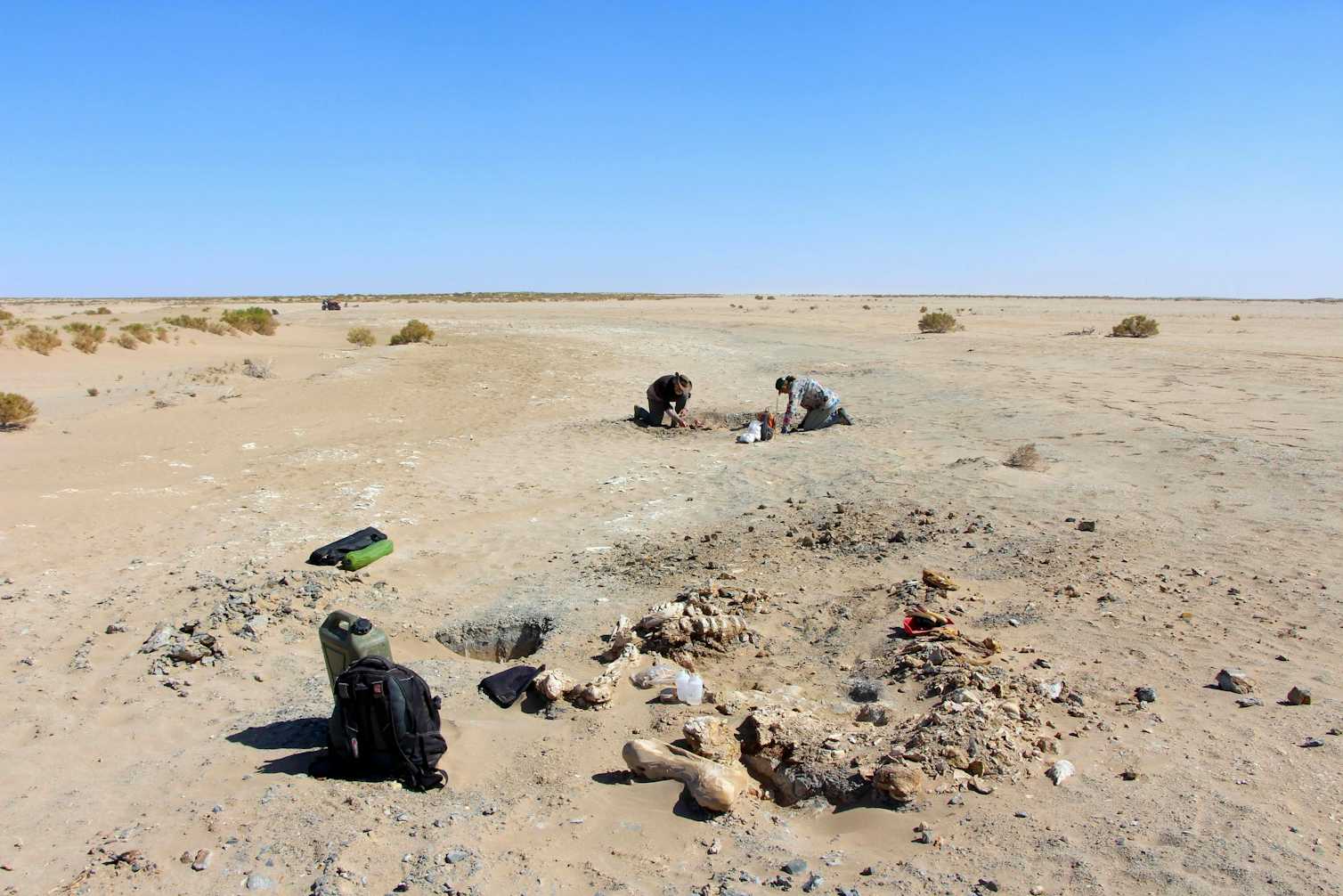
Fossil vertebrae unearthed in a mine in western India are the remains of one of the largest snakes that ever lived, a monster estimated at up to 15 metres in length – longer than a T rex. See the study here.

For millions of years, giant animals or megafauna roamed the lands that are now Australia and New Guinea. Many were like much larger versions of modern animals. There was a four-metre goanna called Megalania (Varanus priscus), for example, which likely ambushed its prey. This beast disappeared by around 40,000 years ago along with almost all the other megafauna aside from remnants such as the red kangaroo and the saltwater crocodile.
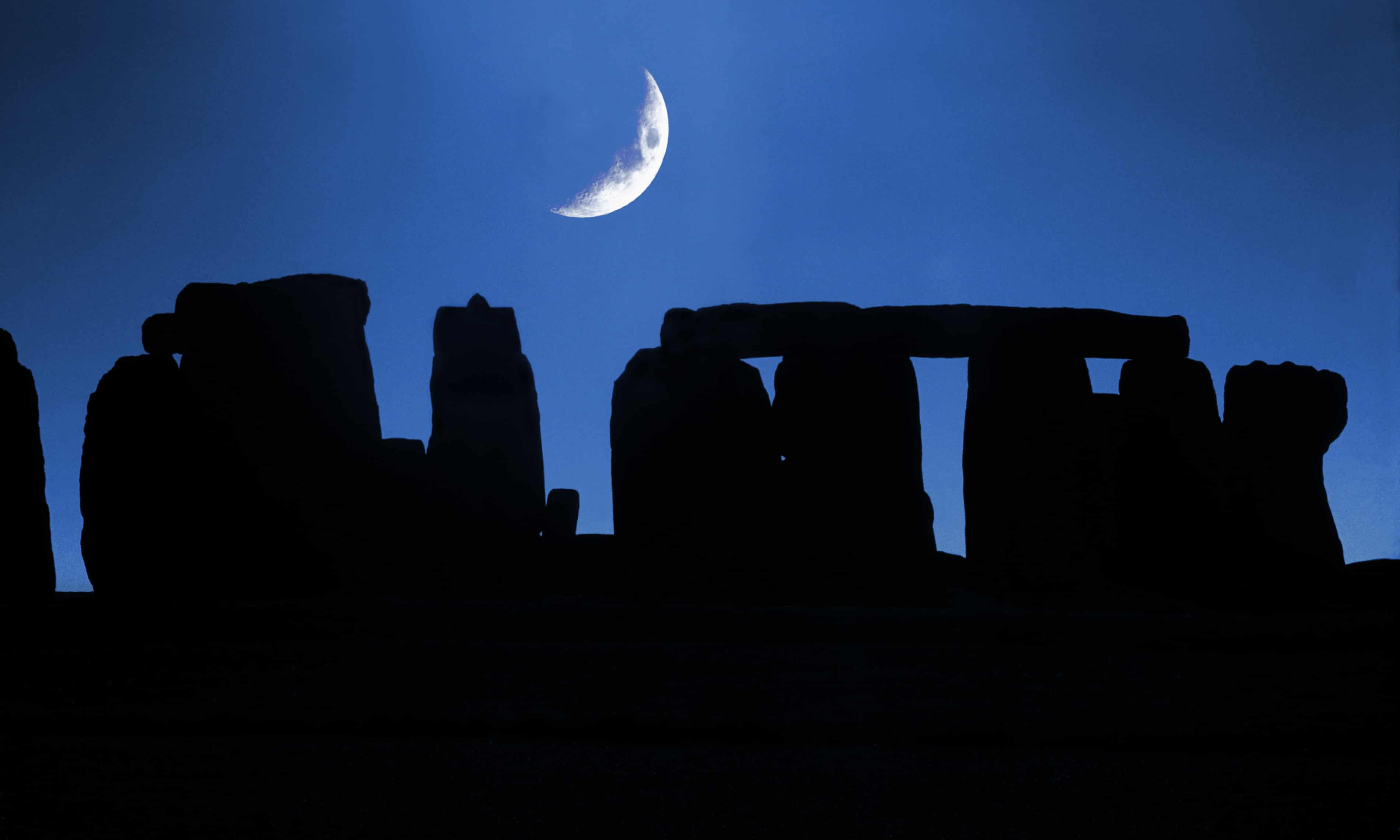

The rising and setting of the sun at Stonehenge, especially during the summer and winter solstices, continues to evoke joy, fascination and religious devotion. Now a project has been launched to delve into the lesser understood links that may exist between the monument and the moon during a rare lunar event.
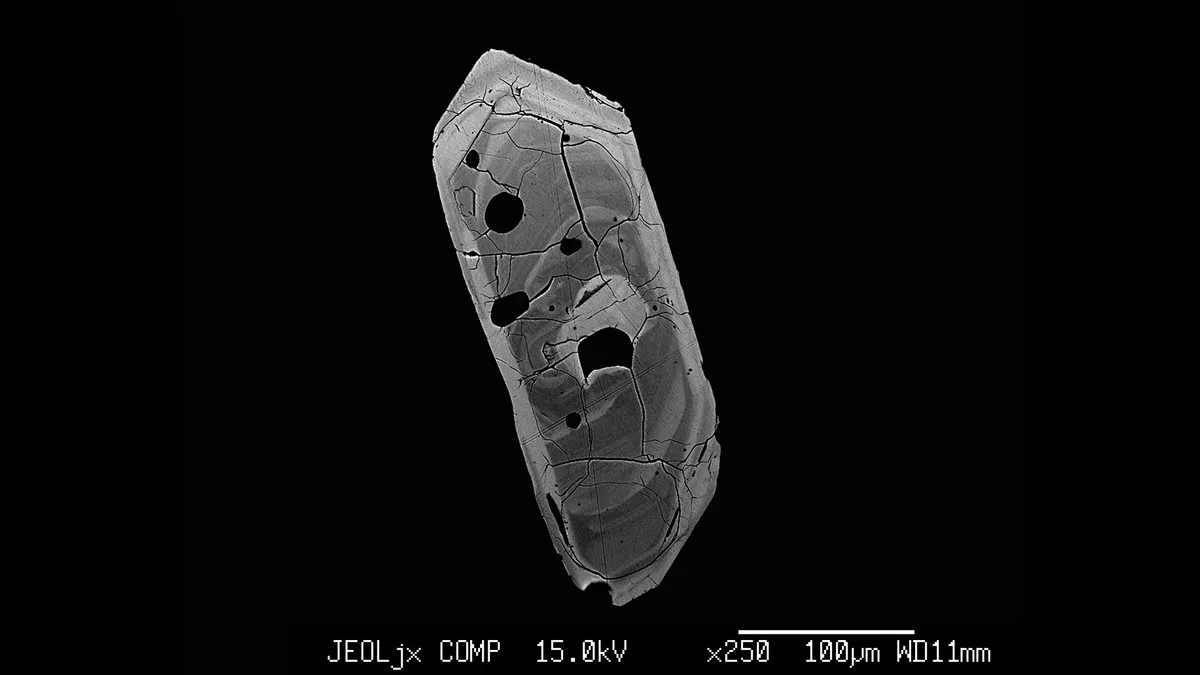

Finland’s river crystals hold clues about the formation of ‘Scandinavia’s’ oldest bedrock 3.75 billion years ago. The analysis revealed that part of the crust is about 250 million years older than scientists previously thought, and that it likely originated in Greenland, according to a University of Copenhagen statement released March 21. See the study here.

Scientists studying rocks in South Africa report evidence for the earliest known earthquake triggered by plate tectonics. The temblor struck more than 3 billion years ago.

This year, the March equinox takes place on 20 March at 03:06 GMT. This means that in certain westward time zones, the equinox will actually fall on 19 March local time.

Sound waves fossilized in the maps of galaxies across the Universe could be interpreted as signs of a Big Bang that took place 13 billion years earlier than current models suggest. This research was published in The Astrophysical Journal.
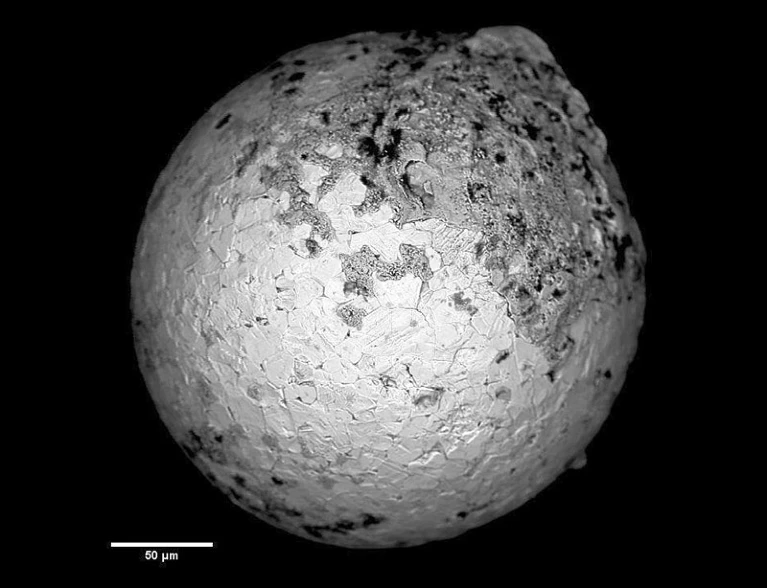

The debate occurred at a packed session featuring Hairuo Fu, a graduate student at Harvard University in Cambridge, Massachusetts, who is a member of the team that found the fragments…Many scientists have said they don’t want to spend much time analysing and refuting these claims.
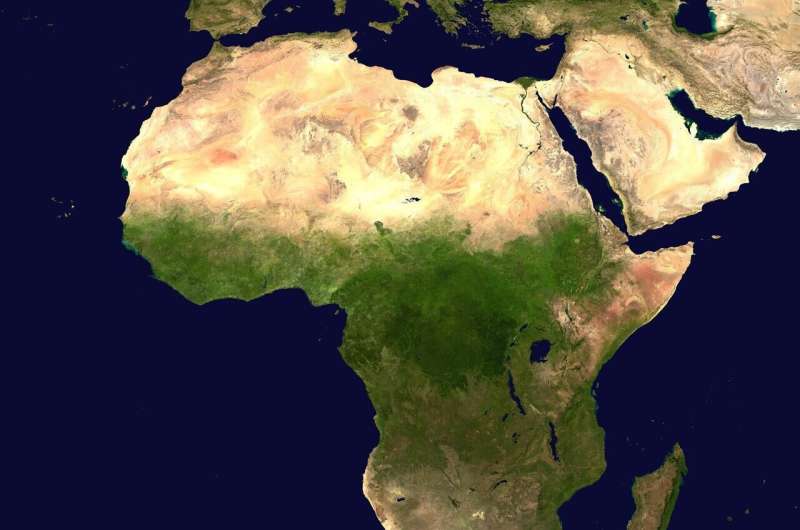
A pair of planetary scientists… have found evidence that the exodus of hominins out of Africa approximately 1 million years ago may have been driven by the first major glaciation of the Pleistocene. See the study here.
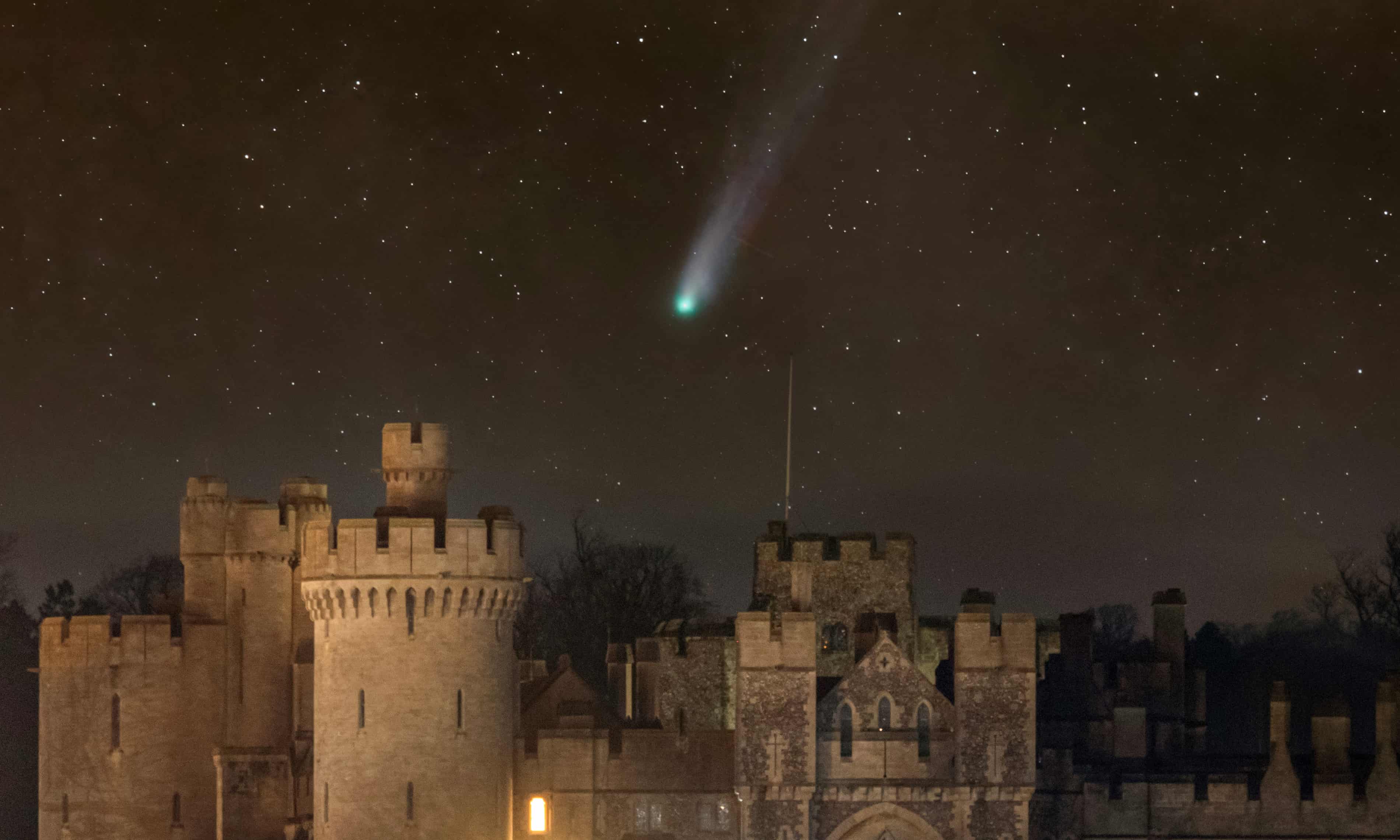

A comet that is larger than Mount Everest could become visible to the naked eye in the coming weeks as it continues its first visit to the inner solar system in more than 70 years, say astronomers.
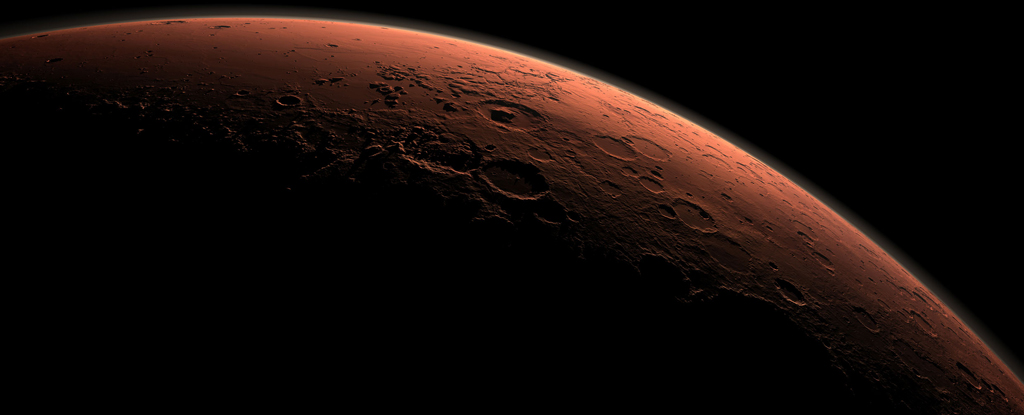
A slow cosmic dance between Earth and Mars has a hidden effect on cycles in the deep ocean. According to a new analysis of the deep-sea geological record, the gravitational interaction between the two planets results in cyclic changes in deep ocean currents that recur every 2.4 million years.








