Ancient news stories
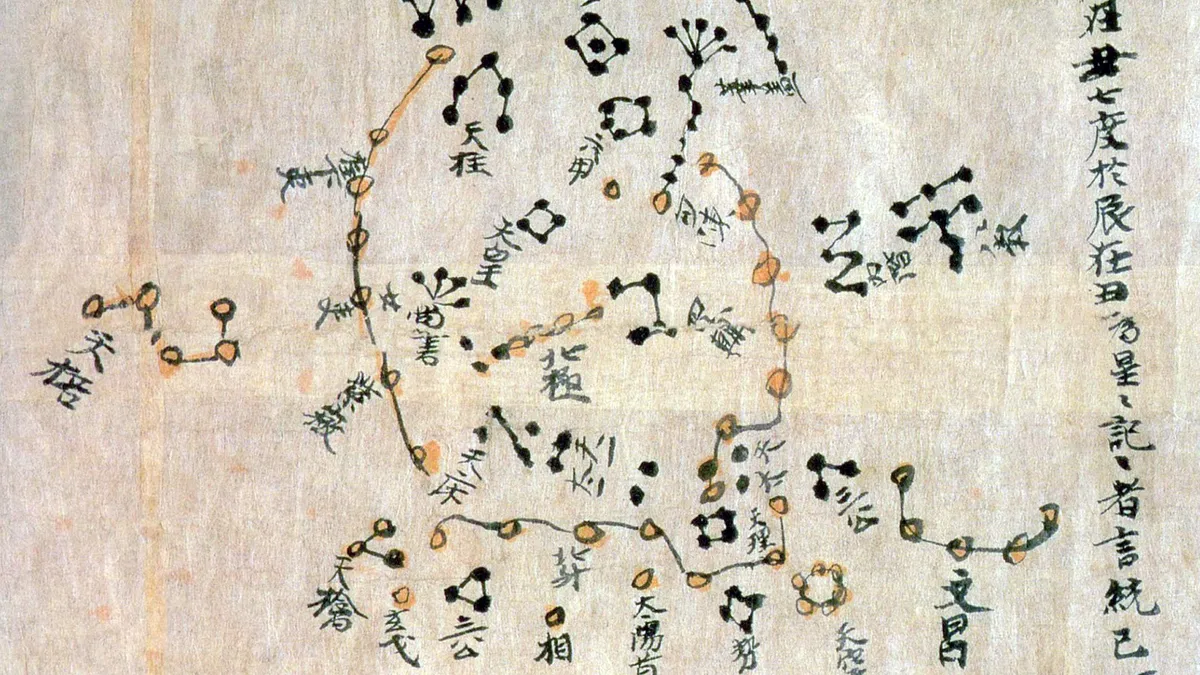
The oldest star chart in the world was made in China more than 2,300 years ago, a hotly debated preprint study finds.

Fossilised claw prints found in Australia suggest amniotes – the ancestors of reptiles, birds and mammals – evolved about 40m years earlier than thought.

Researchers led by the University of Glasgow in Scotland have identified a Late Upper Paleolithic site in the far north of the Isle of Skye, marking the most northerly evidence of Ahrensburgian culture in Britain.

Research found chimpanzees drum with non-random rhythms that suggest building blocks of music may predate humans by millions of years

A set of ancient wooden spears may be younger than scientists thought and wielded by Neanderthals instead of their ancestors. The research was published Friday in the journal Science Advances.

These Homo sapiens—nomadic hunter-gatherers who populated Western Europe between 11,000 and 35,000 years ago—carry with them a leather rucksack containing objects of value: mostly flint cores and flakes that they will use on the journey as hunting tools, or as ornaments. These are pieces of their homeland. See the research here.

Five millennia ago, wealth inequality—which had stayed roughly constant for thousands of years—exploded. It has stayed constant, albeit much higher, ever since…One factor, Bowles and Bocconi University economic historian Mattia Fochesato write in a paper recently published in the Journal of Economic Literature, was the ox-drawn plow.
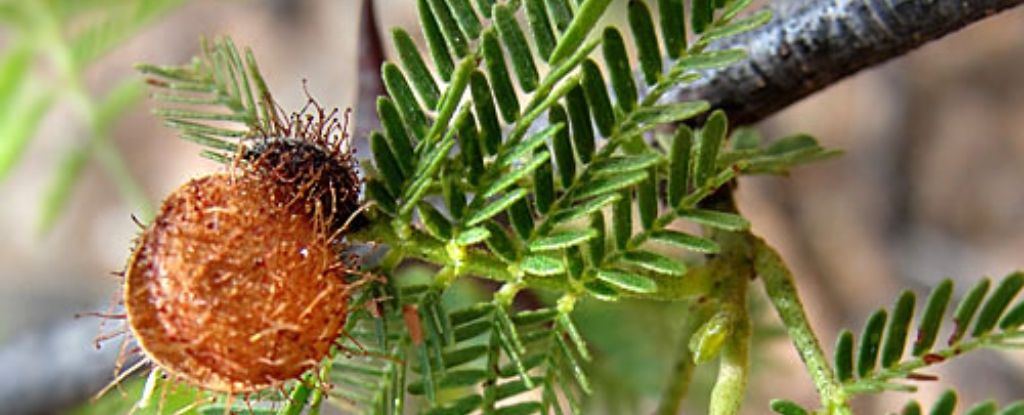

Long used in Indigenous Brazilian rituals, the jurema preta plant, which contains a potent psychedelic, is gaining ground as a potential treatment for depression. The findings were published in the scientific journal Nature in April.

Published in Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences, the findings contradict a widely cited fracture model that credited rock core geometry and stiffness with flaking patterns and predicted that hammer strike angle would have minimal effect on flake formation. Results suggest a greater degree of cognitive control by early human tool makers than previously recognized.

Two thousand years before the Inca empire dominated the Andes, a lesser-known society known as the Chavín Phenomenon shared common art, architecture, and materials throughout modern-day Peru…one of their most powerful tools wasn’t farming. It was access to altered states of consciousness. That’s according to a new study that uncovered the earliest-known direct evidence of the use of psychoactive plants in the Peruvian Andes
“The duration of the Marinoan glaciation (4 to 15 million years) currently has 11 million years of uncertainty”, write the authors of the new paper published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.

Researchers initially believed the unnamed meteorite hit Earth 1.17 billion years ago, creating the Stac Fada Member rock layer in northwestern Scotland. However, a new study has determined that the meteorite actually hit 990 million years ago — around 200 million years later than previously thought.

An interest in understanding the role that the Milky Way played in Egyptian culture and religion has led University of Portsmouth Associate Professor of Astrophysics, Dr. Or Graur to uncover what he thinks may be the ancient Egyptian visual depiction of the Milky Way. Combining astronomy with Egyptology…his findings are now published in the Journal of Astronomical History and Heritage.

The Picuris Pueblo, a sovereign nation in New Mexico, has oral histories and cultural traditions that link the tribe to the region of Chaco Canyon, one of the ancient centers of Pueblo culture and society. “We’ve been telling our stories as long as time immemorial,” said Picuris Lt. Gov. Craig Quanchello. But he said those traditions were often “overlooked and erased.” The findings, published Thursday in the journal Nature.

For decades, scientists believed Vesta, one of the largest objects in our solar system’s asteroid belt, wasn’t just an asteroid and eventually concluded it was more like a planet with a crust, mantle and core. Now, Michigan State University has contributed to research that flips this notion on its head. The paper was published in Nature Astronomy.
Platypus and echidnas are the only surviving members of the monotreme family. This includes the only mammals to lay eggs rather than giving birth to live young. For this reason, they are considered relics of early mammal evolution. The new study was published in the Proccedings of the National Academy of Sciences journal.








