Humans news stories

For decades, scientists believed Vesta, one of the largest objects in our solar system’s asteroid belt, wasn’t just an asteroid and eventually concluded it was more like a planet with a crust, mantle and core. Now, Michigan State University has contributed to research that flips this notion on its head. The paper was published in Nature Astronomy.

A recent study conducted by Dr. Ana Paula Motta and her colleagues, in collaboration with the Balanggarra Aboriginal Corporation, has identified a new mid-to-late Holocene rock art style in Australia’s northeastern Kimberley region. The findings are published in the journal Australian Archaeology.
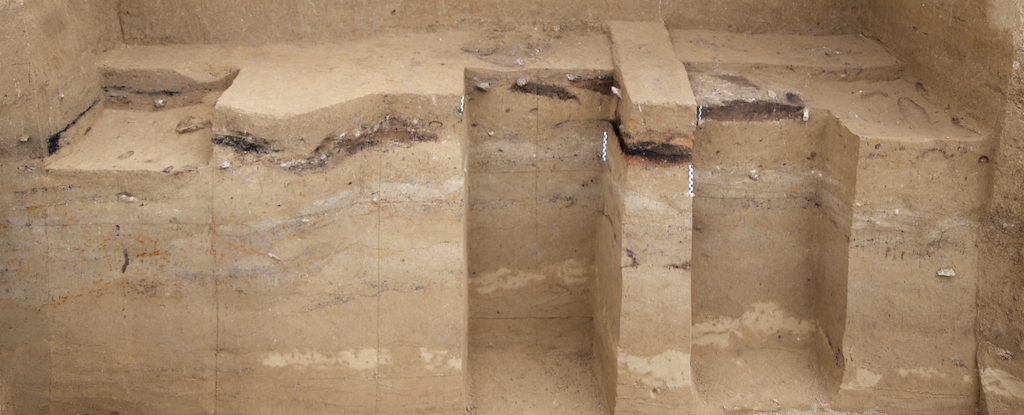

In a new study, researchers analyzed the remains of three ancient fireplaces found at an archaeological site in modern-day Ukraine, all of which are associated with human occupations at the site during the LGM. The study was published in Geoarchaeology.

Archaeologists in Peru said Thursday they found the 5,000-year-old remains of a noblewoman at the sacred city of Caral, revealing the important role played by women in the oldest center of civilization in the Americas.

Mass General Brigham researchers found that interactions between immune and brain cells drive fear responses, but treatment with psychedelics like MDMA and psilocybin may reverse these effects. Results are published in Nature.
Image by Matthew W. Johnson (Wiki Commons)

Following a recent study, Dr. Przemysław Bobrowski and his colleagues published new radiocarbon dates on Holocene (11,700 years ago to the present) sites located in the Tsakhiurtyn Hundi (Flint Valley) region of Mongolia. The work has been published in the journal Radiocarbon

A study led by Prof. Amos Frumkin from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem sheds new light on one of humanity’s most significant turning points: the Neolithic Revolution. Published in the Journal of Soils and Sediments, the study presents compelling evidence that catastrophic wildfires and soil erosion—driven by natural climate shifts—may have sparked the first widespread transition from hunting and gathering to farming in the southern Levant over 8,000 years ago.
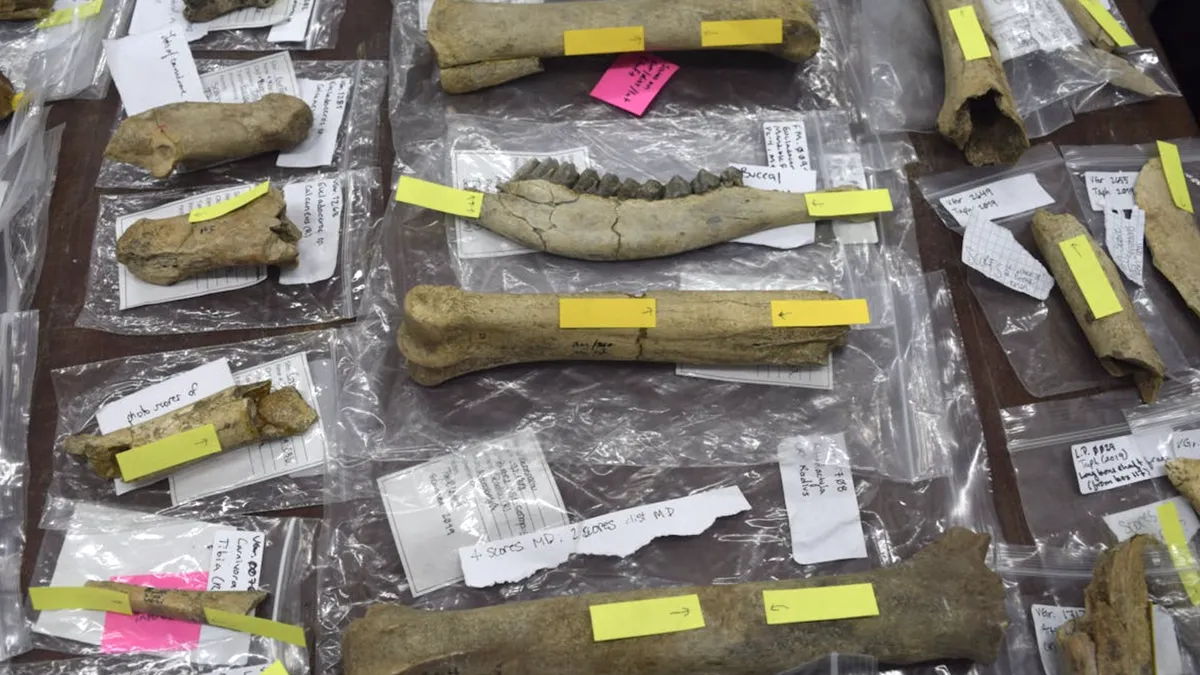
Researchers reexamining fossils identified telltale marks made by human ancestors cutting meat from bones. The discovery pushes back the date hominins started living in Europe by 200,000 years. The research was published in Nature Communications.

Thought to be more than 2,000 years old, the Antikythera mechanism is widely considered the first computer in history, an analog calculator that was way ahead of its time… or was it? The research has yet to be peer-reviewed or published in a journal, but is available on the preprint server arXiv.
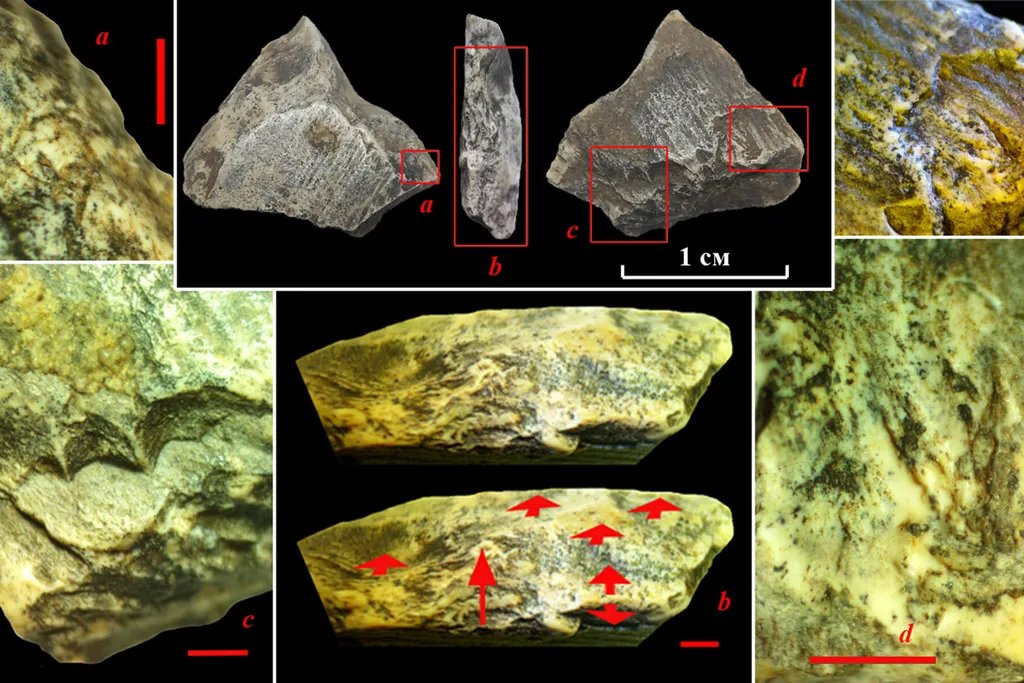

Archaeologists have unearthed mysterious 400,000-year-old artifacts made from mammoth tusks that may be the oldest human-made ivory objects ever found. They describe their findings in a recent paper published in the International Journal of Osteoarchaeology.
Crows have a sense of geometric intuition much like our own, a new study reveals. The research was published in Science Advances.

A study by Dr. Matthew S. Taylor, published in the Journal of Osteoarchaeology, reports on the reanalysis of modified human bones discovered at several prehistoric South Texas archaeological sites.
Scientists have cooked up a non-hallucinogenic version of LSD, which they say has “extremely high therapeutic potential” for conditions like schizophrenia.
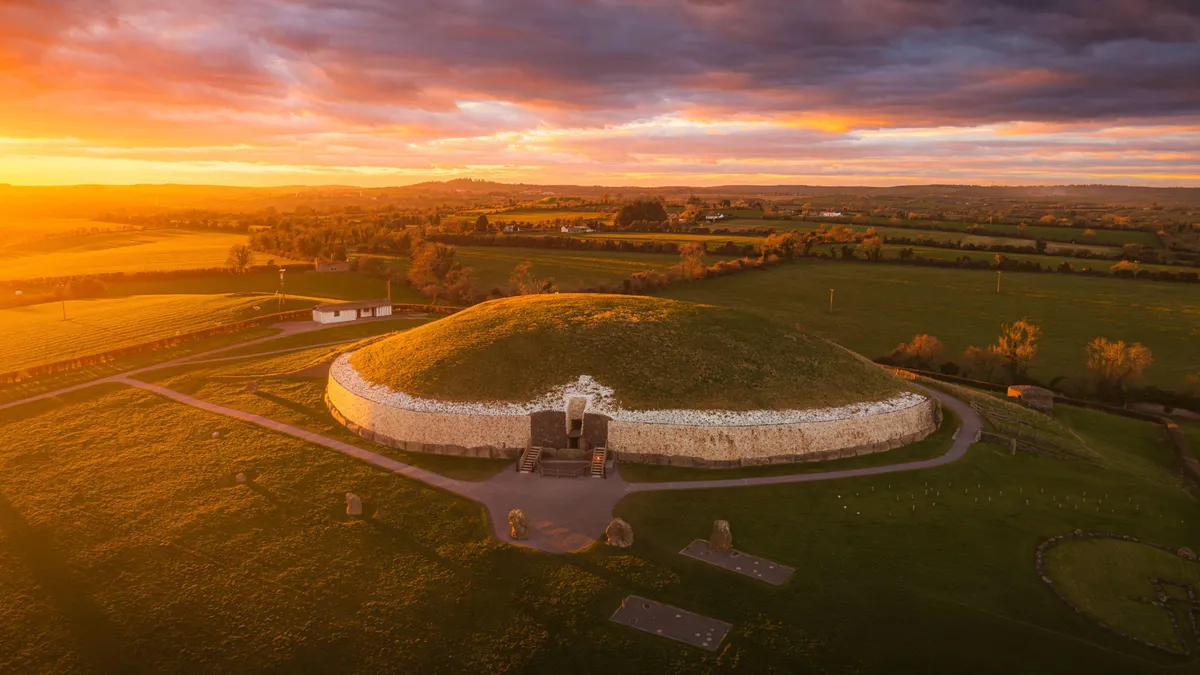

Archaeologists have long assumed that Stone Age tombs in Ireland were built for royalty. But a new analysis of DNA from 55 skeletons found in these 5,000-year-old graves suggests that the tombs were made for the community, not for a ruling dynasty. The study was published April 2 in the Cambridge Archaeological Journal

In a study published in the Journal of Paleolithic Archaeology, researchers analyzed these stone tools and discussed how the different techniques used to make them hint at the ways that prehistoric people traveled, interacted, and shared their craft.
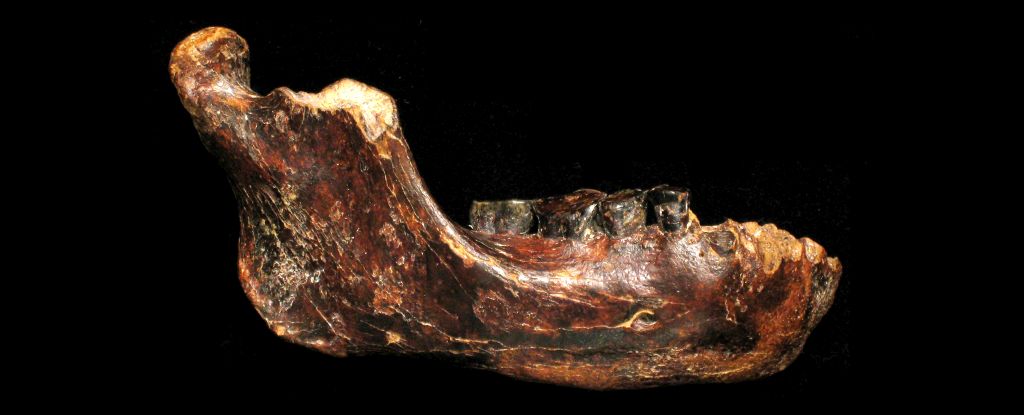
Analysis of a perfect jawbone found in Taiwan has given us new clues to the Denisovans, an enigmatic people with whom our ancestors had relations. The research has been published in Science.








