Humans news stories
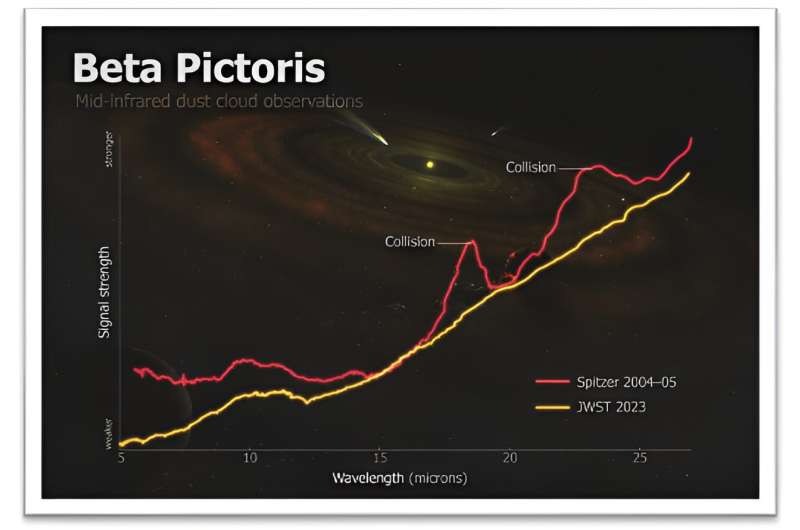
Astronomers have captured what appears to be a snapshot of a massive collision of giant asteroids in Beta Pictoris, a neighboring star system known for its early age and tumultuous planet-forming activity.
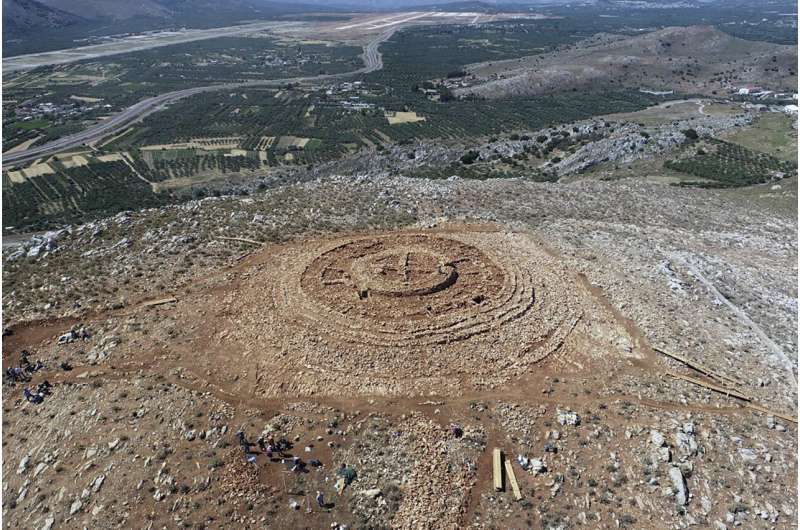

Greece’s Culture Ministry said Tuesday that the structure is a “unique and extremely interesting find” from Crete’s Minoan civilization, famous for its sumptuous palaces, flamboyant art and enigmatic writing system.
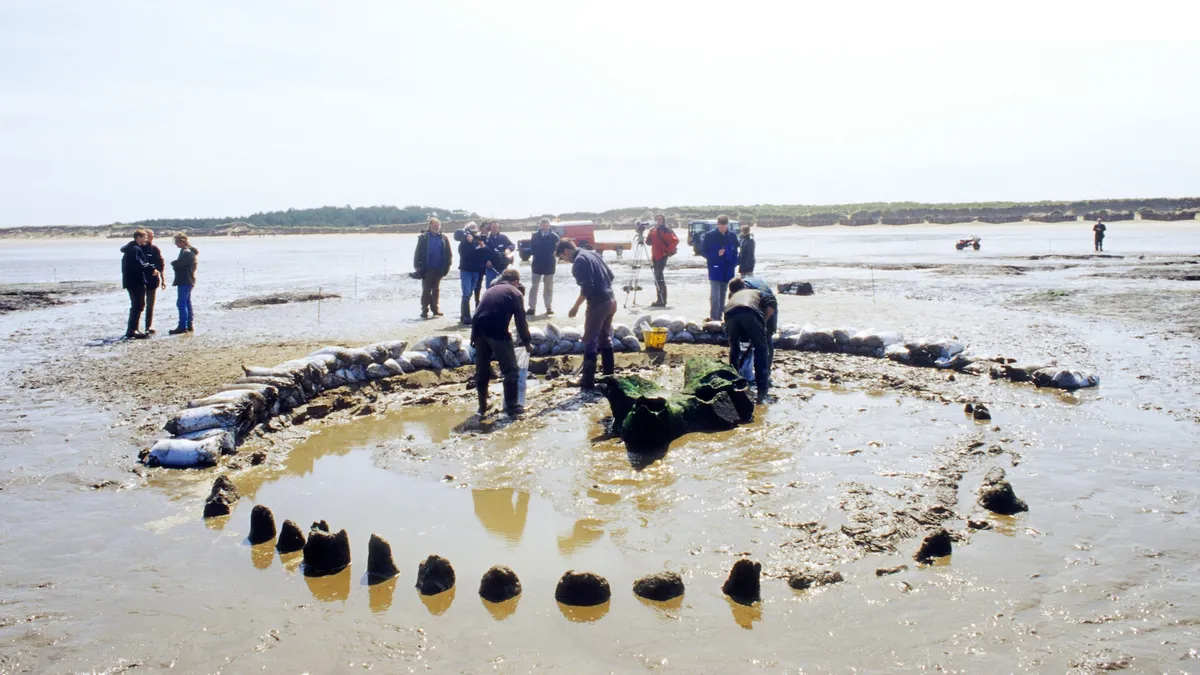

A mysterious Bronze Age wooden circle known as “Seahenge” on England’s east coast was built more than 4,000 years ago in an effort to bring back warmer weather during an extreme cold spell, a new study suggests.
The universal equation has been shown to accurately predict the flapping frequency of birds, insects and even long-extinct prehistoric creatures like the flying reptiles, pterosaurs. It even translates to the flapping flippers of swimming creatures like whales and penguins. The study is published in the open-access journal PLOS ONE.
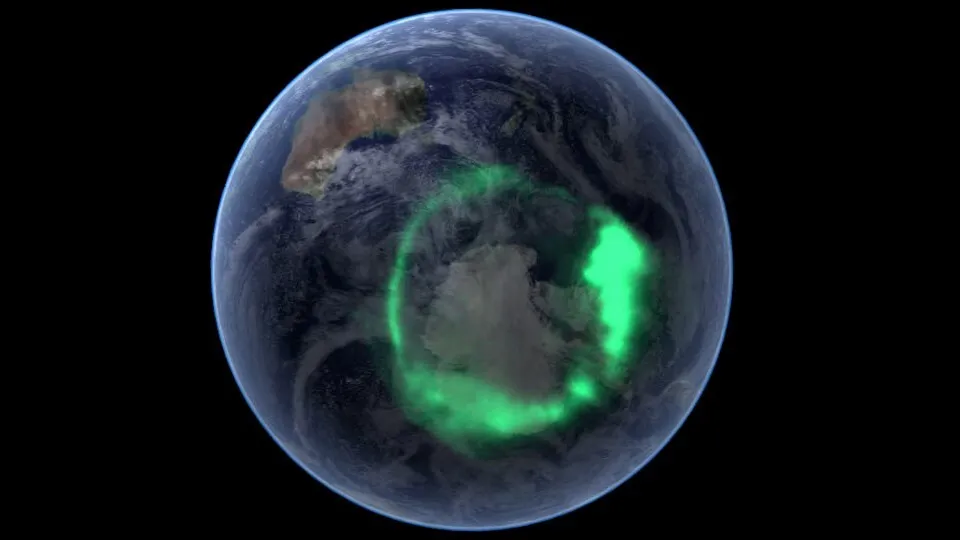

Mysterious dark matter could slosh over our planet like a wave. If it does, it may produce telltale radio waves in Earth’s atmosphere, new theoretical research suggests.
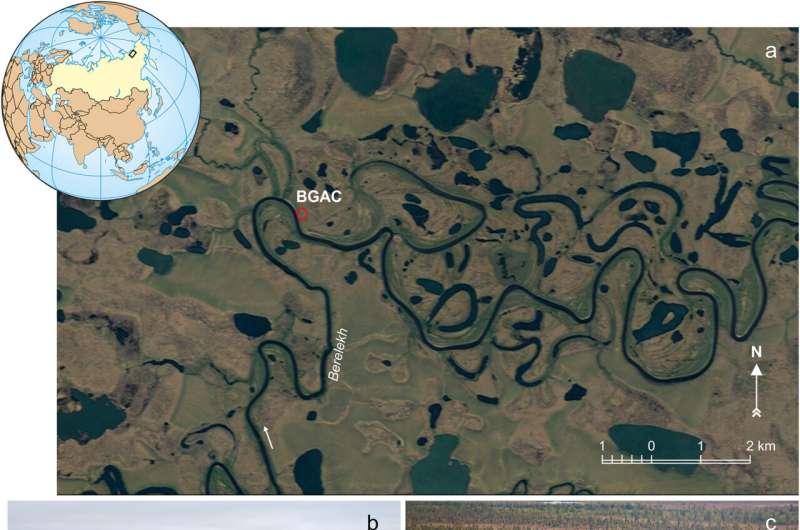
In the East Siberian Arctic (>70 °N), there is not only evidence of significant woolly mammoth populations, but also how humans interacted with them, the focus of new research in Quaternary Science Reviews.
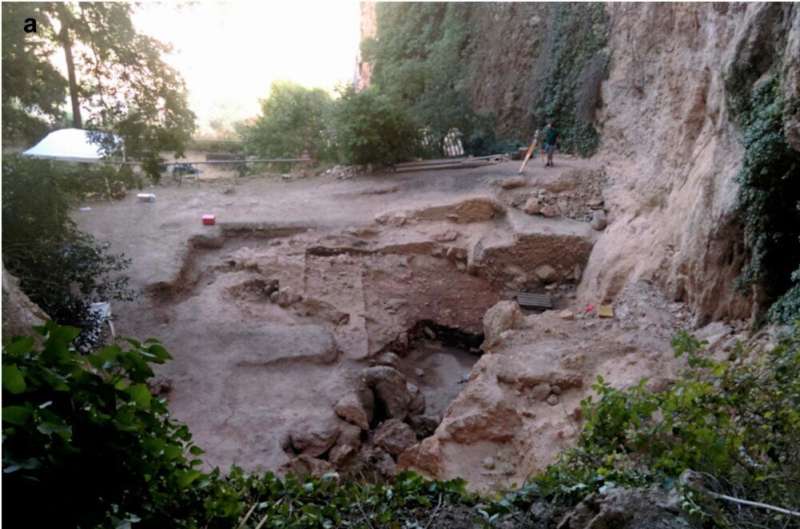

A new dating technique is used to more accurately estimate time differences between Paleolithic-age hearth fires. In a paper published in the journal Nature, the group describes how their new dating technique works, its accuracy range, and what their findings reveal about Neanderthals living in a river valley in what is now Spain approximately 50,000 years ago.
Psychedelic experiences can lead to a reduction in death anxiety, potentially through altering an individual’s metaphysical beliefs, according to new research published in the journal Death Studies.
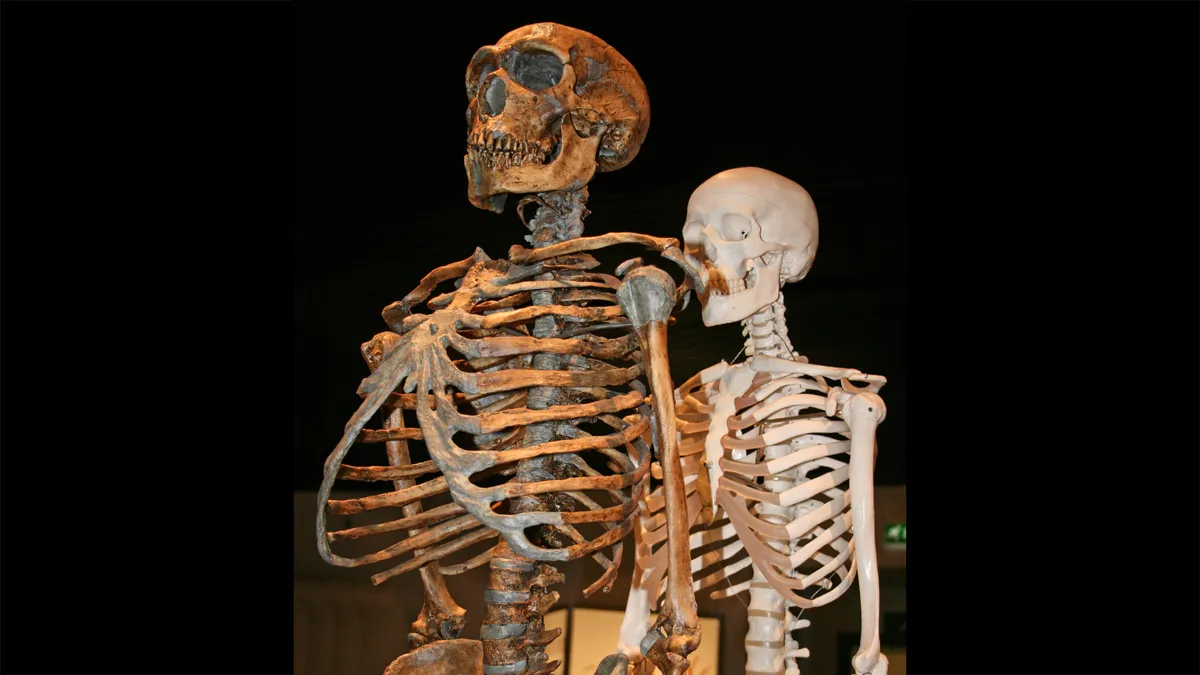

Neanderthal genes seen in modern humans may have entered our DNA through an interval of interbreeding starting about 47,000 years ago that lasted nearly 7,000 years, new research finds.
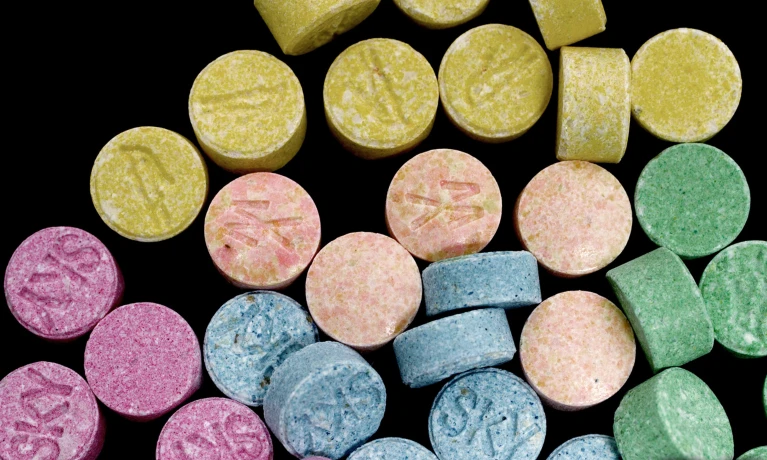
In a decision that shocked some observers, key advisers to the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) voted that the effectiveness of the party drug MDMA for treating post-traumatic stress disorder is unproven.
Details of the “highly unusual” neutron star’s discovery is published in Nature Astronomy. There have been more than 3,000 radio-emitting neutron stars discovered. The newly found star’s spin is well outside what astrophysicists predict of neutron star behaviour.
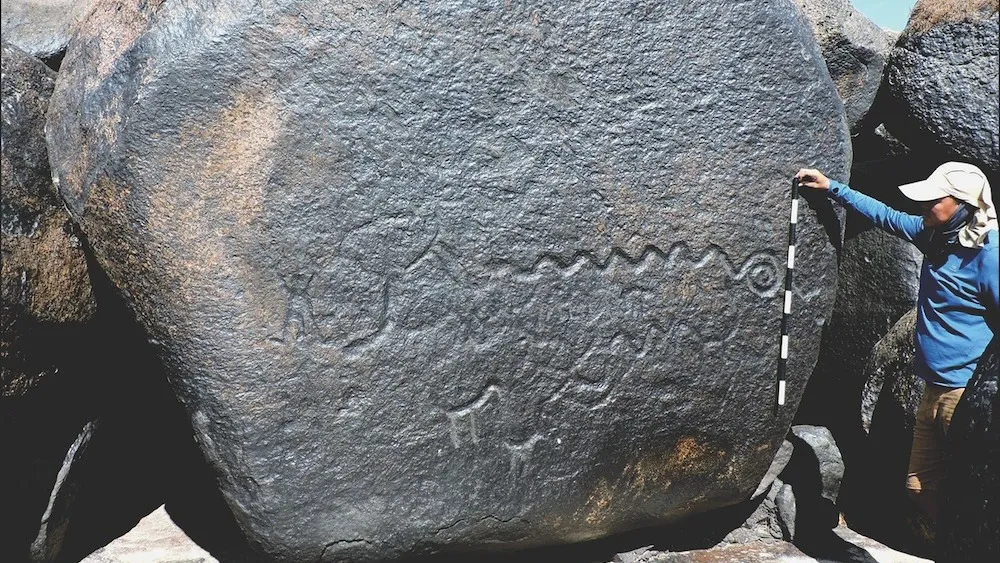

Archaeologists have fully mapped a series of ancient rock art in Venezuela and Colombia, including the world’s largest monumental engraving, using photography and drone footage. The study was published on Tuesday (June 4) in the journal Antiquity.

Researchers have explored how the River Nile evolved over the past 11,500 years and how changes in its geography could have helped shape the fortunes of ancient Egyptian civilisation. The research is published in Nature Geoscience.
Image by: Marc Ryckaert (MJJR – Wiki Commons)
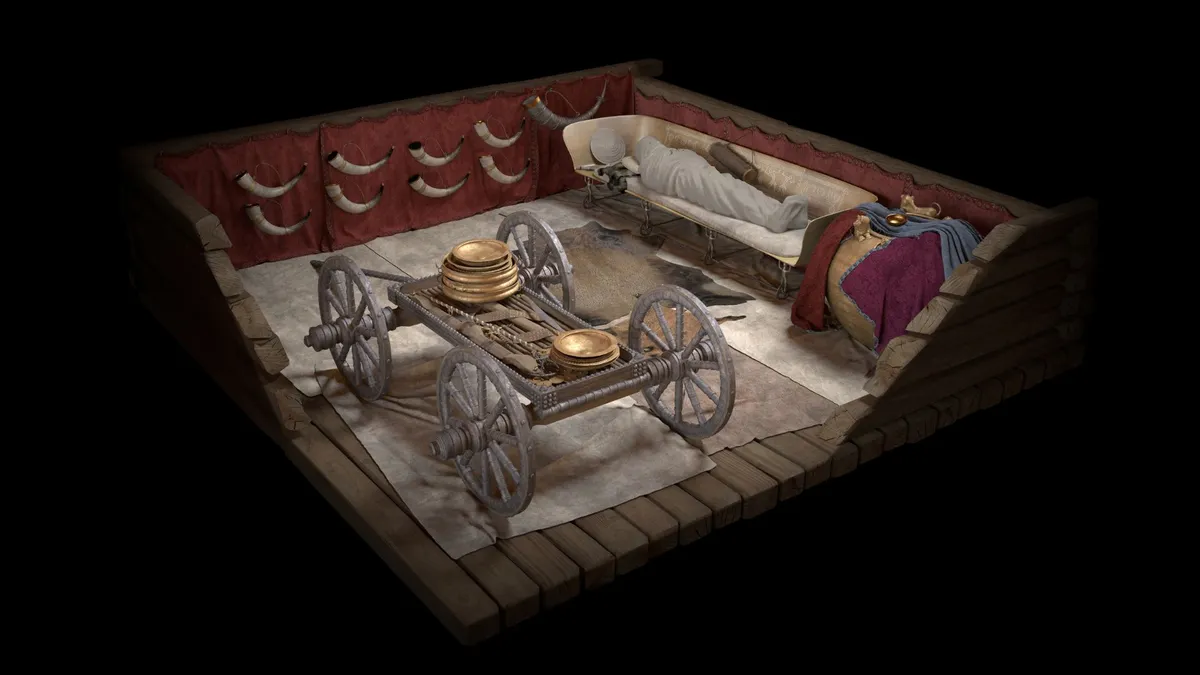

An uncle and nephew buried in two of the richest burial mounds, along with evidence of first-cousin inbreeding, point strongly toward matrilineal dynasties of elite power, according to the study, which was published Monday (June 3) in the journal Nature Human Behaviour

Despite decades of study, this Ice Age mystery remains unsolved. Researchers simply don’t have sufficient evidence at this point to rule out one scenario or the other—or indeed other explanations that have been proposed (e.g. disease, an impact event from a comet, or a combination of factors)… A new work published in Frontiers in Mammal Science set out to address this information deficit.
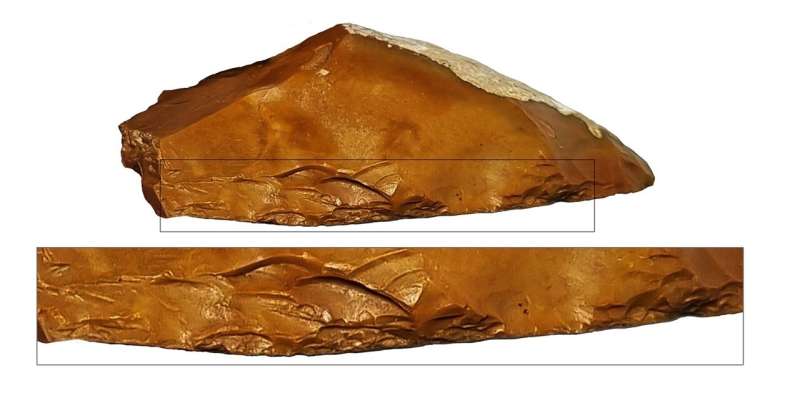

A new study from Tel Aviv University identified the earliest appearance worldwide of special stone tools, used 400,000 years ago to process fallow deer. The paper was published in Archaeologies.








