Humans news stories

Study described as ‘necessary first step’ in discovering whether dogs and humans can use push-button devices to communicate.

A study by researchers from the Insper Research Institute in São Paulo and the University of Bonn now shows an interesting side effect: where the measures were implemented, not only did deforestation decrease, but so did the number of homicides.

Astronomers have traced the origins of 200 meteorites to five impact craters in two volcanic regions on Mars, known as Tharsis and Elysium.

Since the end of the last Ice Age, growth of the human population has been far from uniform, marked instead by periods of rapid expansion followed by sharp declines. The reasons behind these fluctuations remain only partially understood. See the study published in the Journal of the Royal Society Interface.
The significance of ancient human fossils found in Africa is undeniable. But new research questions whether African fossil sites tell the whole story. See the study here.

In the deep human past, highly skilled seafarers made daring crossings from Asia to the Pacific Islands. It was a migration of global importance that shaped the distribution of our species — Homo sapiens — across the planet.

A ruined building in Kafr El Sheikh was where ancient Egyptians once stood, gazing at the stars above.
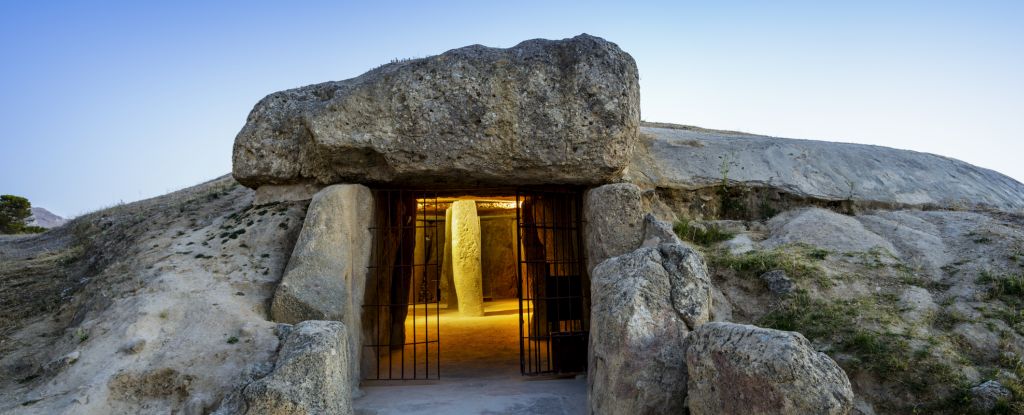

A new study has found that the Neolithic humans who built Menga were highly skilled, highly knowledgeable, and adept at solving complex engineering problems. The research has been published in Science Advances.

The long-lost divinatory list represents the oldest-known compilation of lunar eclipse omens from Babylonia – an ancient culture in Mesopotamia famed for its astrological beliefs…The study was published in the Journal of Cuneiform Studies.
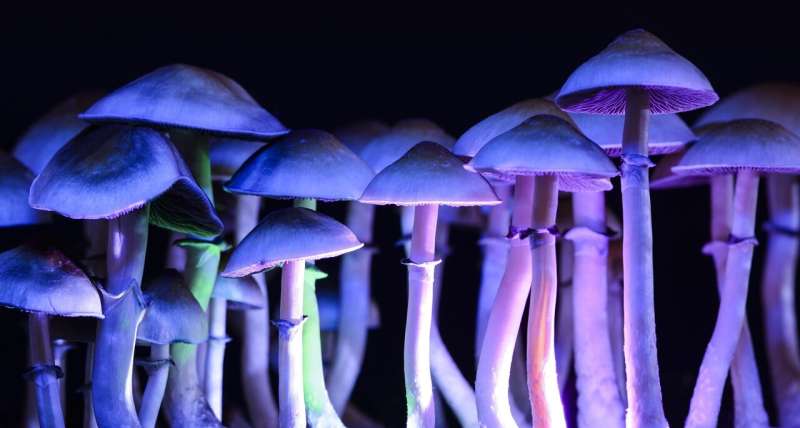

High doses of psilocybin—the active ingredient in magic mushrooms—appears to have a similar effect on depressive symptoms as the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) drug escitalopram, suggests a systematic review and meta-analysis published in The BMJ on the 21st of August.
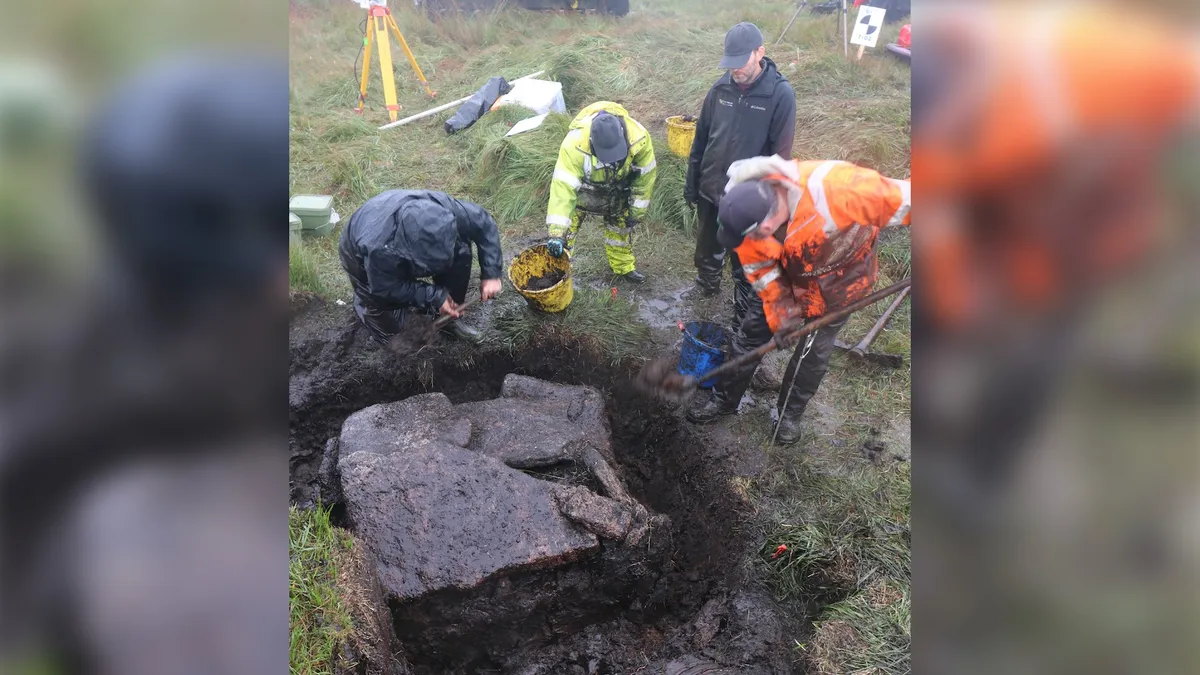

A “stunning” tomb found on an isolated moor in southwest England could help archaeologists understand what life was like 4,000 years ago in the Bronze Age.
A recent research published in the journal Heliyon suggests that LSD might modulate how the brain processes pain. The study reveals that LSD can alter the brain’s pain neural network, offering potential insights that could influence future research in cognitive science and pharmacology.
The first comprehensive review of tooth ablation in Taiwan from the Neolithic to the modern era has been conducted. The research, published in the Archaeological Research in Asia journal, aims to fill gaps in our knowledge of the origins and development of the practice in Taiwan.
A new neuroimaging study has revealed how the powerful psychedelic N,N-dimethyltryptamine, commonly known as DMT, alters the brain’s primary visual cortex, potentially explaining the intense visual distortions experienced by users. The findings arde published in NeuroImage.
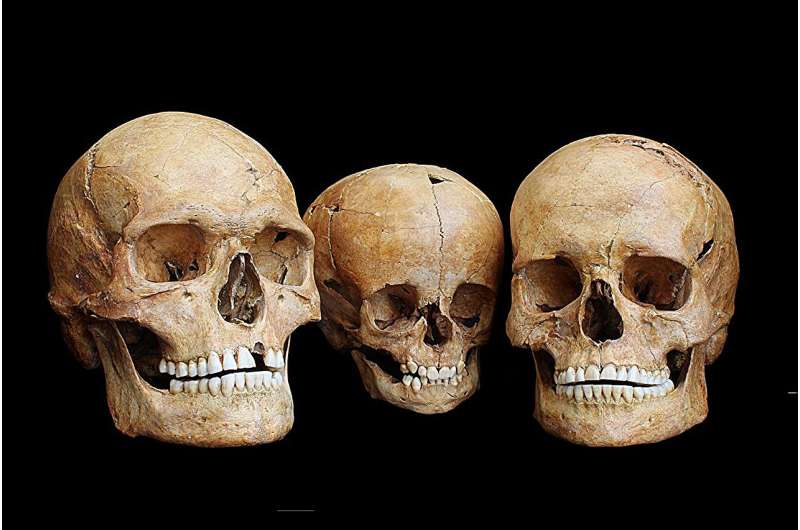
Population sizes declined sharply during the coldest period, and in the West, Ice Age Europeans even faced extinction, according to the study published August 16 in the journal Science Advances.
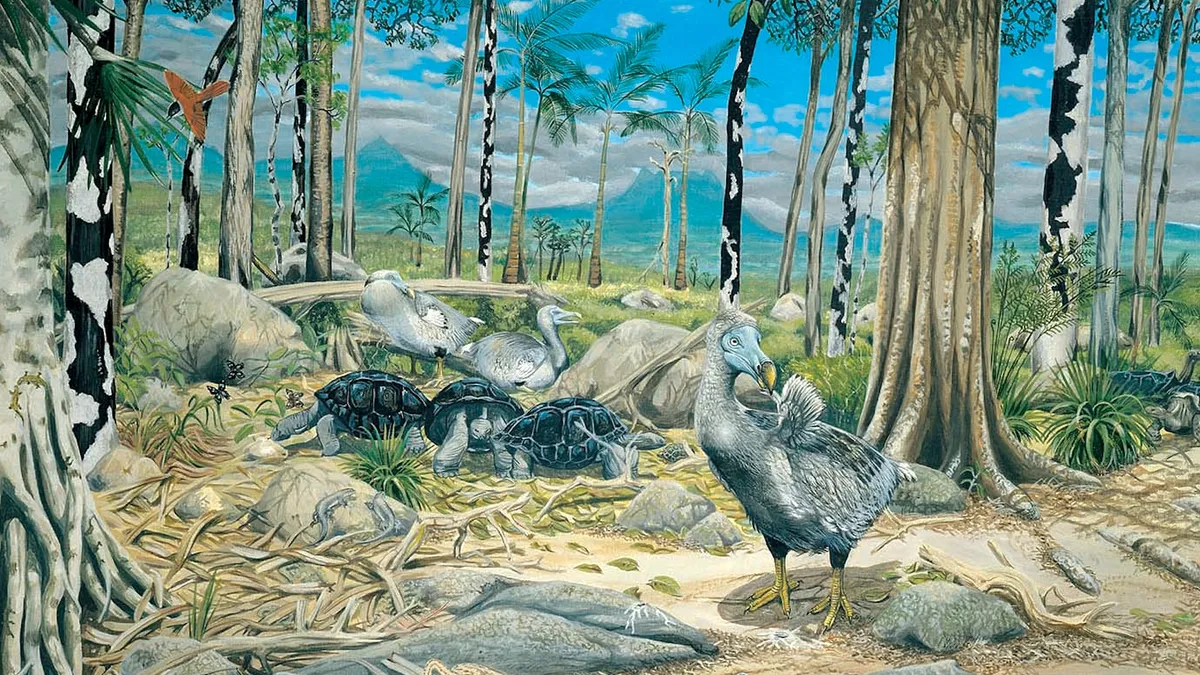

A new study has cleared up misconceptions about the extinct dodo, identifying the reference specimen for the species and showing they were fast and powerful.








