Earth news stories
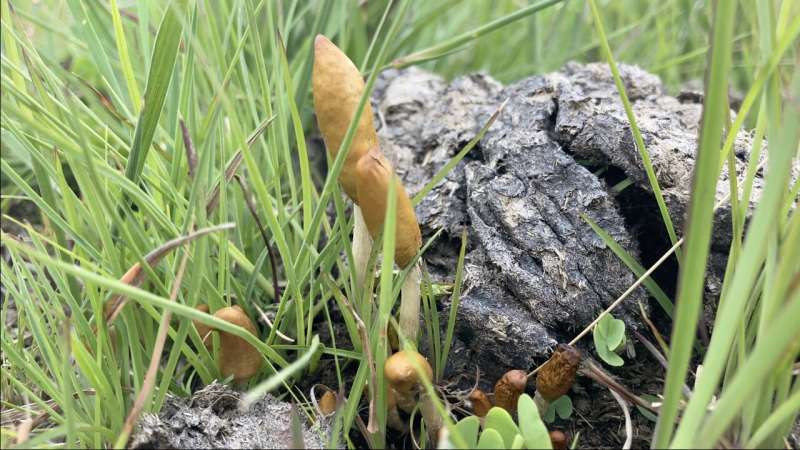

In a paper published in the journal Mycologia this week, researchers from Stellenbosch University (SU) and citizen mycologists describe the two new species as Psilocybe ingeli and Psilocybe maluti.

A giant 280m-year-old salamander-like creature that was an apex predator before the age of the dinosaurs has been discovered by fossil hunters in Namibia.

The discovery offers a glimpse into the Earth’s history and hints at how extreme climate change could alter the planet, according to their findings, published June 5 in the journal Science Advances.
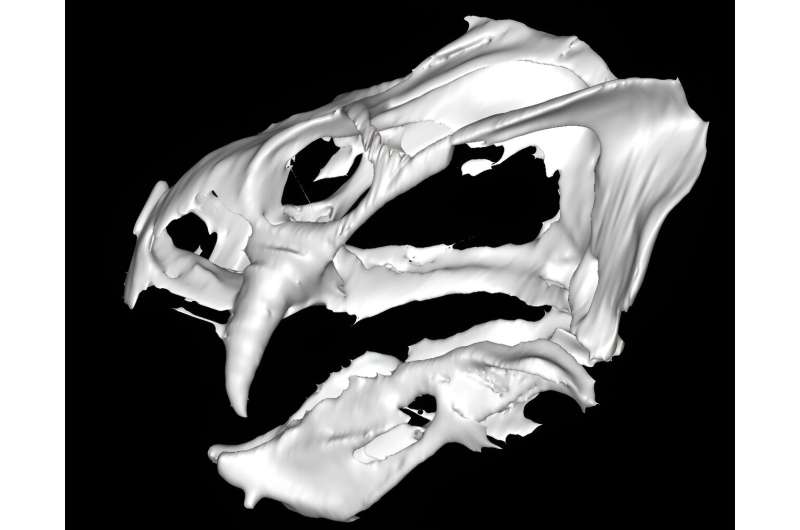
Details of an ancient cousin of modern-day mammals are being revealed for the first time. Hi-tech scanning of an ancient fossil, which was captured in sandstone around 252–254 million years ago, is giving experts valuable insight into the animal’s anatomy and evolution. The study, published in the Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society.
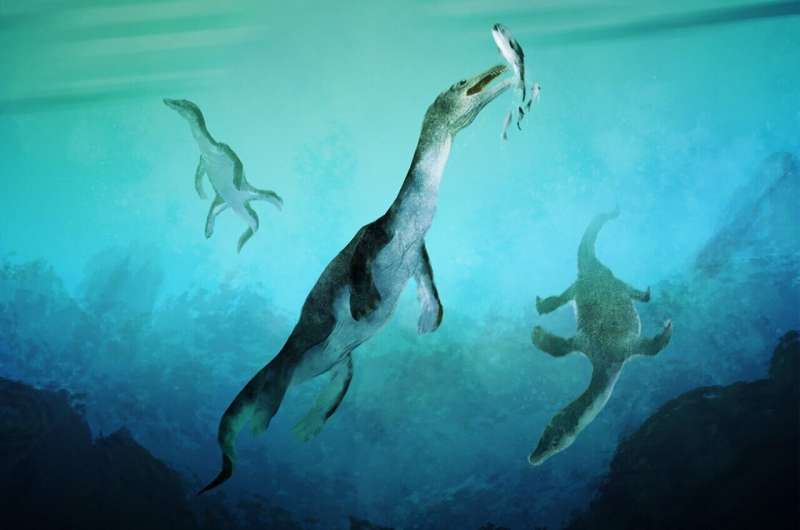

An international team of scientists has identified the oldest fossil of a sea-going reptile from the Southern Hemisphere—a nothosaur vertebra found on New Zealand’s South Island. 246 million years ago, at the beginning of the Age of Dinosaurs, New Zealand was located on the southern polar coast of a vast super-ocean called Panthalassa.
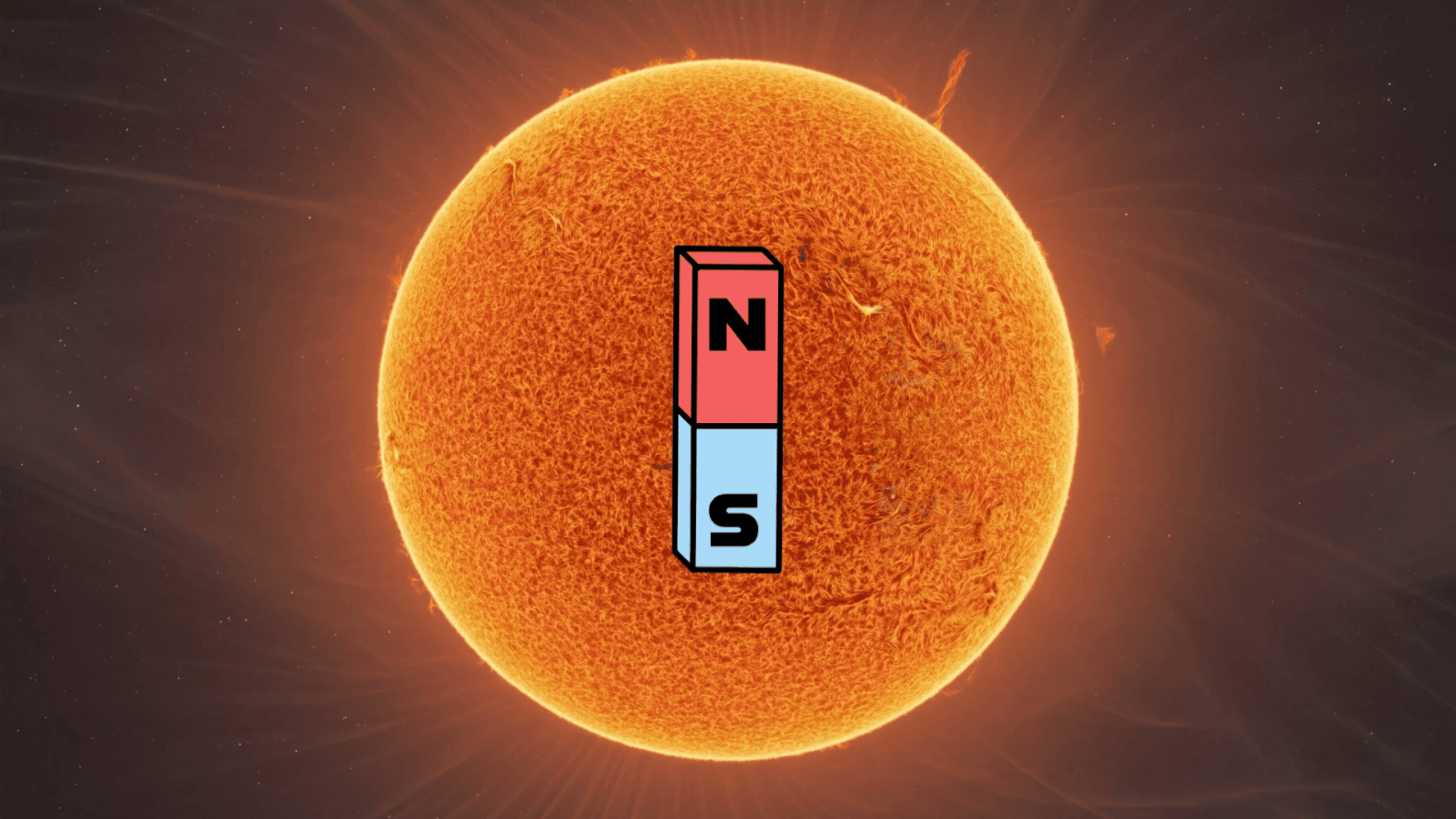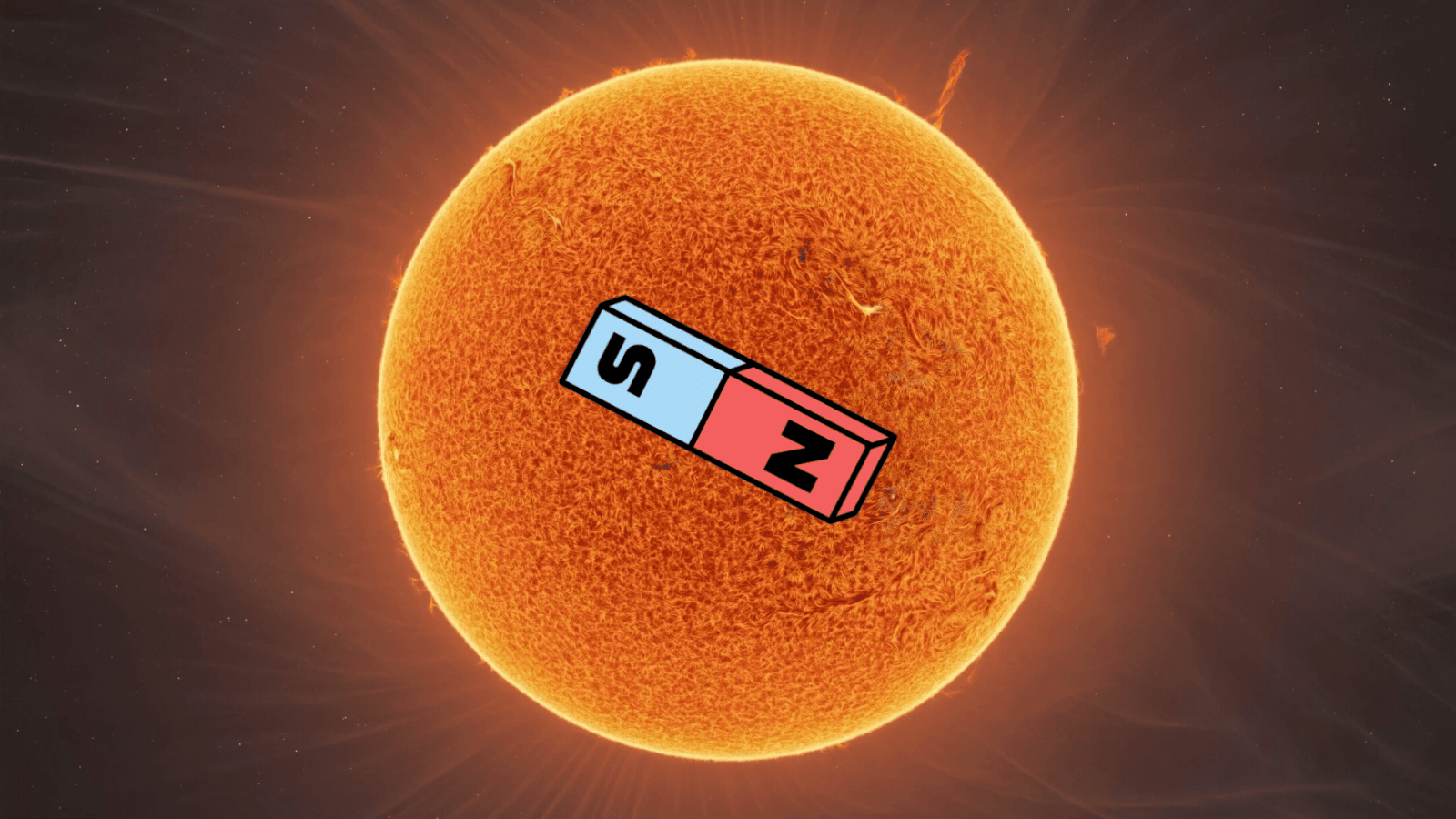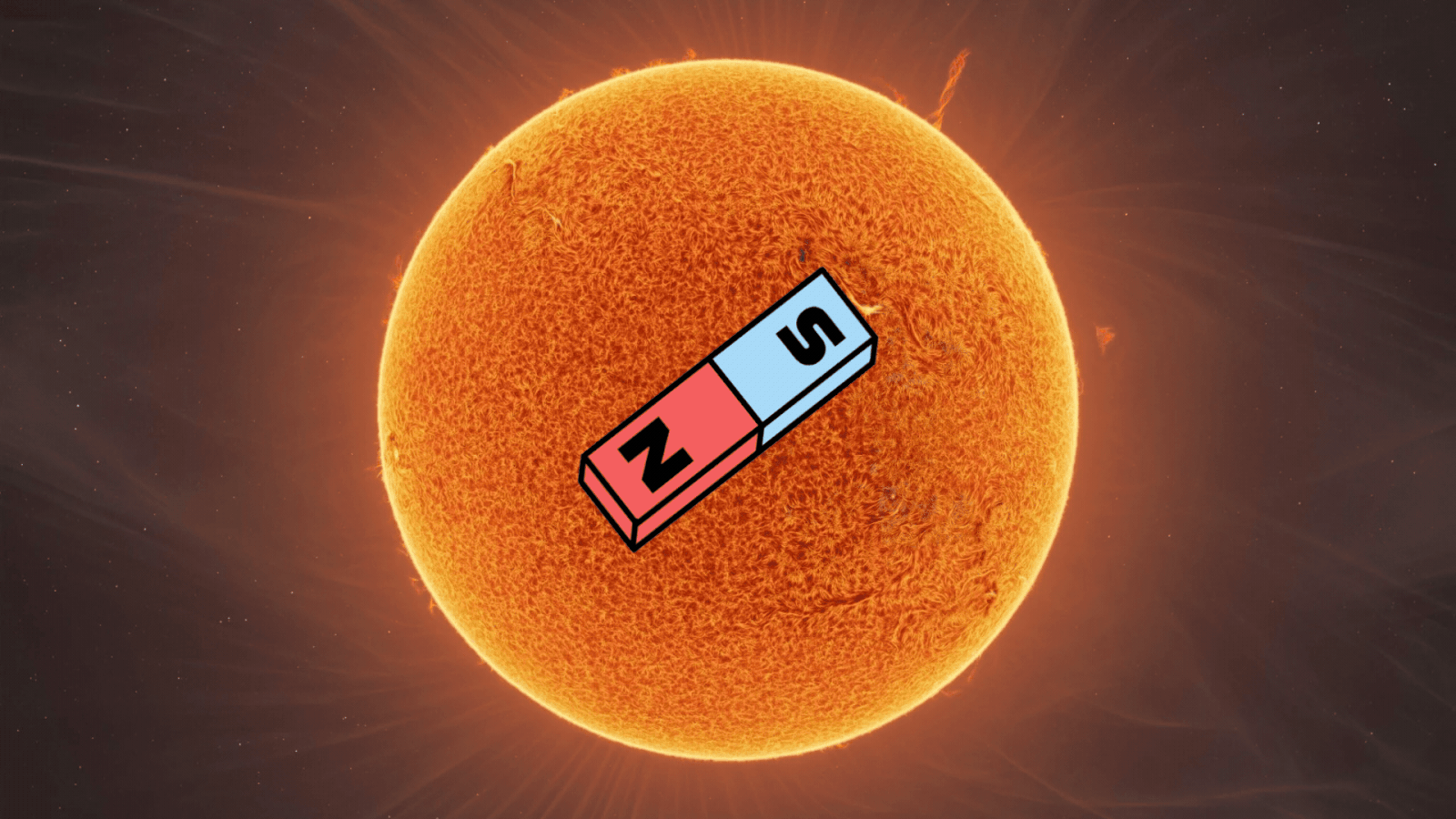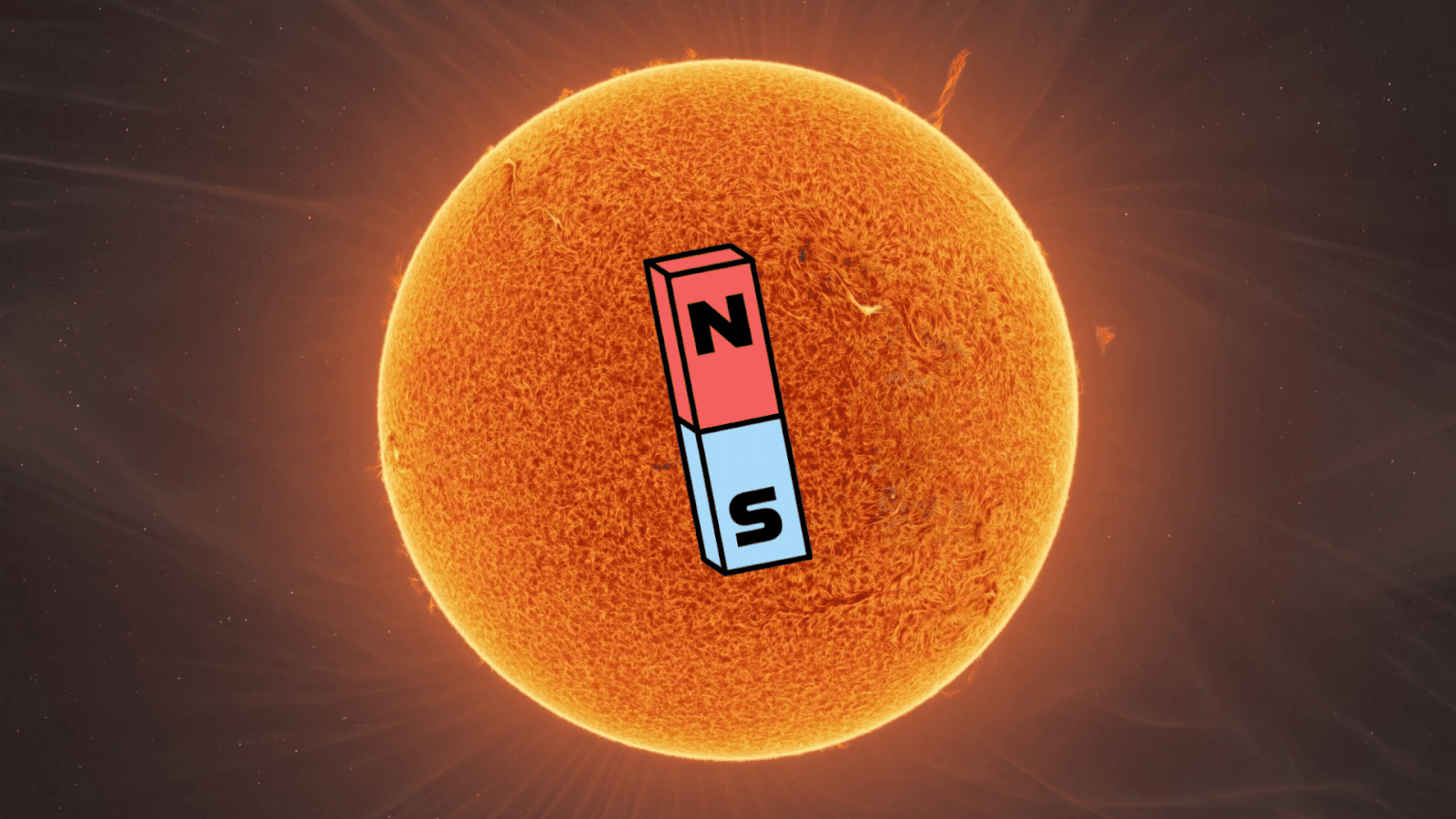
This phenomenon happens roughly every 11 years and marks an important stage in the solar cycle. The shift in polarity indicates the halfway point of solar maximum, the height of solar activity, and the beginning of the shift toward solar minimum.
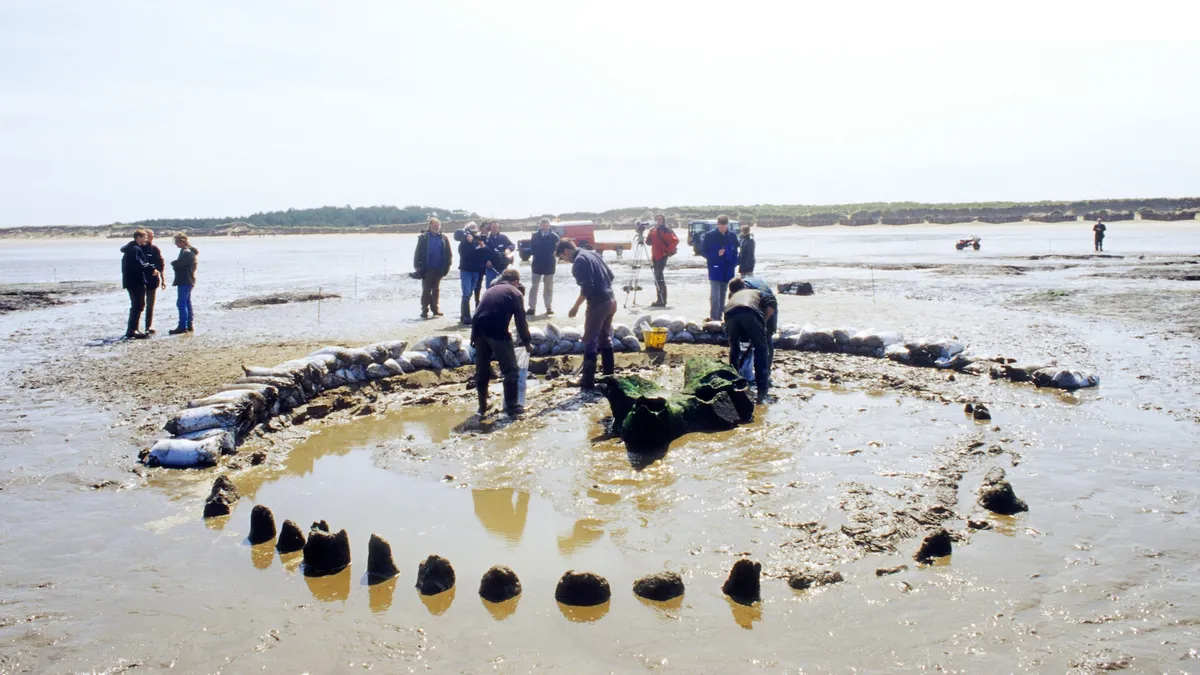

A mysterious Bronze Age wooden circle known as “Seahenge” on England’s east coast was built more than 4,000 years ago in an effort to bring back warmer weather during an extreme cold spell, a new study suggests.
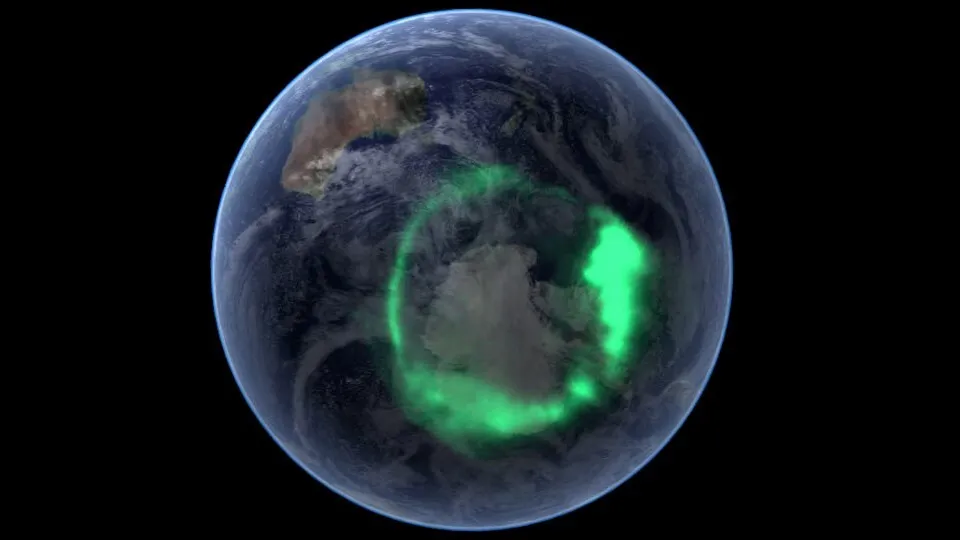

Mysterious dark matter could slosh over our planet like a wave. If it does, it may produce telltale radio waves in Earth’s atmosphere, new theoretical research suggests.
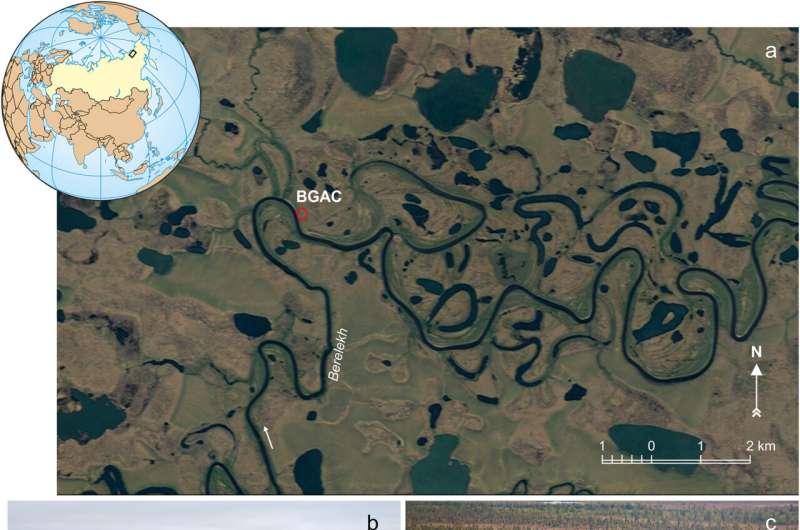
In the East Siberian Arctic (>70 °N), there is not only evidence of significant woolly mammoth populations, but also how humans interacted with them, the focus of new research in Quaternary Science Reviews.
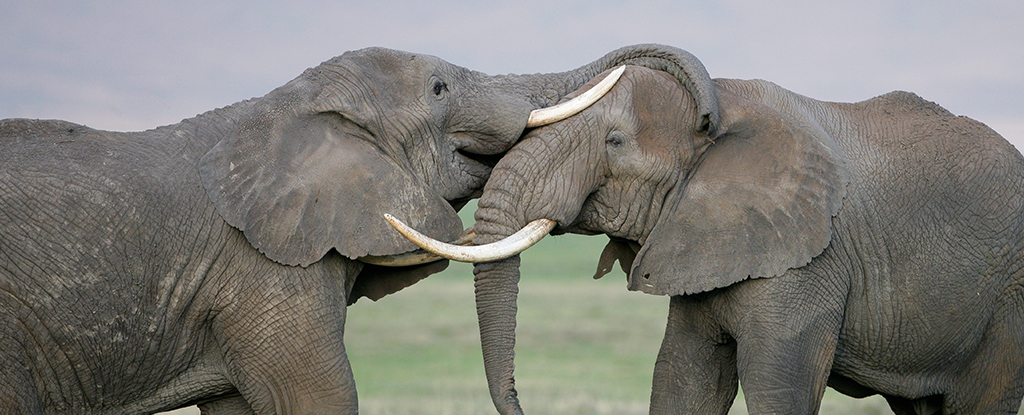

Elephants call out to each other using individual names that they invent for their fellow pachyderms, a study said on Monday.
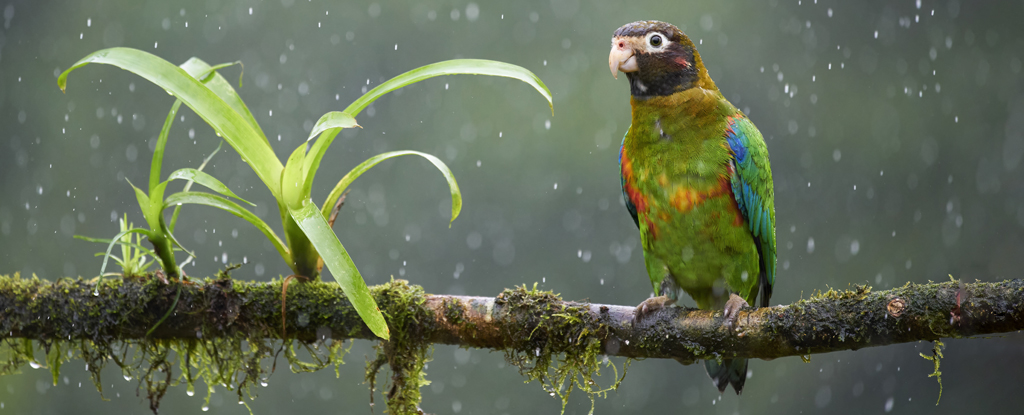

Earth’s largest remaining tract of tropical rainforest is kept alive by a complex water cycle that we’re only just beginning to understand. Yet our activities are changing it before we can see the full picture, a new report finds.
New research led by geologists at Western Australia’s Curtin University provides evidence that fresh water emerged on Earth about 4 billion years ago – half a billion years earlier than previously thought. The study is published in the journal Nature Geoscience.

Researchers have explored how the River Nile evolved over the past 11,500 years and how changes in its geography could have helped shape the fortunes of ancient Egyptian civilisation. The research is published in Nature Geoscience.
Image by: Marc Ryckaert (MJJR – Wiki Commons)
New research published in the journal Science Advances might explain the Earth-shaking processes that led to the end-Cambrian mass extinction.

Despite decades of study, this Ice Age mystery remains unsolved. Researchers simply don’t have sufficient evidence at this point to rule out one scenario or the other—or indeed other explanations that have been proposed (e.g. disease, an impact event from a comet, or a combination of factors)… A new work published in Frontiers in Mammal Science set out to address this information deficit.
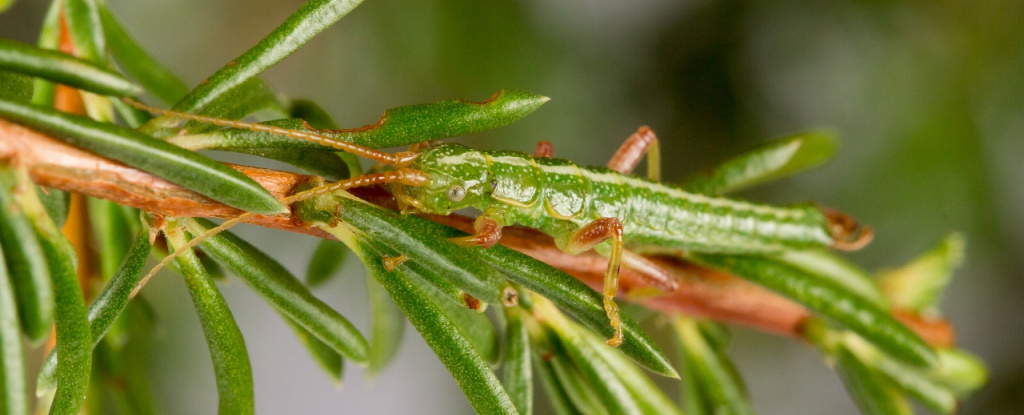

A new study of stick insects suggests that evolution may sometimes repeat itself in a predictable manner, which could help our understanding of how organisms may change in response to selection pressures. The study has been published in Science Advances.








