Earth news stories

Researchers exploring the Indian Ocean have discovered the remains of a collapsed underwater volcano with an uncanny resemblance to the all-seeing “Eye of Sauron” from J.R.R. Tolkien’s famous fantasy series “The Lord of the Rings,” as well as two other seafloor structures named after places in Tolkien’s Middle-earth.
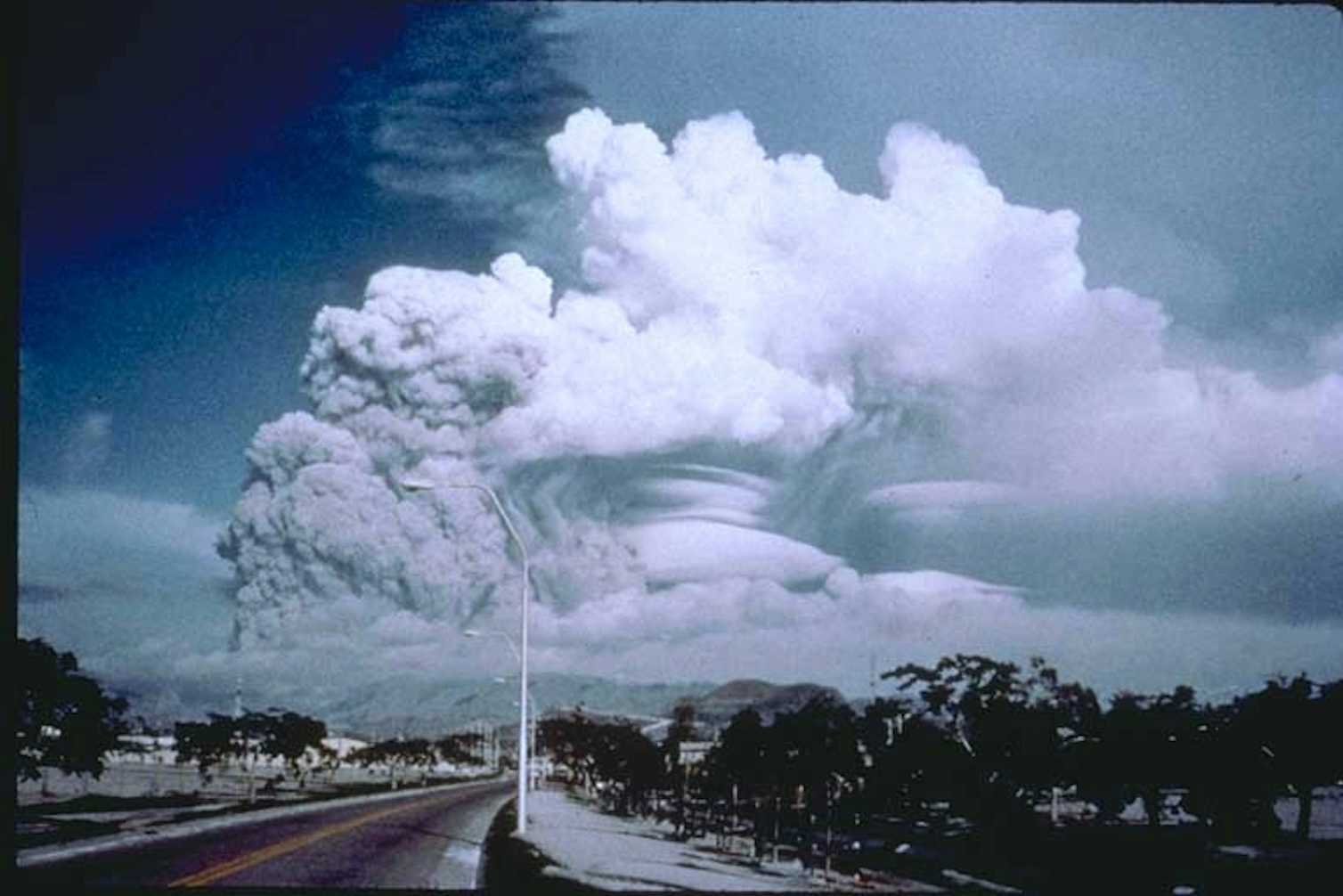

Around 74,000 years ago, a “supereruption” on the island of Sumatra, Indonesia, blasted out an estimated 5,000 cubic kilometres of magma.
Researchers have discovered the fossilised remains of 3.4-billion-year-old methane-cycling microbes that lived in a hydrothermal system beneath the ancient seafloor – the oldest microfossils of this type found to date.
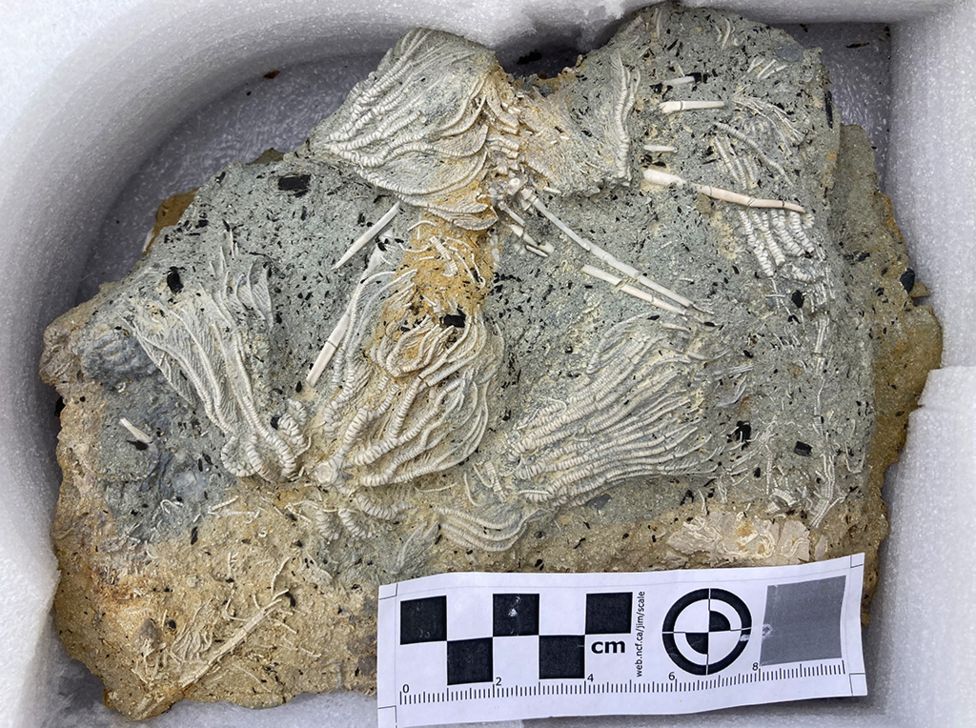

Palaeontologist Tim Ewin is standing in a quarry, recalling the calamity that’s written in the rocks under his mud-caked boots.
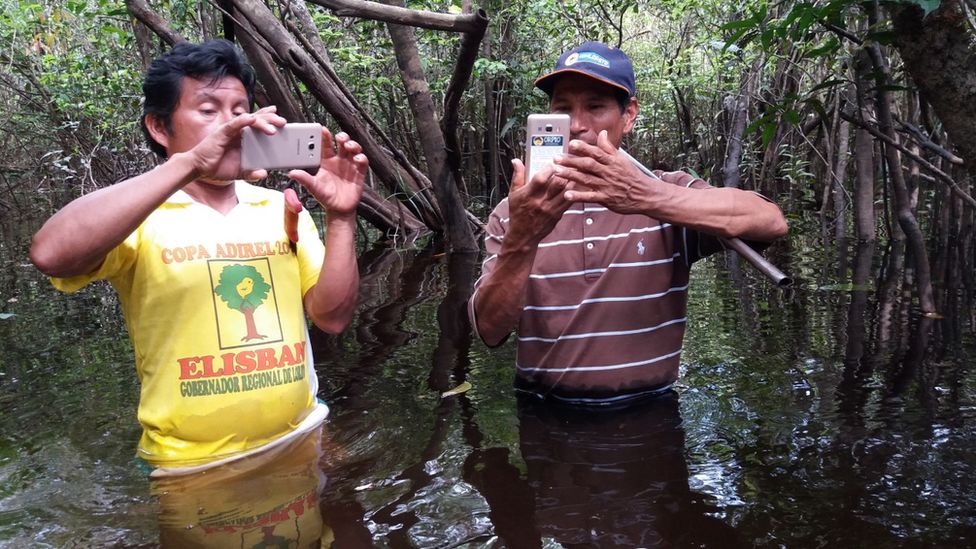

Technology can help indigenous communities to significantly curb deforestation, according to a new study. Indigenous people living in the Peruvian Amazon were equipped by conservation groups with satellite data and smartphones.

For almost 2 decades, genomes isolated from fossils have galvanized the study of human evolution. Yet despite vast improvements in retrieving and analyzing that DNA, researchers have deciphered whole genomes from just 23 archaic humans, 18 of them Neanderthals. This week, however…

Scientists at the University of Southampton have discovered that changes in Earth’s orbit may have allowed complex life to emerge and thrive during the most hostile climate episode the planet has ever experienced.
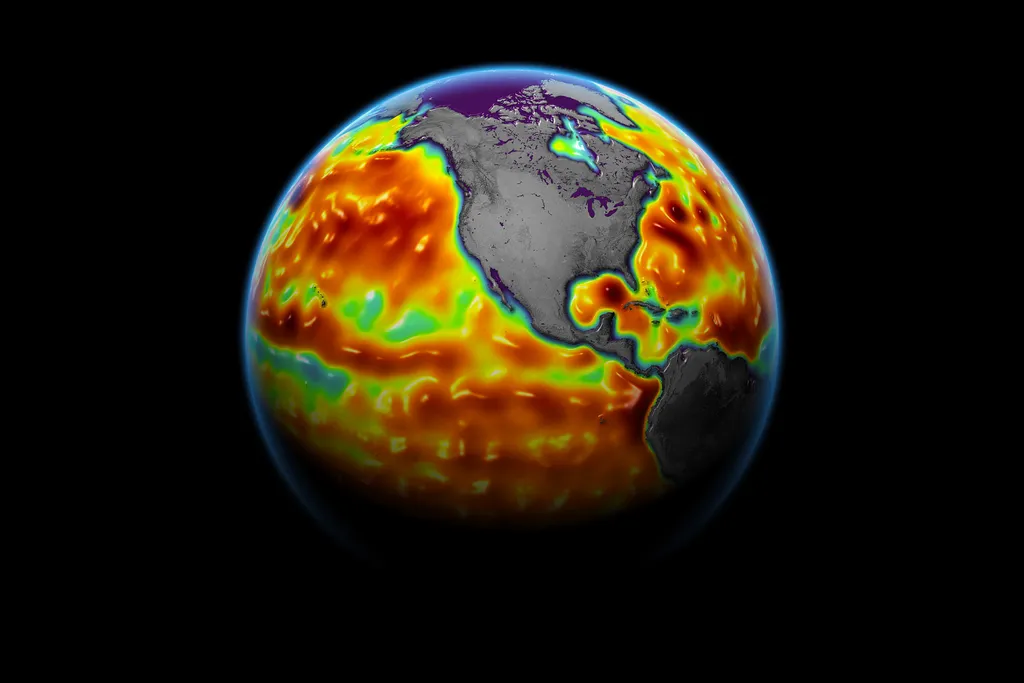
Climate change has already increased the frequency and severity of hurricanes and other extreme weather events around the world. — But there’s a smaller, less splashy threat on the horizon that could wreak havoc on America’s coasts.
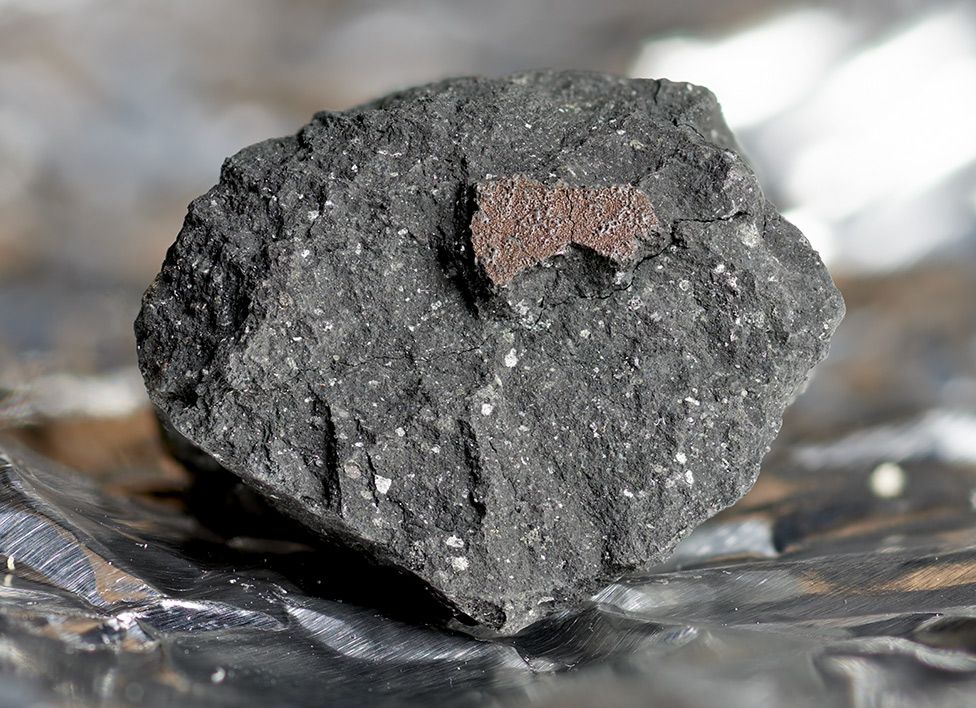

Early work by UK scientists indicates the Winchcombe object dates back to the very beginning of the Solar System, some 4.6 billion years ago.
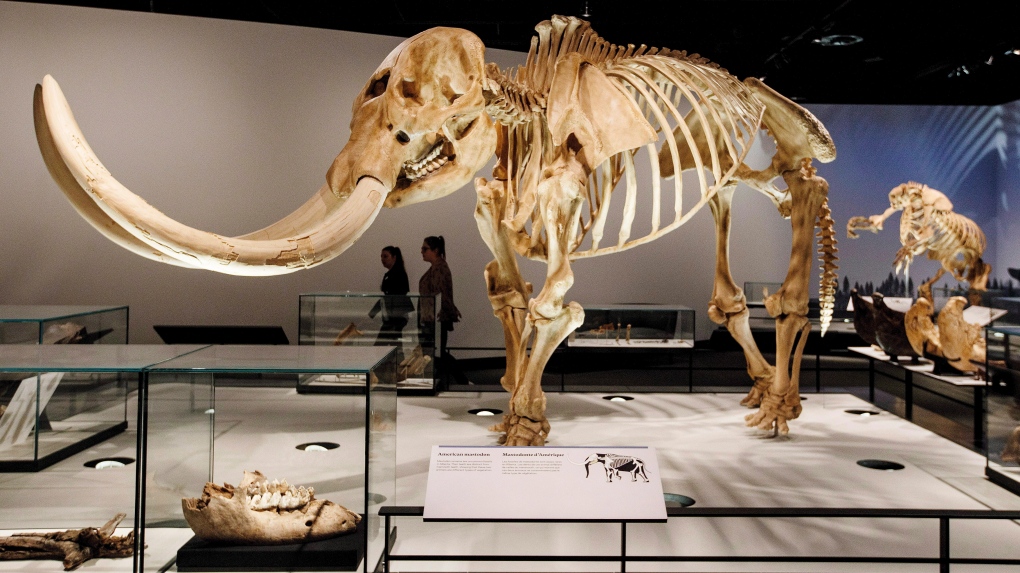

A new study suggests that prehistoric elephants like the mastodon and woolly mammoth were wiped out by waves of extreme global environmental change, rather than being hunted to extinction by early humans.

Dinosaurs were facing a crisis even before the asteroid hit, with extinctions outpacing the emergence of new species — a situation that made them “particularly prone to extinction,” a new study suggests.
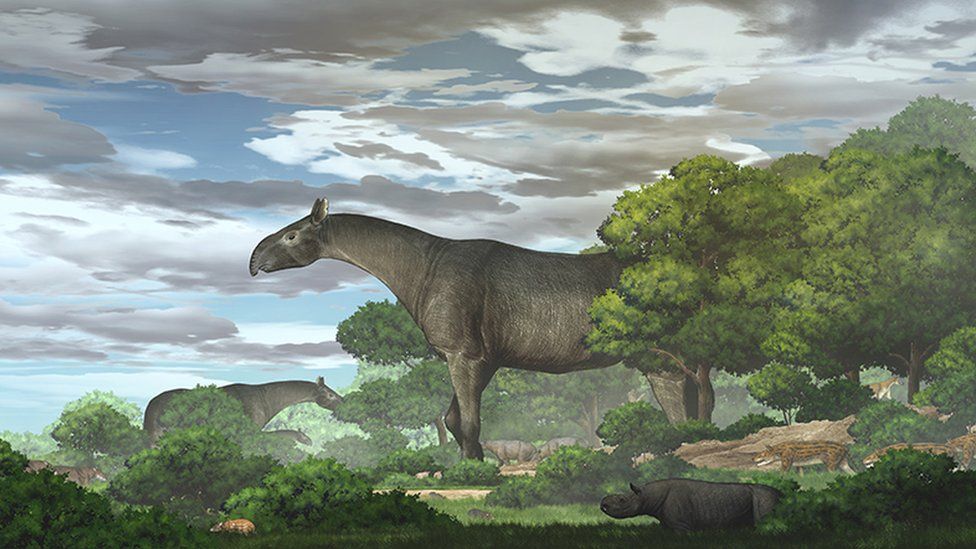

A new species of the ancient giant rhino – among the largest mammals to walk on land – has been discovered in north-western China, researchers say.
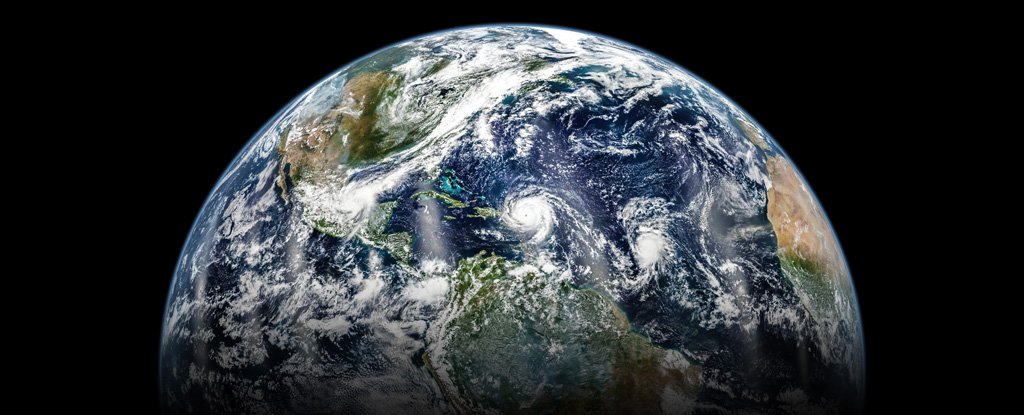

A new study of ancient geological events suggests that our planet has a slow, steady ‘heartbeat’ of geological activity every 27 million years or so.

They may be vine-smothered ruins today, but the lost cities of the ancient tropics still have a lot to teach us about how to live alongside nature.

Caves, often their deepest reaches, were humanity’s first art galleries, where early artists produced star maps, hunting scenes and friezes of ice age animals.
Image from: Iakubivskyi (Wiki Commons)
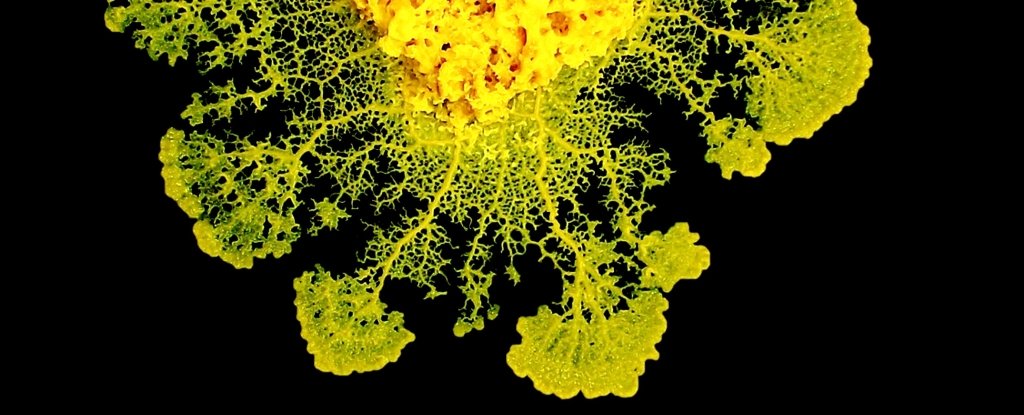
This bizarre little organism doesn’t have a brain, or a nervous system – its blobby, bright-yellow body is just one cell. This slime mold species has thrived, more or less unchanged, for a billion years in its damp, decaying habitats. And, in the last decade, it’s been changing how we think about cognition and problem-solving.








