Earth news stories

Scientists at Yale and the Southwest Research Institute (SRI) say they’ve hit the jackpot with some valuable new information about the story of gold. Details are provided in a study in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Analysis of ancient tree rings from the French Alps has revealed a massive solar storm – the largest ever identified to date – occurred about 14,300 years ago.
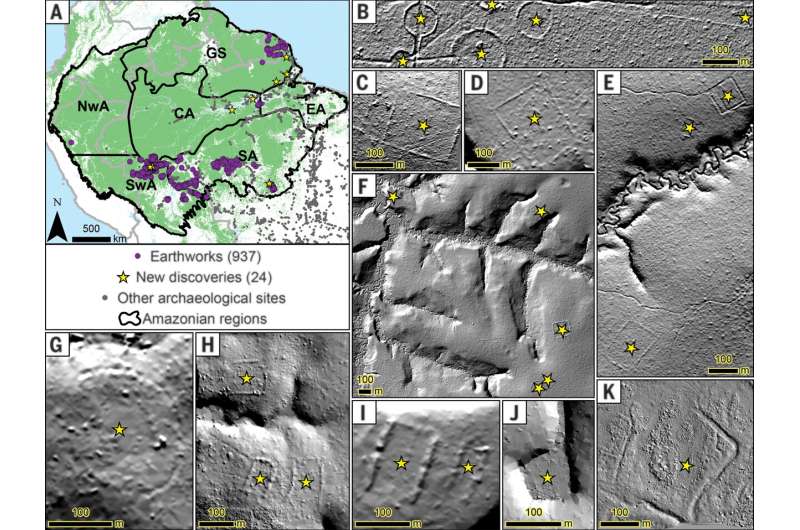
The world’s most diverse forest, the Amazon, may also host more than 10,000 records of pre-Columbian earthworks (constructed prior to the arrival of Europeans), according to a new study.
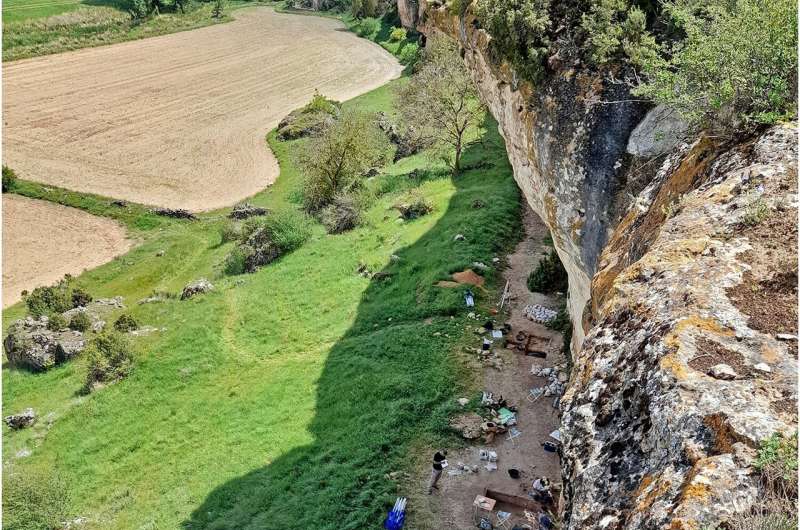

Paleolithic human populations survived even in the coldest and driest upland parts of Spain, according to a study published October 4, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Manuel Alcaraz-Castaño of the University of Alcalá, Spain, Javier Aragoncillo-del Rió of the Molina-Alto Tajo UNESCO Global Geopark, Spain and colleagues.

Fluorescence in mammals is much more common than previously thought, new research suggests.

Agriculture in Syria started with a bang 12,800 years ago as a fragmented comet slammed into the Earth’s atmosphere. The explosion and subsequent environmental changes forced hunter-gatherers in the prehistoric settlement of Abu Hureyra to adopt agricultural practices to boost their chances for survival. That’s the assertion made by an international group of scientists in one of four related research papers, all appearing in the journal Science Open: Airbursts and Cratering Impacts.

For decades, scientists have vigorously debated whether an asteroid strike or massive volcanic eruptions ended the reign of the dinosaurs 66 million years ago…Now, researchers have devised a new way to identify the true dino killer: Let computers take a crack at it. See the study here.
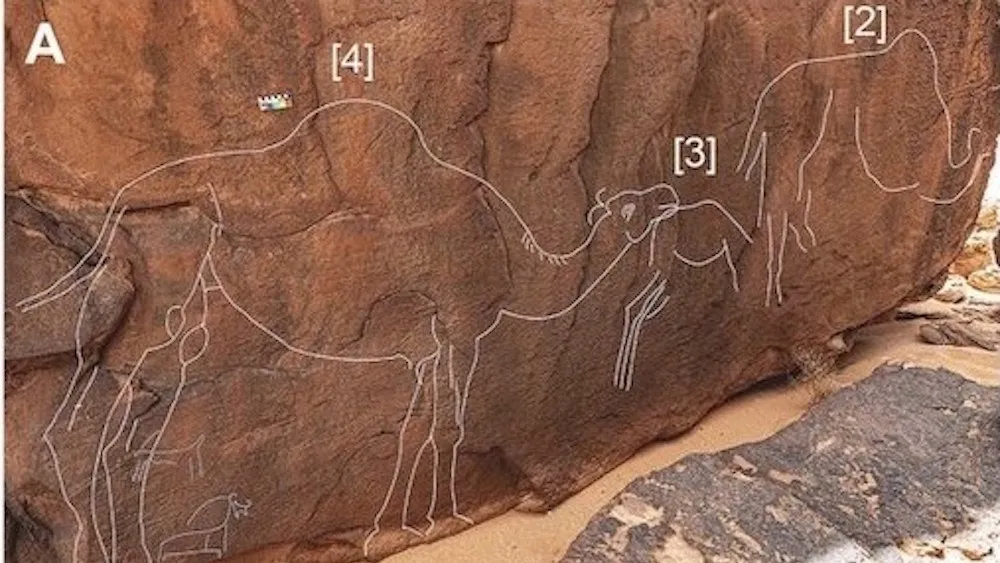

Life-size carvings of camels have been found in the Saudi Arabian desert, but archaeologists aren’t sure who created them and when….Radiocarbon dating of two trenches and two hearths nearby indicate that the Sahout site was repeatedly occupied between the Pleistocene (2.6 million to 11,700 years ago) and the Middle Holocene (7,000 to 5,000 years ago), according to the study.
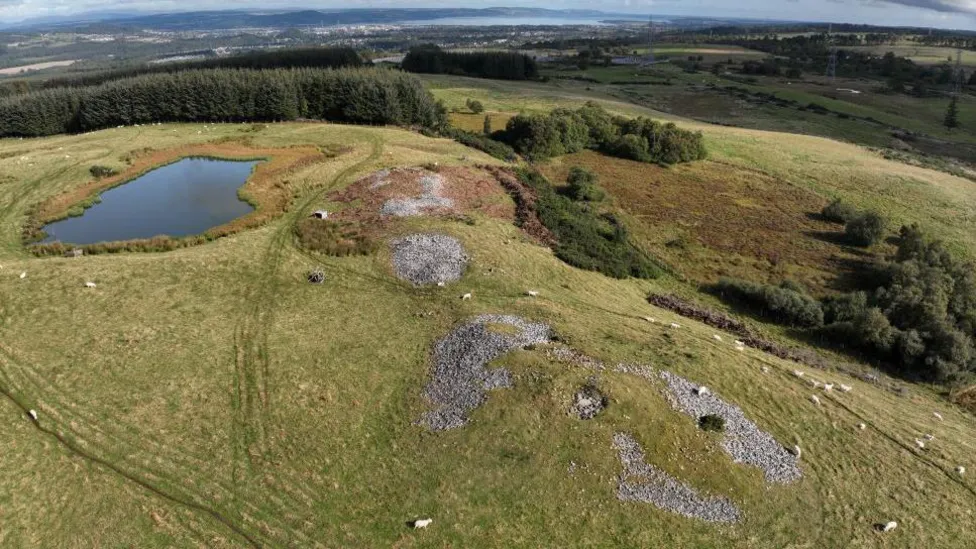

New images have been made of one of Scotland’s most significant prehistoric burial sites. Carn Glas, near Inverness, is thought to date to the Neolithic period and be about 5,000 years old.

Our planet has changed a lot over billions of years, from the location of the continents to the makeup of the atmosphere, and a new study looks in detail at the history of the Sahara desert – which wasn’t always an arid wilderness.
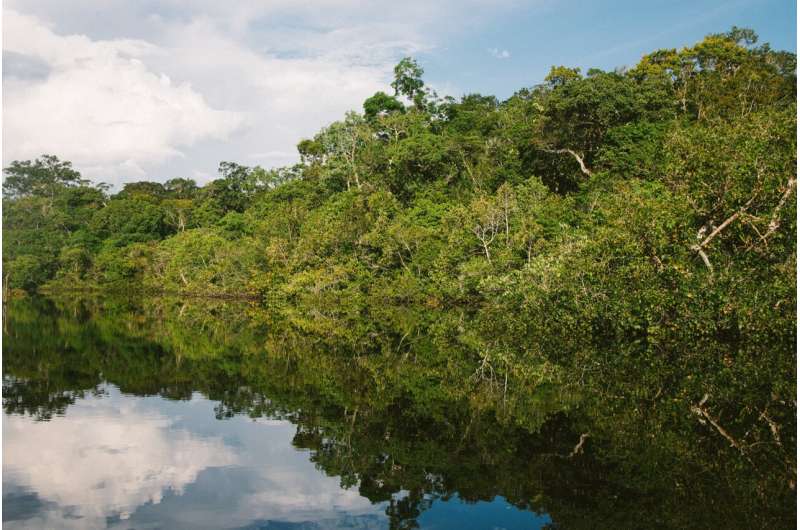

A study led by researchers at MIT, the University of Florida, and in Brazil aims to settle the debate over dark earth’s origins. The team has pieced together results from soil analyses, ethnographic observations, and interviews with modern Indigenous communities, to show that dark earth was intentionally produced by ancient Amazonians as a way to improve the soil and sustain large and complex societies.
More than 1.3 billion years ago, two continents collided at modern-day Argyle in Western Australia, causing pressures so intense that it forced carbon deep underground to form diamonds with glittering pink, red and brown hues. Or, at least, that’s the theory proposed by a study in Nature Communications.
A study in the journal Cell sheds new light on the evolution of neurons, focusing on the placozoans, a millimetre-sized marine animal. Researchers at the Centre for Genomic Regulation in Barcelona find evidence that specialized secretory cells found in these unique and ancient creatures may have given rise to neurons in more complex animals.
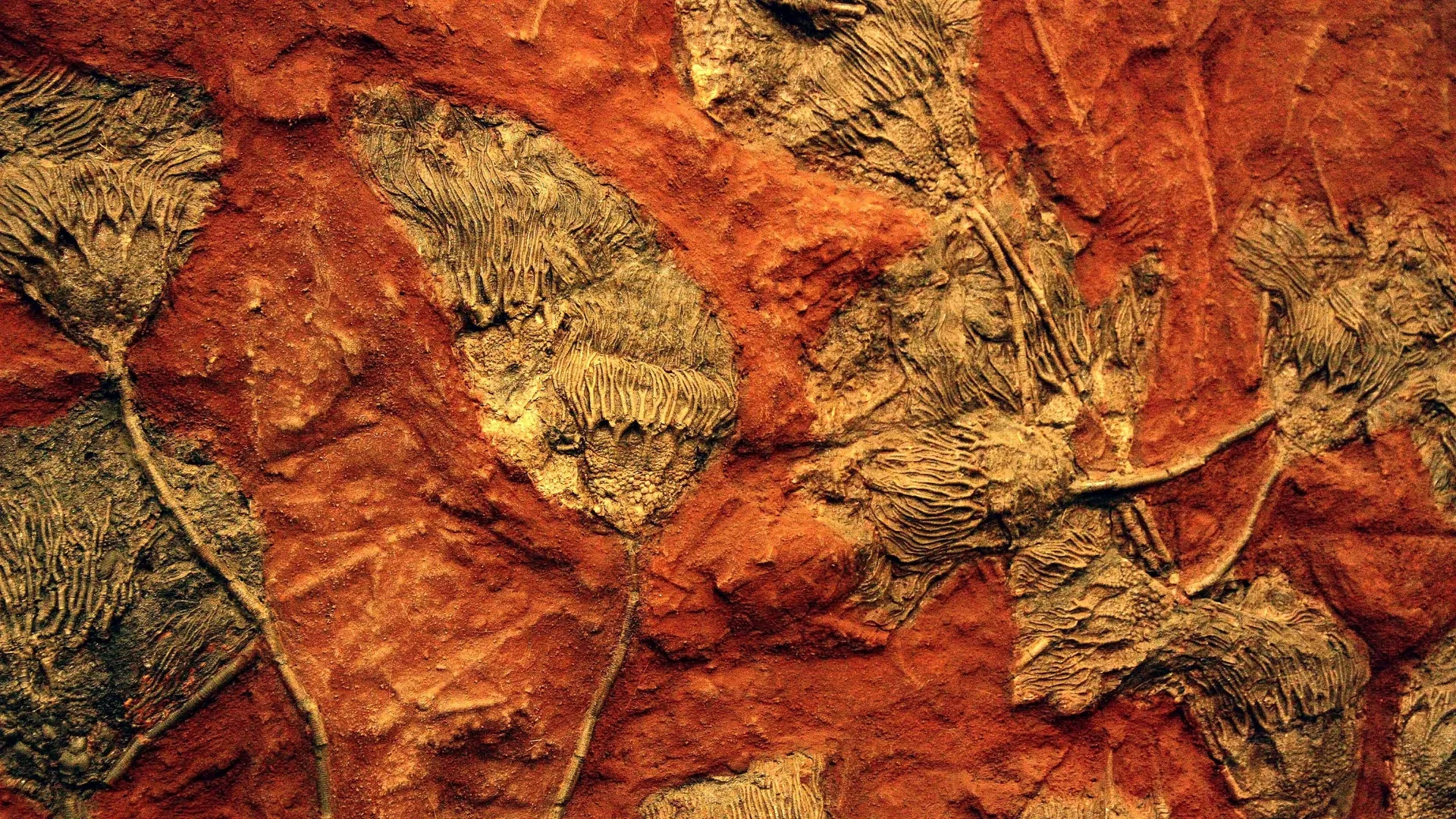

The giant asteroid that snuffed out the dinosaurs at the end of the Cretaceous period (145 million to 66 million years ago) left flowers relatively unharmed, and the blooms thrived in the aftermath, a new study has found.

Somewhere between plants and animals lies a group of organisms among the most captivating life forms on Earth: Mushrooms.
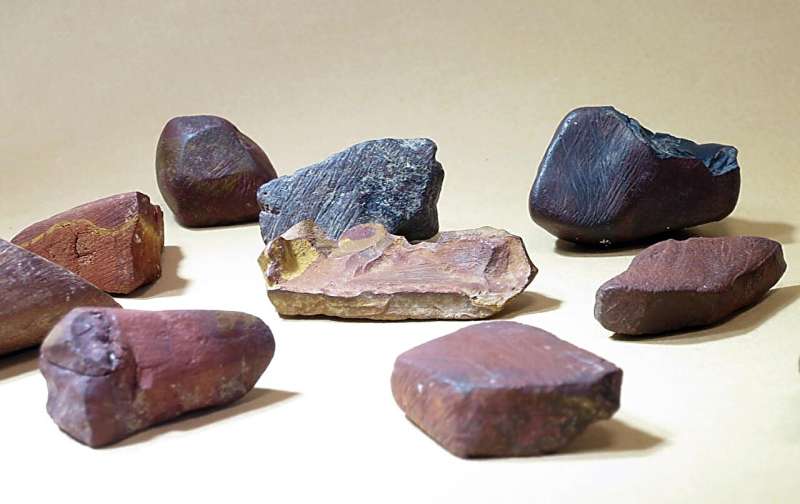

An international research team from Spain and France has carried out the chemical and technological analysis of the largest known collection of red and yellow mineral pigments, commonly called ochre, dated to the Middle Stone Age, between 300,000 and 40,000 years ago, and found at Porc-Epic cave, Ethiopia. See the research here.








