Earth news stories

The evidence comes from a chemical analysis of more than 100 tiny pieces of rock entrained within the White Continent’s ice, researchers report in the Feb. 1 Earth and Planetary Science Letters.
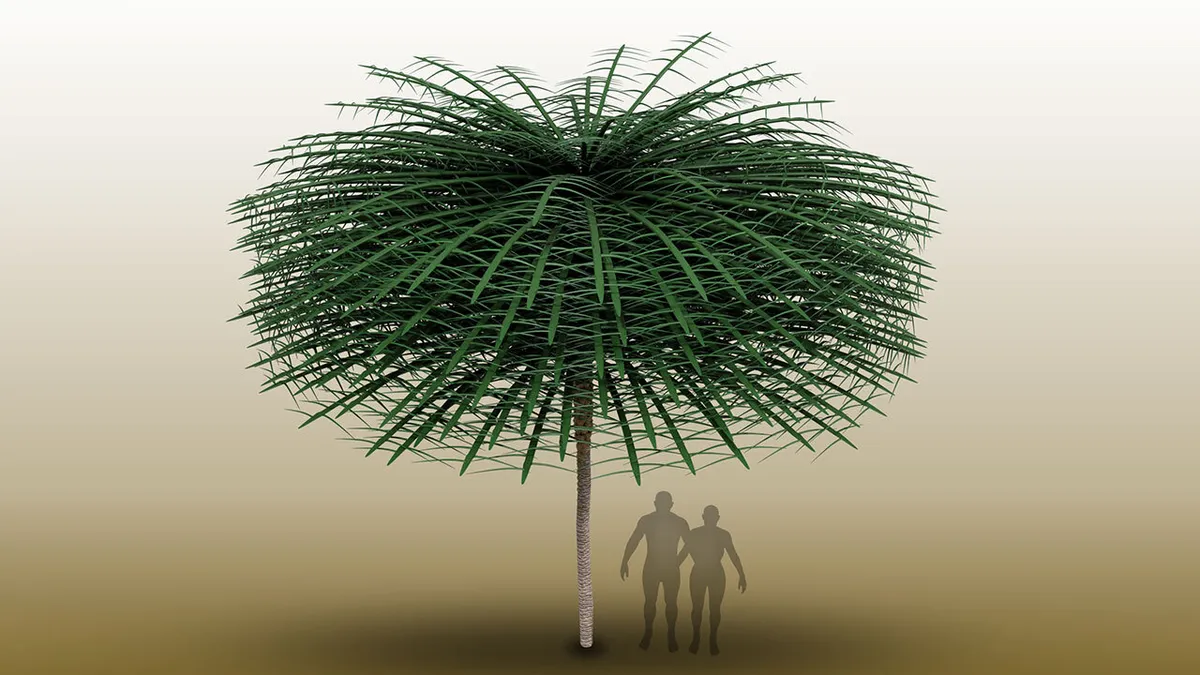

Rare tree fossils preserved with their leaves have an architecture unlike any plant known today and represent the earliest evidence of smaller trees growing beneath the forest canopy. See the study, published in the journal Current Biology.
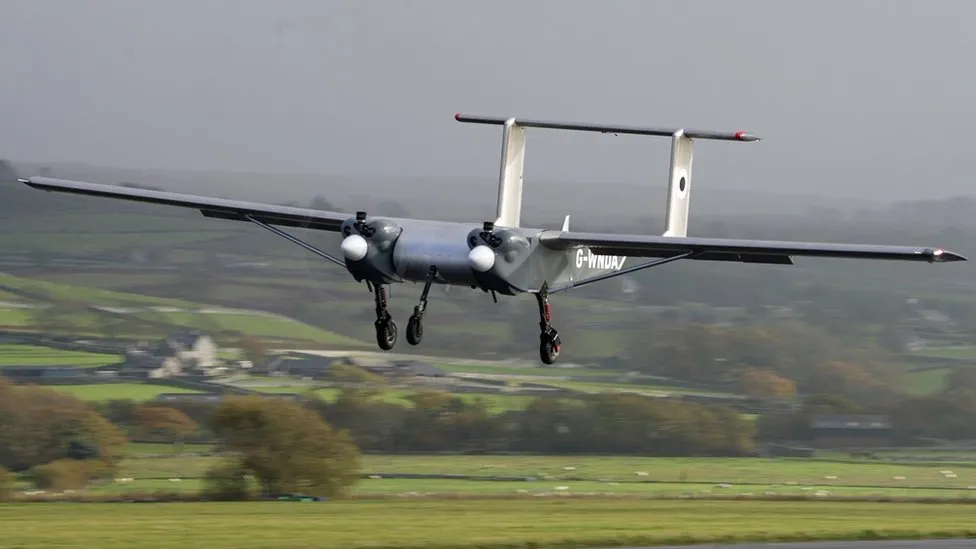

The autonomous plane will map areas of the continent that have been out of bounds to researchers.
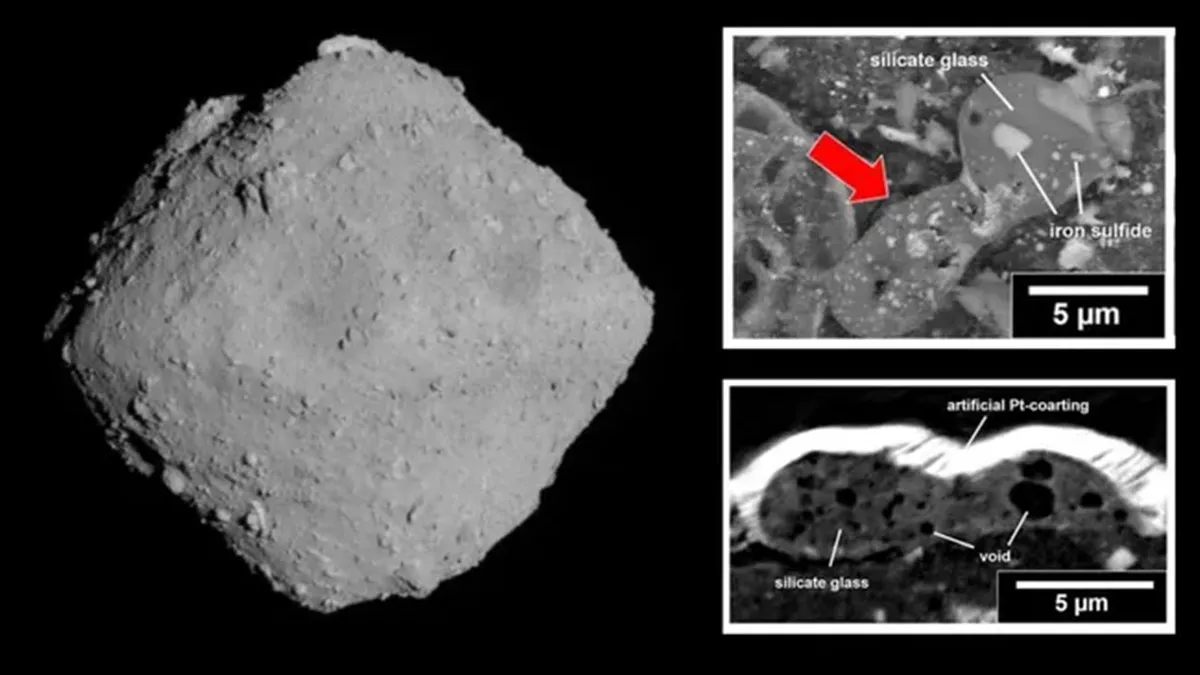

A detailed investigation of asteroid Ryugu samples has provided further evidence that the organic molecules which gave rise to life to our planet were brought here by ancient comets.
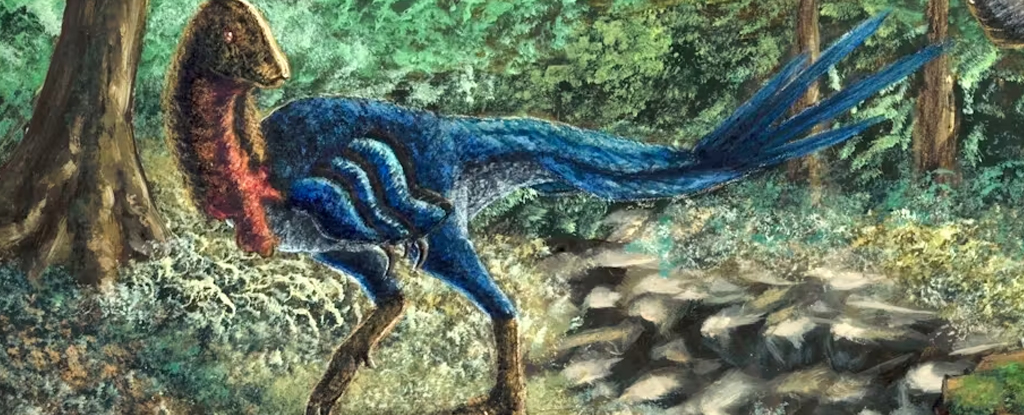

Were dinosaurs already on their way out when an asteroid hit Earth 66 million years ago, ending the Cretaceous, the geologic period that started about 145 million years ago? It’s a question that has vexed paleontologists like us for more than 40 years.

This story begins with a funeral. On my 33rd birthday in June, I entered my coffin on five grams of mushrooms, had it “nailed” shut, and listened while sixteen friends delivered eulogies as the soundtrack to my trip.

About 8,200 years ago, an underwater landslide known as the Storegga slide near Norway triggered a tsunami that engulfed parts of northern Europe. Around the same time, there was a massive dip in Britain’s population. See the research here.

The random nature of genetic mutation implies evolution is largely unpredictable. But recent research suggests this may not be entirely so, with interactions between genes playing a bigger role than expected in determining how a genome changes.

Amid the discovery of a lost city in the Amazon rainforest, scientists are uncovering a different kind of relic underground – one that’s still being used today.

Crocodile-like skin belonging to an early species of reptile is the oldest fossilized skin ever discovered, dating back almost 290 million years — 130 million years older than the previous record holder.

As analytical methods get more sophisticated, existing scientific models are constantly reexamined. The latest to come under scrutiny is the way molecules are organized at the surface of a volume of salt water. See the research here.
Complex, multicellular life emerged on Earth 600-700 million years ago. For the first time, scientists have accurately dated some of the oldest examples of complex life. See the research here.

In a study published Tuesday in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers from the US, UK and Mexico analyzed the genomes of more than 50 mushrooms from the Psilocybegenus—the group whose members almost all contain the psychedelic compounds psilocybin and psilocin.

A study led by an international team of researchers is shedding new light on the mystery of Gigantopithecus blacki, a giant prehistoric primate that once lived in what is now southern China.
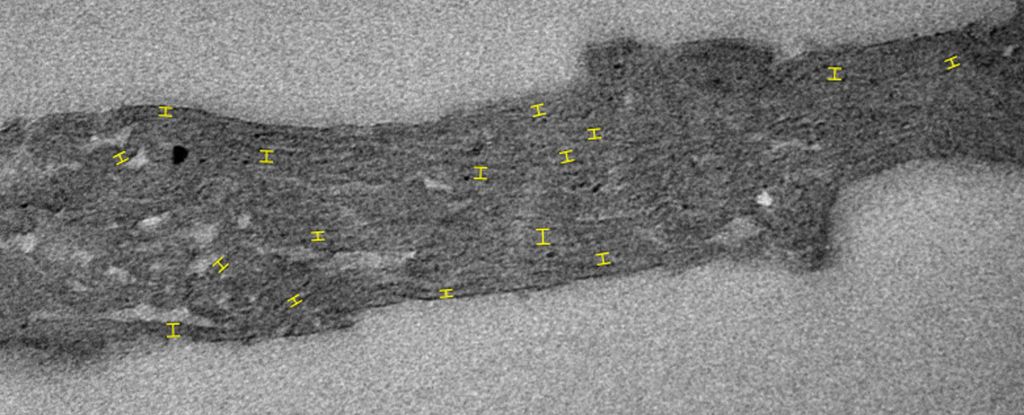
Tiny fossils that have spent nearly 2 billion years locked up in chunks of ancient rock are giving us the earliest evidence yet for photosynthesis on Earth. The research has been published in Nature.









