Ancient news stories
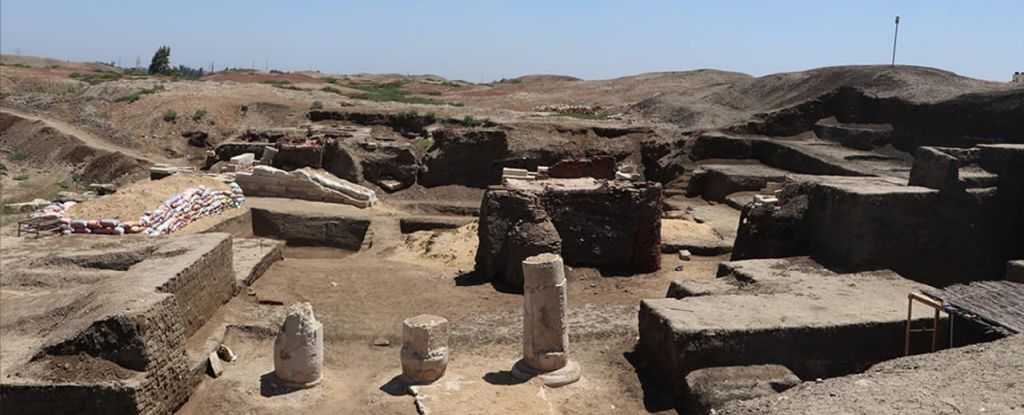

A ruined building in Kafr El Sheikh was where ancient Egyptians once stood, gazing at the stars above.
A new paper published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences focuses on testates to better understand the evolution of ecosystems on Earth and predict what the planet may look like in the future.
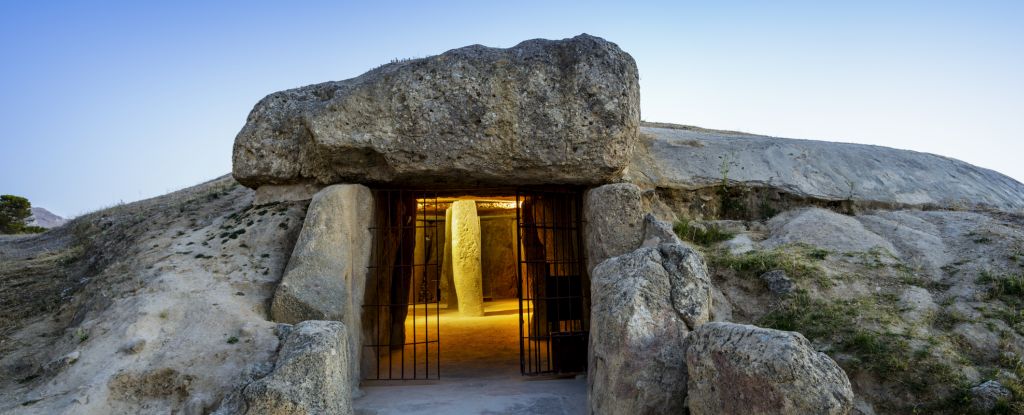

A new study has found that the Neolithic humans who built Menga were highly skilled, highly knowledgeable, and adept at solving complex engineering problems. The research has been published in Science Advances.
Scientists have mapped the path of an ancient underwater avalanche which travelled 2,000km across the seafloor off the northwest coast of Africa. The new study appears in Science Advances.
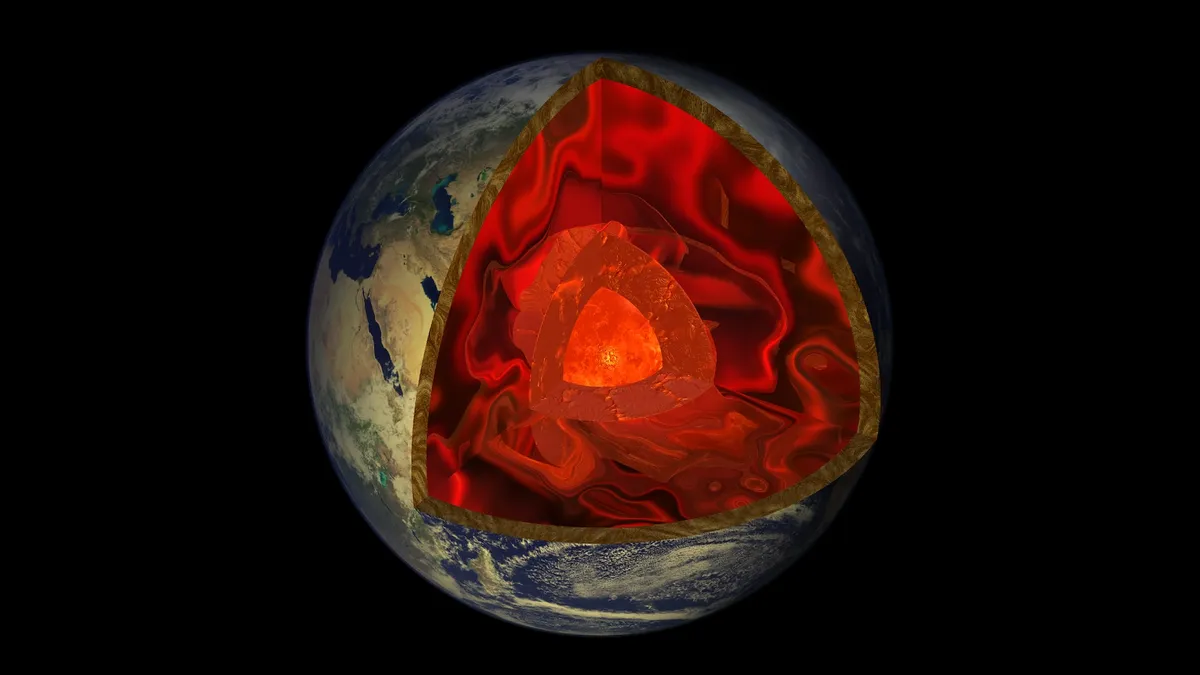
Mysterious zones in the deep mantle where earthquake waves slow to a crawl may actually be everywhere, new research finds.

The long-lost divinatory list represents the oldest-known compilation of lunar eclipse omens from Babylonia – an ancient culture in Mesopotamia famed for its astrological beliefs…The study was published in the Journal of Cuneiform Studies.
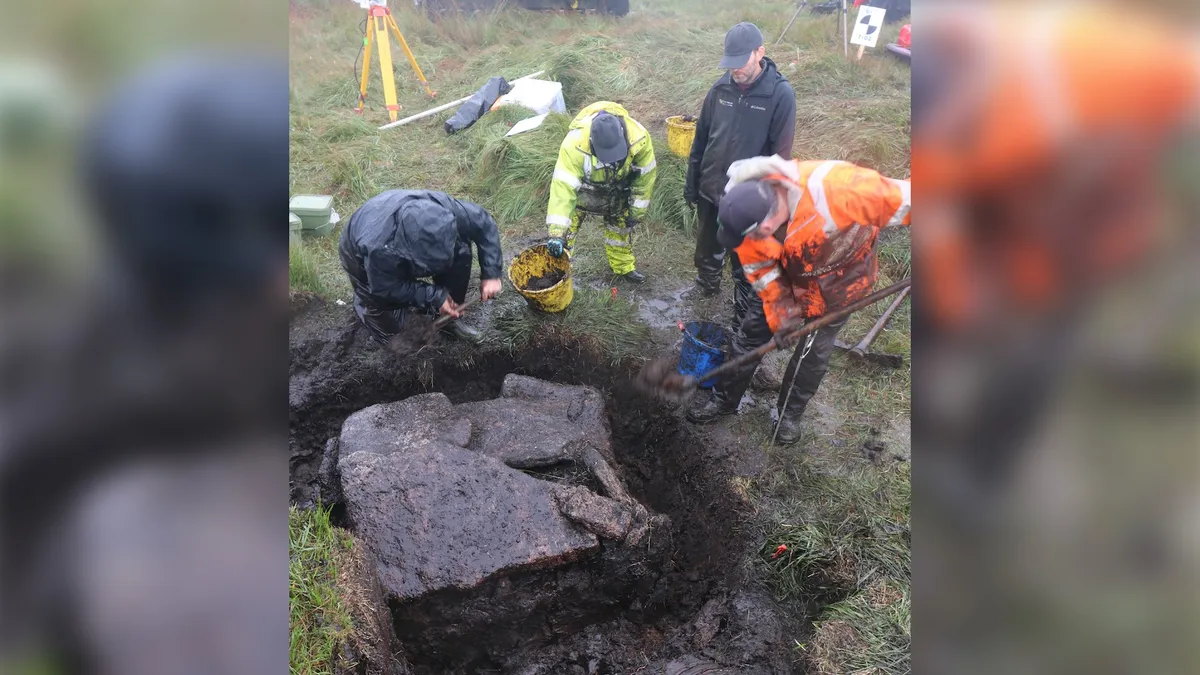

A “stunning” tomb found on an isolated moor in southwest England could help archaeologists understand what life was like 4,000 years ago in the Bronze Age.
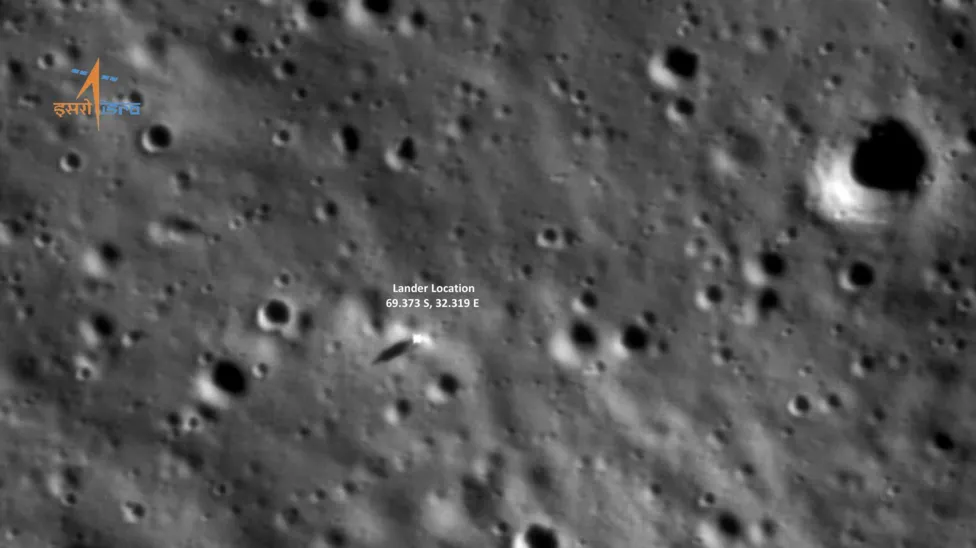

The Moon’s south pole was once covered in an ocean of liquid molten rock, according to scientists. The findings back up a theory that magma formed the Moon’s surface around 4.5 billion years ago.
The first comprehensive review of tooth ablation in Taiwan from the Neolithic to the modern era has been conducted. The research, published in the Archaeological Research in Asia journal, aims to fill gaps in our knowledge of the origins and development of the practice in Taiwan.
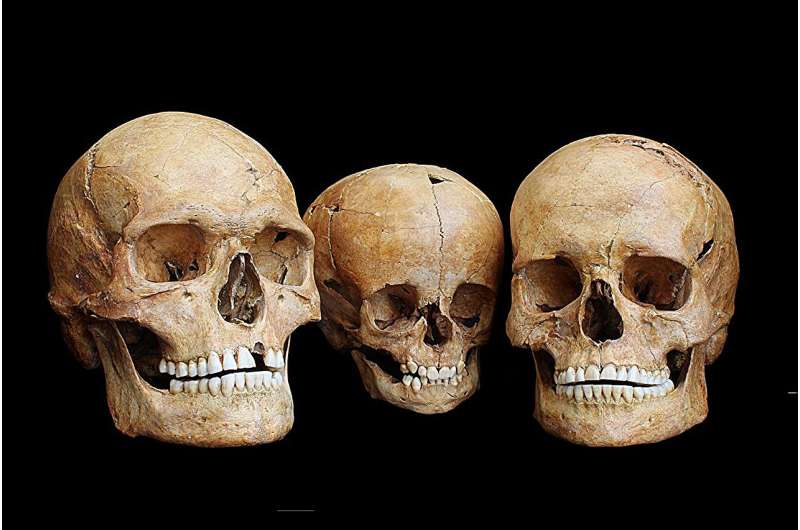
Population sizes declined sharply during the coldest period, and in the West, Ice Age Europeans even faced extinction, according to the study published August 16 in the journal Science Advances.
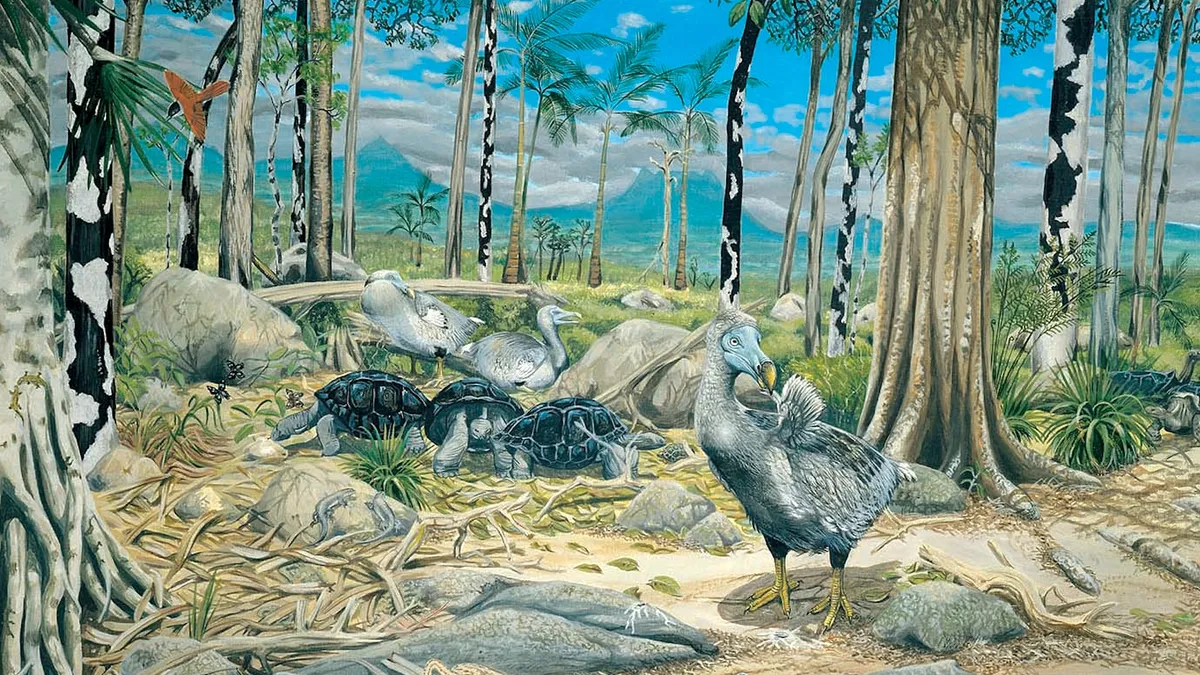

A new study has cleared up misconceptions about the extinct dodo, identifying the reference specimen for the species and showing they were fast and powerful.
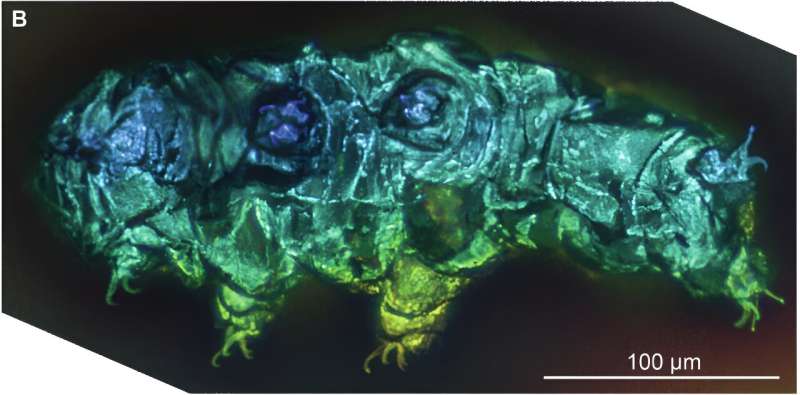
A trio of evolutionary biologists at Harvard University’s Museum of Comparative Zoology has learned more about the evolutionary history of tardigrades by studying two fossils embedded in amber. Their study is published in Communications Biology.
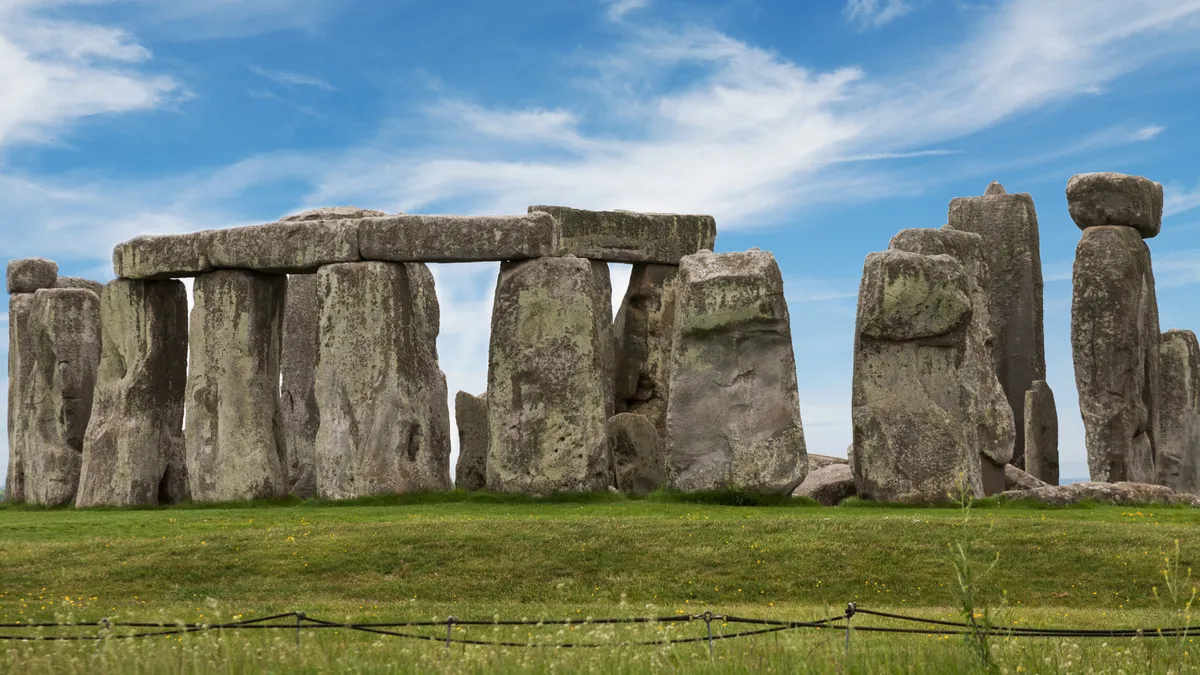

Researchers analyzed Stonehenge’s Altar Stone and determined that its chemical makeup is similar to that of stones found in northeastern Scotland. The finding is part of a new study published Wednesday (Aug. 14) in the journal Nature.
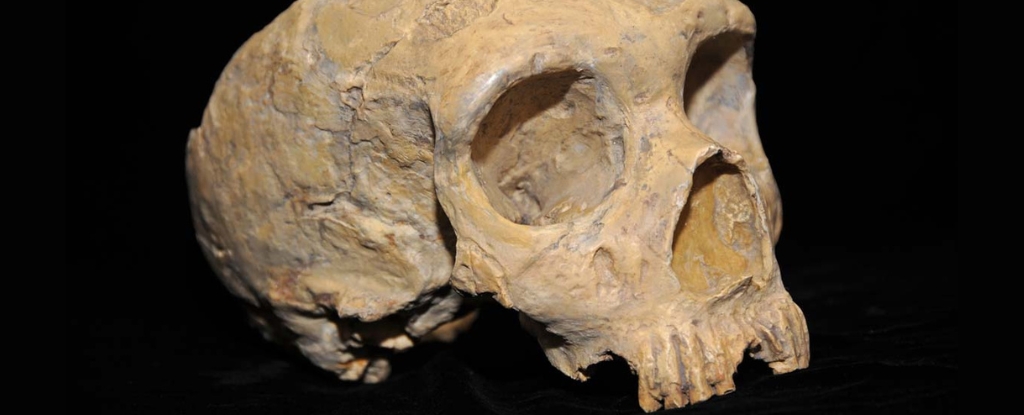
The excavation of a recently discovered rock shelter site called Abric Pizarro has turned up thousands of artifacts dated to between 65,000 and 100,000 years ago, including stone tools and animal bones that can tell us a lot about the Neanderthal way of life during a period for which few remnants remain. The research has been published in the Journal of Archaeological Science.
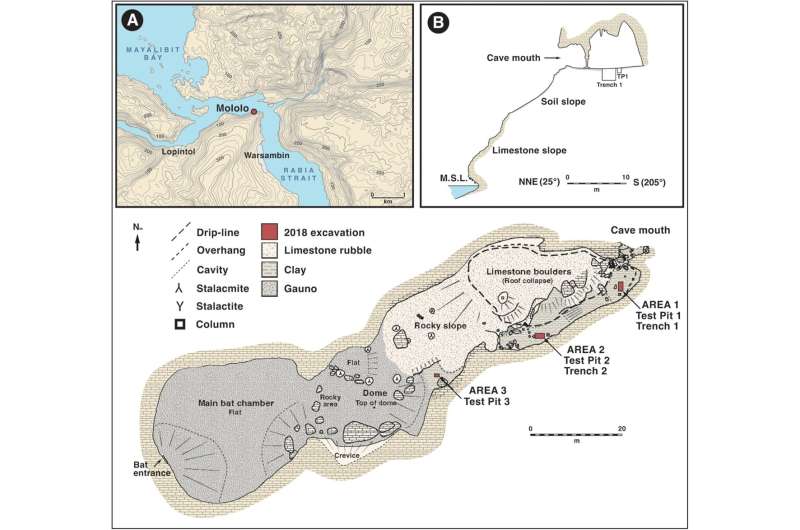
In the deep human past, highly skilled seafarers made daring crossings from Asia to the Pacific Islands. It was a migration of global importance that shaped the distribution of our species—Homo sapiens—across the planet…For the first time, our new research published in Antiquity provides direct evidence that seafarers traveled along the equator to reach islands off the coast of West Papua more than 50 millennia ago.

In stark contrast to the severe environmental destruction that we see all around us, our excavations reveal the ancestral Maya’s profound respect for nature and animals.








