News Desk

Is Stonehenge aligned with the moon? Scientists hope to find out during a rare ‘major lunar standstill, which happens once every 18.6 years.
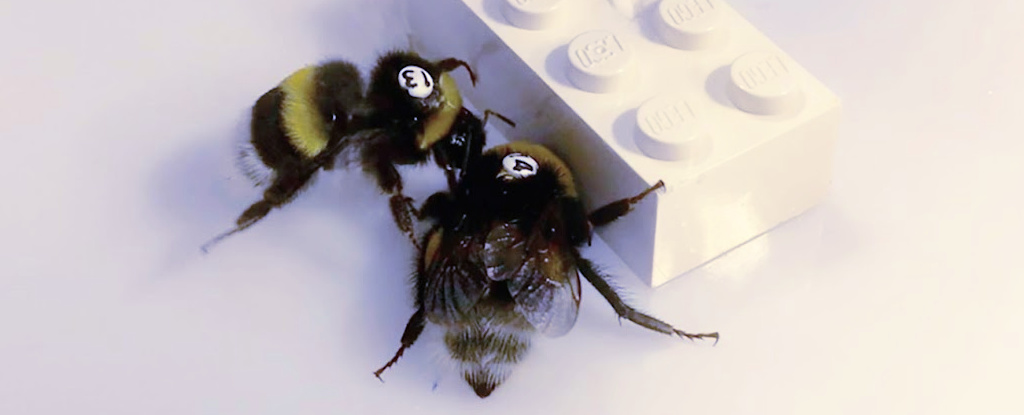

In a series of lab experiments, bumblebees (Bombus sp.) that trained together on tasks to retrieve a sugary reward were more likely to wait for their partner before returning to the task than bees that trained alone.

For the first time in nearly a century, physicists have identified a brand new type of magnetic material. Physicists have reported a new class of magnetic materials called altermagnets, which could lead to new technologies such as faster, more efficient computer hard drives.
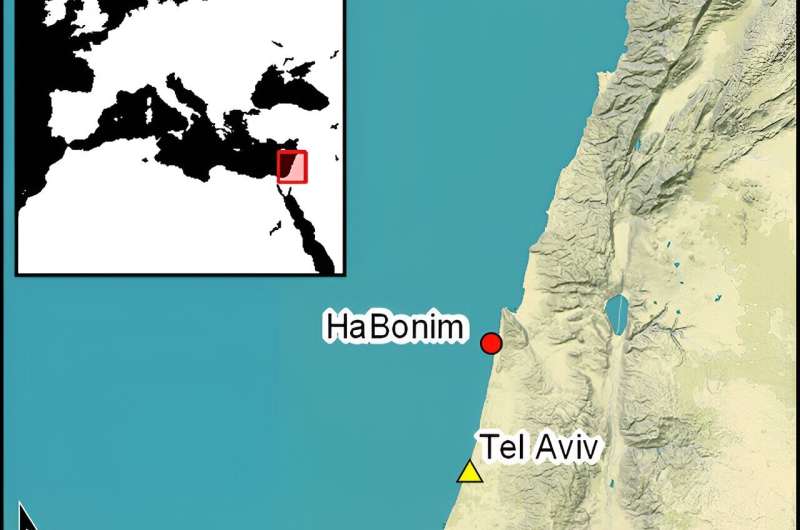
Around 6,200 BCE, the climate changed. Previously, archaeologists believed that this abrupt shift in global climate, called the 8.2ka event, may have led to the widespread abandonment of coastal settlements in the southern Levant. In a recent study published in the journal Antiquity, researchers…share new evidence suggesting at least one village formerly thought abandoned not only remained occupied, but thrived throughout this period.

A team of Brown University researchers are launching a study to test the combined use of the drug MDMA and talk therapy as a treatment for post-traumatic stress disorder and alcohol use disorder in military veterans. The study is the first at Brown on MDMA-assisted therapy and the first anywhere to test the treatment’s effectiveness for dual disorders.
Image from Photo the U.S. Marine Corps, Wiki Commons
A new study published in the Journal of Psychedelic Studies raises important concerns. It suggests that while there may be benefits, there are also significant risks. The study focuses on the negative effects reported by therapists who facilitate such treatments, highlighting that the impacts of psilocybin are not universally beneficial and can vary widely from one individual to another.
Archaeologists have uncovered the oldest evidence of ceremonial offerings on sportsgrounds by the ancient Maya in Mexico. Environmental DNA (eDNA) analysis shows that the courts built by the Mayans for their ballgames were blessed. In research published in PLOS ONE, the researchers identified a collection of plants used in ceremonial rituals.
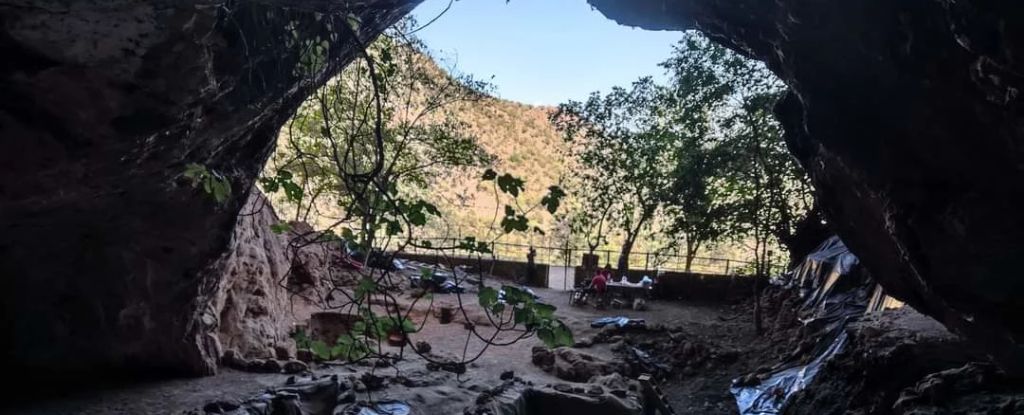

The teeth and bones of pre-agricultural human hunter-gatherers who lived some 15,000 years ago in what is now Morocco reveal that their diet – long thought to have been significantly loaded with animal protein – was actually weighted much further in the direction of plant-based food. It seems plants may have even been used to wean infants, the study found.
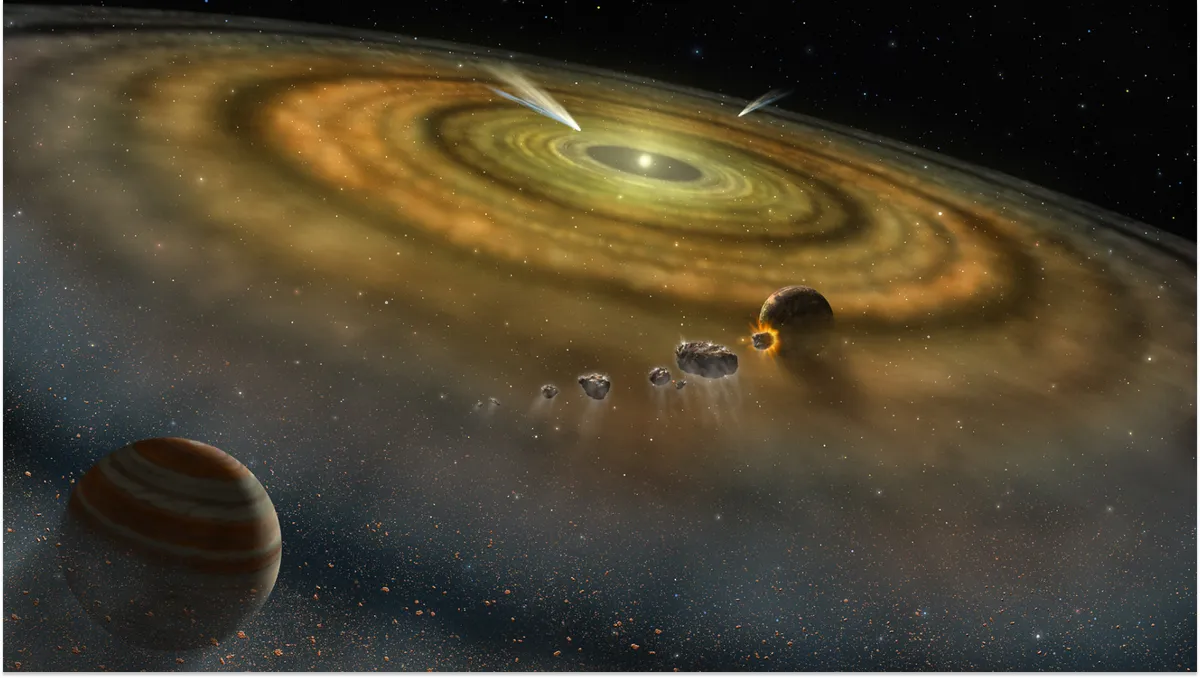

The great planetary instability, which saw Jupiter and the other gas giants wander chaotically through the solar system, coincides with the collision that formed Earth’s moon. Could the two events be linked?

Stoners are not as lazy and unmotivated as stereotypes suggest, according to new U of T Scarborough research. The study, published by the journal Social Psychological and Personality Science, surveyed chronic cannabis users to see what effect getting high has on their everyday lives.

The hunt for the elusive Planet Nine goes on, and new research claims to have the “strongest statistical evidence yet” that there is such a planet orbiting somewhere around the far edges of the Solar System.
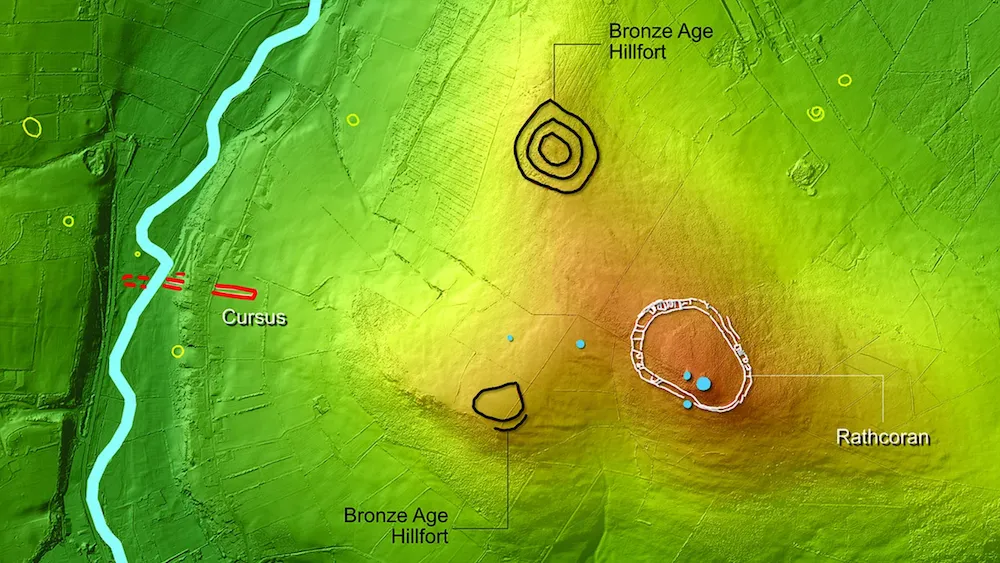
Archaeologists used lidar to detect a cluster of rare Neolithic monuments hidden in farmland in Ireland. See the study published Thursday (April 25) in the journal Antiquity.
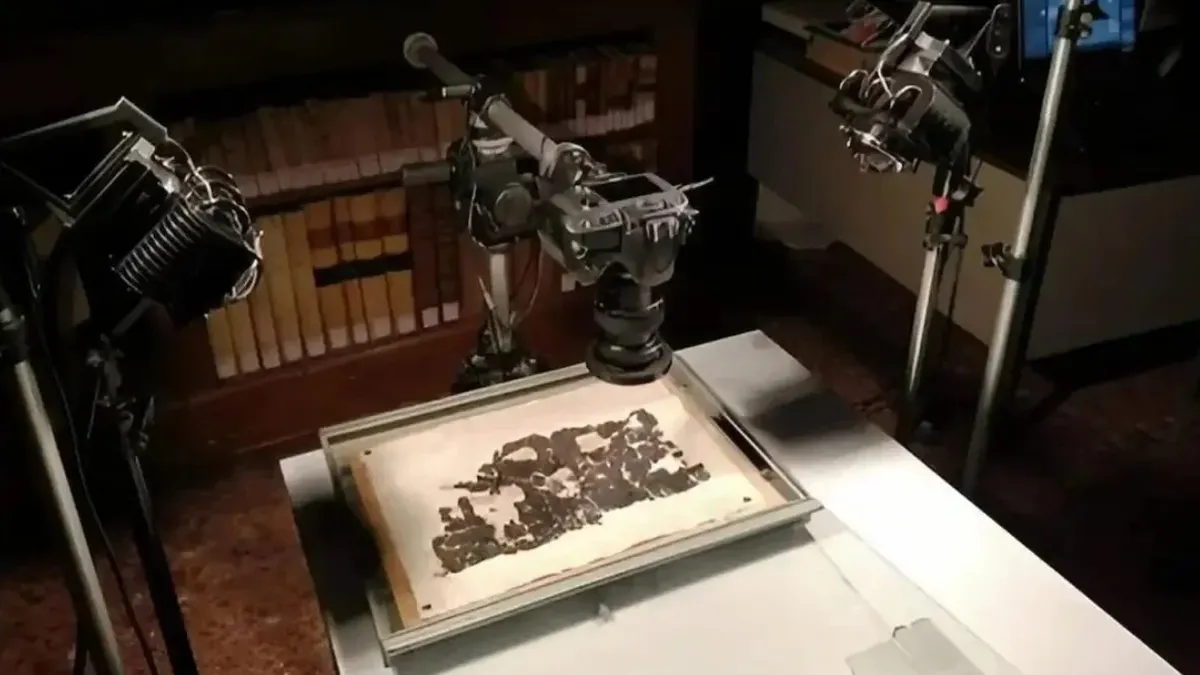

Researchers used AI to decipher an ancient papyrus that includes details about where Greek philosopher is buried.
Recent research published in the journal Drug Science, Policy and Law challenges the common belief that childhood trauma affects the experience of ayahuasca, a plant-based psychedelic. Surprisingly, the study finds no connection between prior childhood trauma and the intensity of challenges faced when under the influence of ayahuasca.
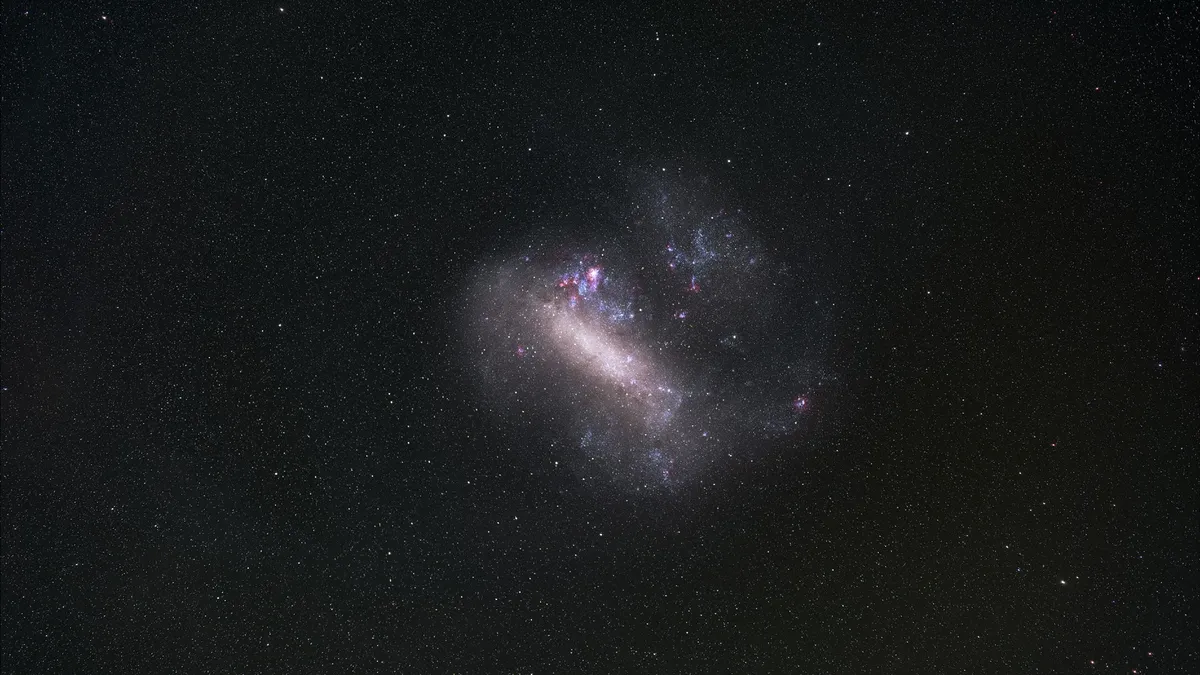

Scientists have identified one of the oldest known stars outside the Milky Way. The discovery, reported in March in the journal Nature Astronomy, has uncovered a relic from the early days of the universe in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way — and it’s revealing the conditions from a time before the sun even existed.
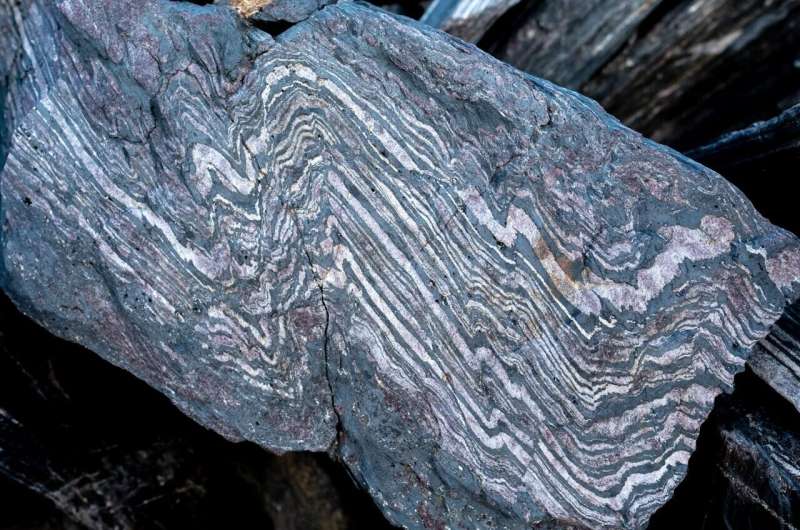

A new study, led by the University of Oxford and MIT, has recovered a 3.7-billion-year-old record of Earth’s magnetic field and found that it appears remarkably similar to the field surrounding Earth today. The findings have been published in the Journal of Geophysical Research. Without its magnetic field, life on Earth would not be possible…








