News Desk
A new neuroimaging study has revealed how the powerful psychedelic N,N-dimethyltryptamine, commonly known as DMT, alters the brain’s primary visual cortex, potentially explaining the intense visual distortions experienced by users. The findings arde published in NeuroImage.
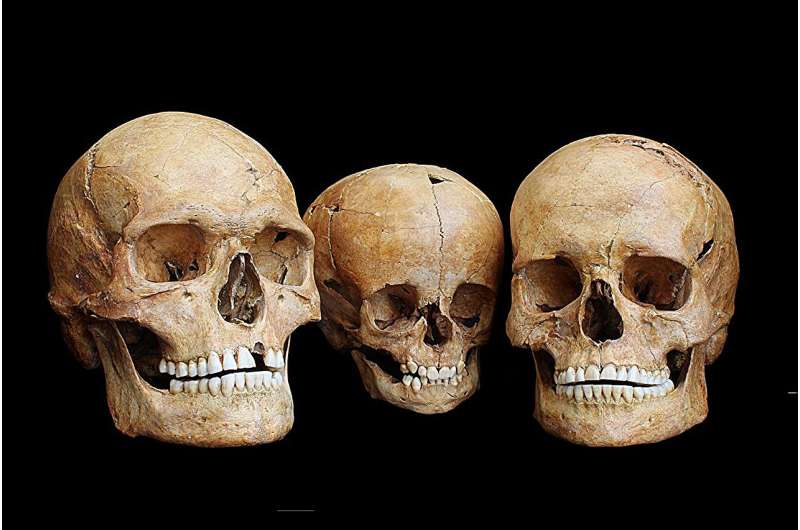
Population sizes declined sharply during the coldest period, and in the West, Ice Age Europeans even faced extinction, according to the study published August 16 in the journal Science Advances.
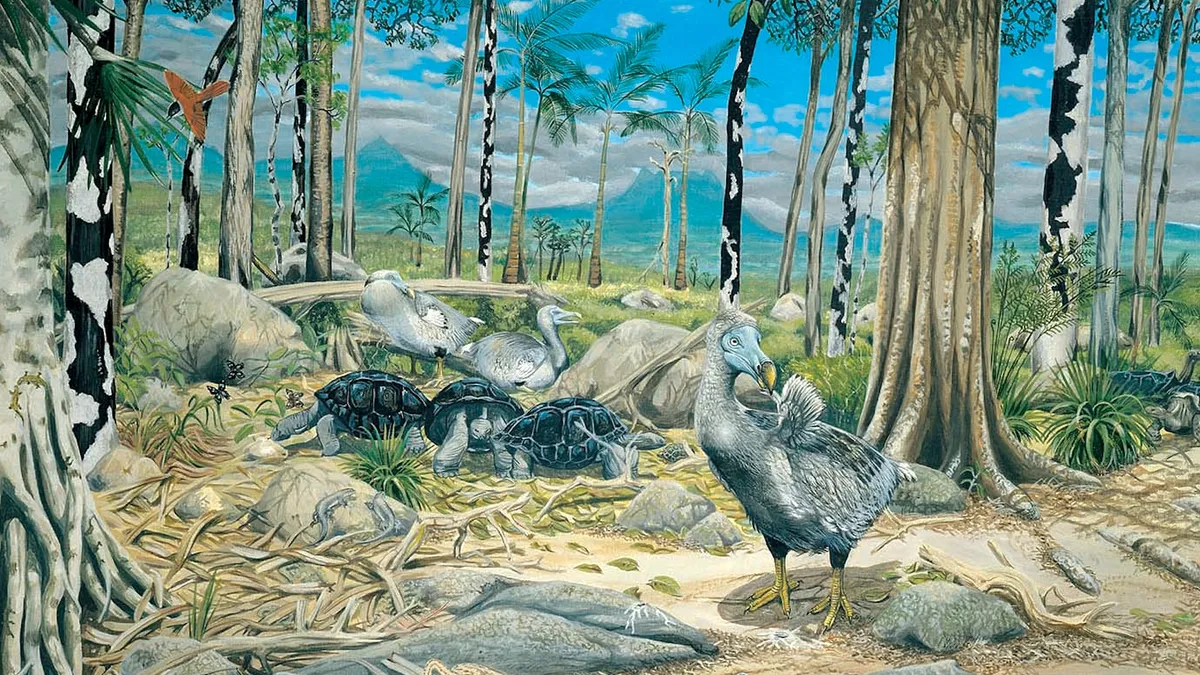

A new study has cleared up misconceptions about the extinct dodo, identifying the reference specimen for the species and showing they were fast and powerful.
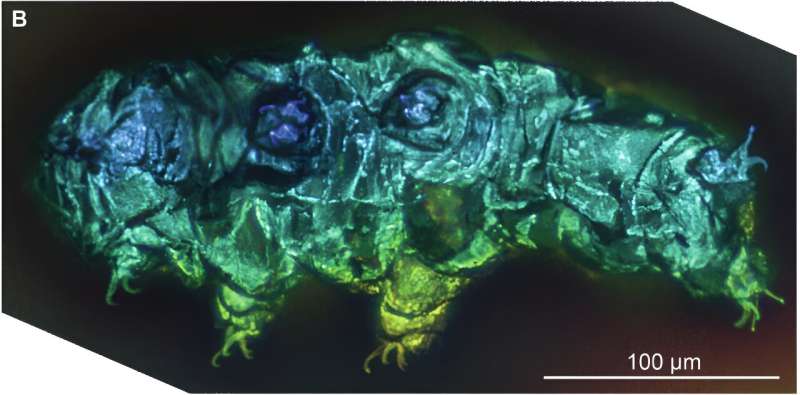
A trio of evolutionary biologists at Harvard University’s Museum of Comparative Zoology has learned more about the evolutionary history of tardigrades by studying two fossils embedded in amber. Their study is published in Communications Biology.
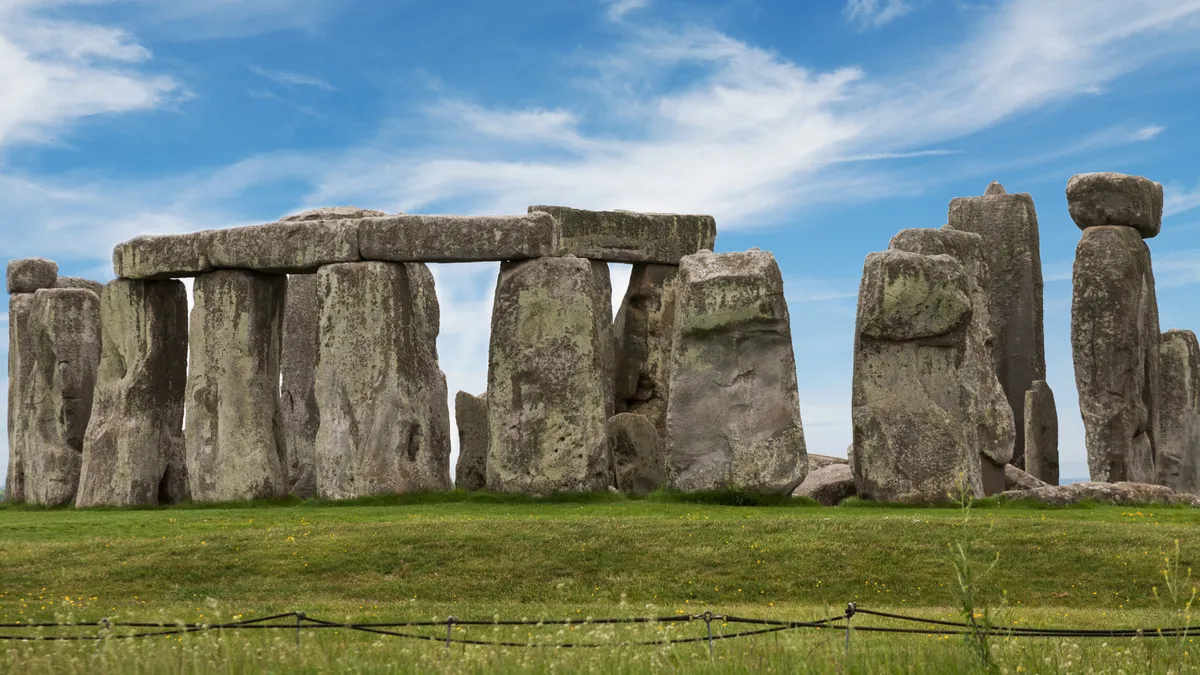

Researchers analyzed Stonehenge’s Altar Stone and determined that its chemical makeup is similar to that of stones found in northeastern Scotland. The finding is part of a new study published Wednesday (Aug. 14) in the journal Nature.
The excavation of a recently discovered rock shelter site called Abric Pizarro has turned up thousands of artifacts dated to between 65,000 and 100,000 years ago, including stone tools and animal bones that can tell us a lot about the Neanderthal way of life during a period for which few remnants remain. The research has been published in the Journal of Archaeological Science.
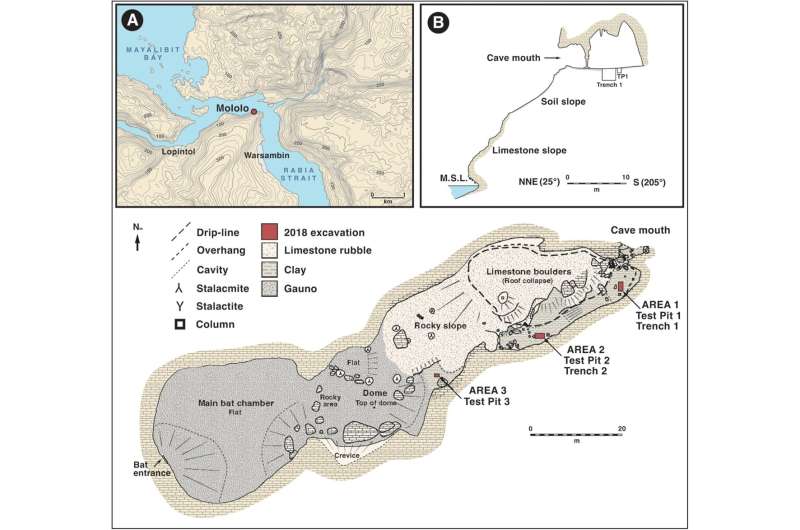
In the deep human past, highly skilled seafarers made daring crossings from Asia to the Pacific Islands. It was a migration of global importance that shaped the distribution of our species—Homo sapiens—across the planet…For the first time, our new research published in Antiquity provides direct evidence that seafarers traveled along the equator to reach islands off the coast of West Papua more than 50 millennia ago.
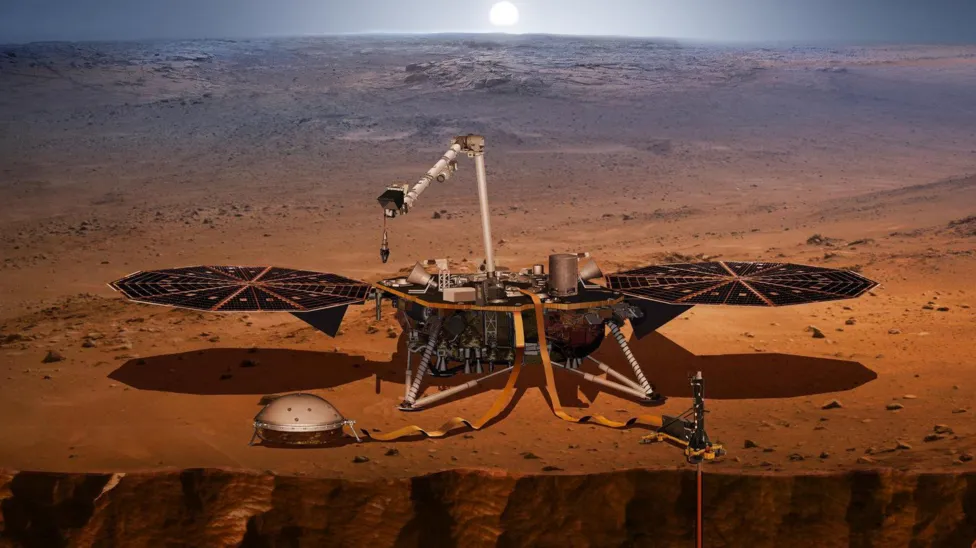

Scientists have discovered a reservoir of liquid water on Mars – deep in the rocky outer crust of the planet. The findings come from a new analysis of data from NASA’s Mars Insight Lander, which touched down on the planet back in 2018.

New research from the University of Southern California shows that cannabis might help some people stop or cut down on their opioid use.

In stark contrast to the severe environmental destruction that we see all around us, our excavations reveal the ancestral Maya’s profound respect for nature and animals.

Resin is solidified tree sap. The resin artifact was dated with the University of Oxford’s radiocarbon accelerator to about 55,000 to 50,000 years ago. The archaeologists don’t suggest it was art. They suggest it was the prehistoric version of a matchstick.

Scholars have finally deciphered 4,000-year-old cuneiform tablets found more than 100 years ago in what is now Iraq. The tablets describe how some lunar eclipses are omens of death, destruction and pestilence. See the paper published recently in the Journal of Cuneiform Studies.
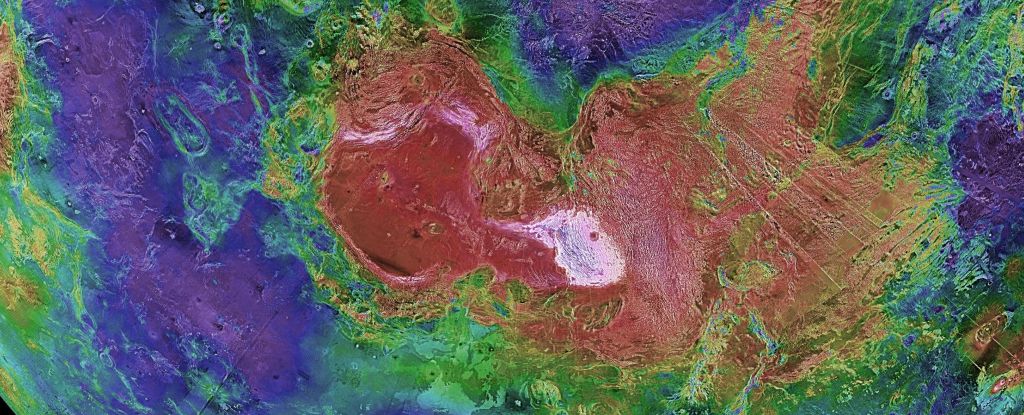
Venus and Earth seem like twins who, through dramatically different circumstances and choices, ended up leading dramatically different lives. The research has been published in Nature Geoscience.
Ketamine treatment not only alleviates symptoms of treatment-resistant depression but also enhances social pleasure and empathetic behaviors, according to new research published in the American Journal of Psychiatry.

Some with terminal cancer have said psilocybin helped them confront death. But how that happens is still unclear
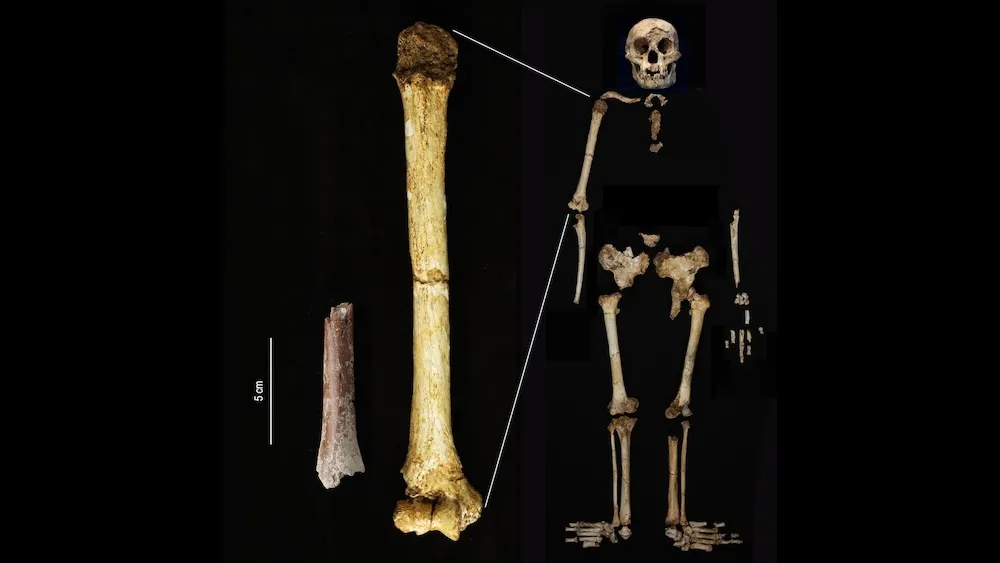
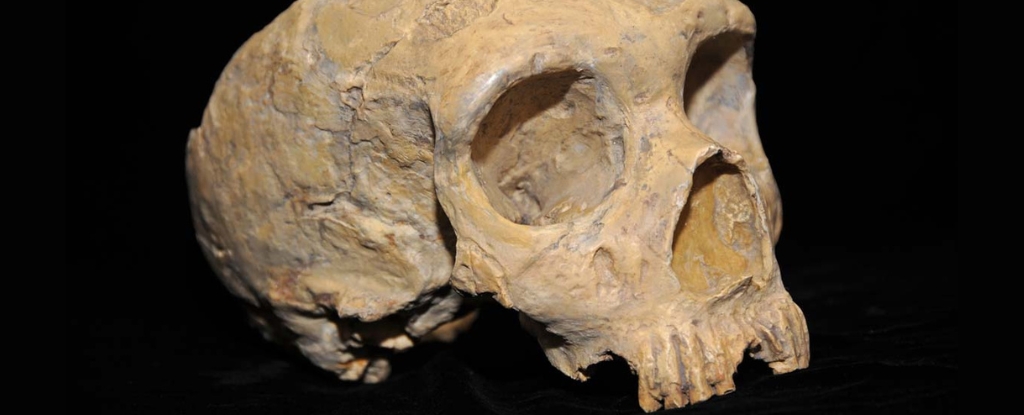
The 700,000-year-old fossilized remains belonged to Homo floresiensis, an extinct species of exceedingly small humans that once inhabited Flores, an island south of mainland Indonesia, according to a study published Tuesday (Aug. 6) in the journal Nature Communications.








