News Desk
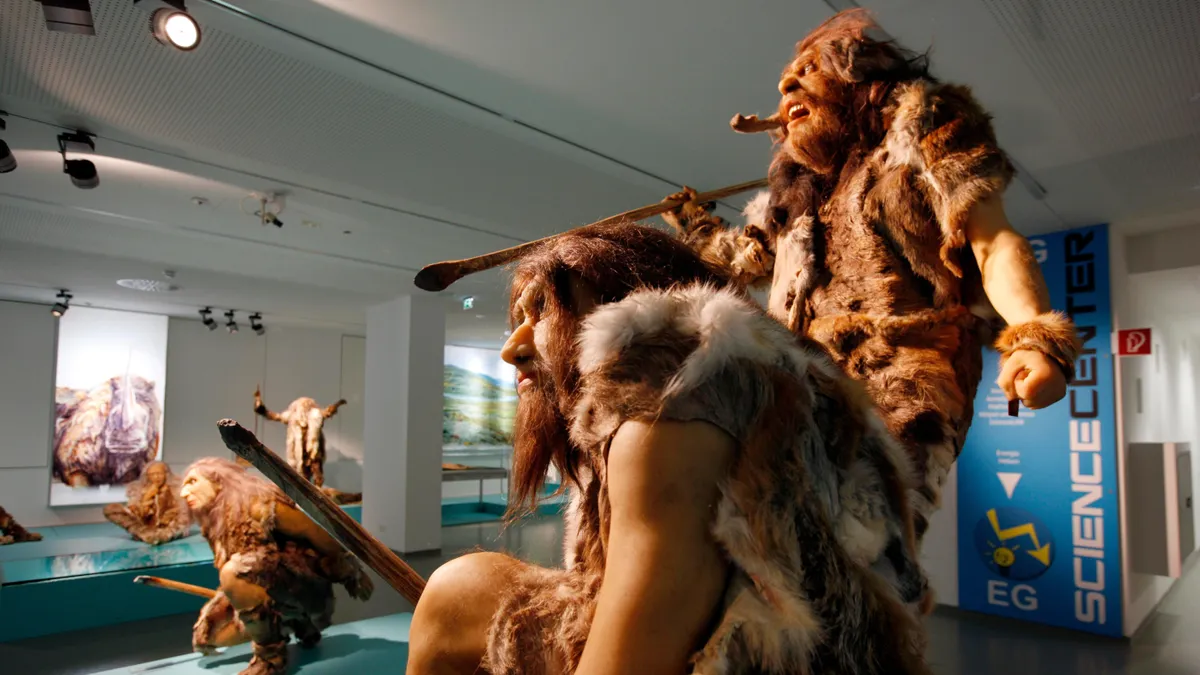

The research, published Wednesday (July 2) in the journal Science, reveals that these archaic human relatives had a process for extracting grease from animal bones — and it may have saved them from a lethal condition.
A new study has found that a psychedelic formulation inspired by ayahuasca can significantly alter how the brain processes faces—especially one’s own. The research shows that the compound changes both early visual perception and later self-referential processing, effectively weakening the brain’s usual distinction between self and others.

Excavation uncovers evidence of 4 ancient human species, obsidian tools dating back over 300,000 years…Archaeologists have uncovered rare artifacts from the Paleolithic era at Ulukoy Cave in Türkiye’s southeastern Mardin province, revealing the earliest known evidence of human activity in northern Mesopotamia, officials said.
The findings suggest that early Egyptians once lived in a melting pot of cultures, with migrants and traders arriving from other parts of Africa and Mesopotamia, an ancient region that now encompasses parts of Iraq, Türkiye, and Iran. The study was published in Nature.
A new, advanced technique for studying fossils has revealed that squids evolved more than 50 million years earlier than previously thought and dominated Earth’s ancient seas. The new study was published in the journal Science.

In the course of a collaboration with the University of Baghdad, LMU’s Enrique Jiménez has rediscovered a text that had been lost for a thousand years. A paper on this discovery is published in the journal Iraq.
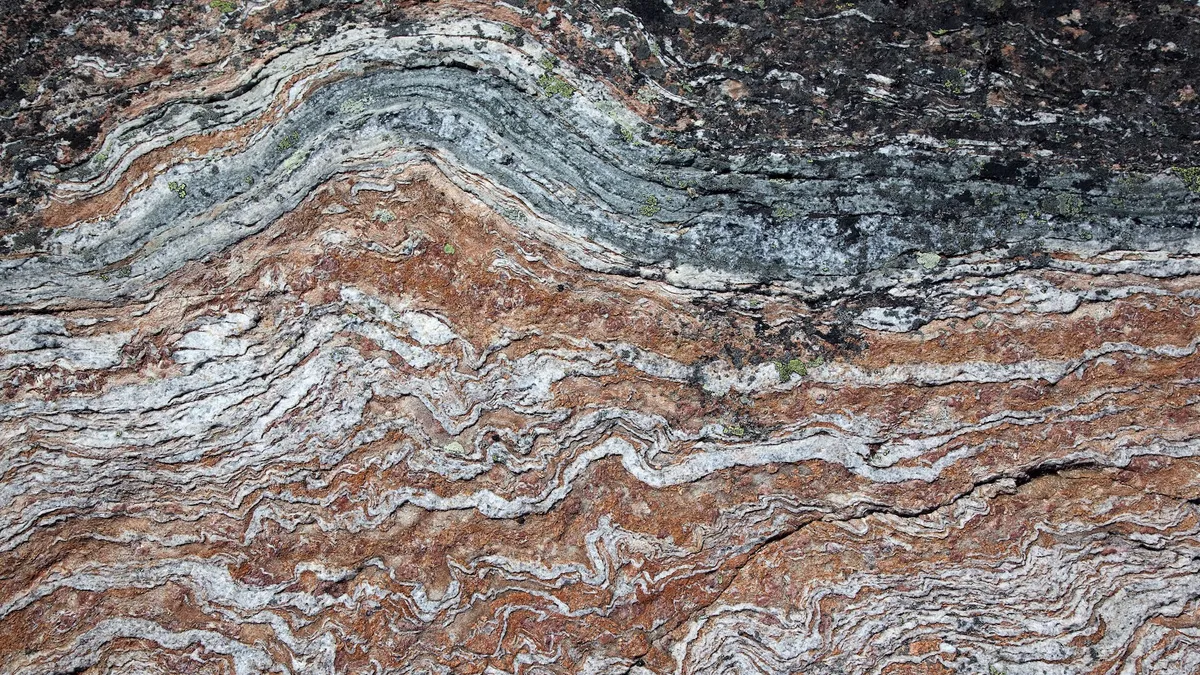

An obscure rock formation on the eastern shore of Canada’s Hudson Bay may contain the oldest known rocks on Earth, a new study claims. Their findings are published June 26 in the journal Science.
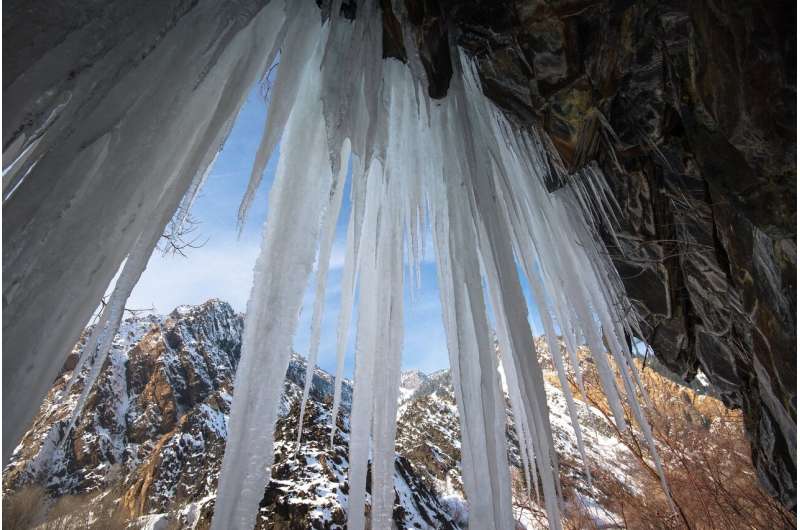

A new study analyzes stone tools from the cave that date to about 19,000 to 18,000 years ago, and discusses how the techniques used to make them hint at the ways that prehistoric people traveled, interacted, and shared their craft.

Ketamine leads to increased communication between areas of the brain that don’t typically engage with each other, new research suggests.

A new study supports the 2021 findings—this time relying on ancient mud to radiocarbon date the footprints, not seeds and pollen, and an independent lab to make the analysis. The paper was published in the journal Science Advances.

One of the latest developments is a recent study from the University of Michigan, published in the journal Science Advances. It proposes that Neanderthals went extinct for astrophysical reasons.
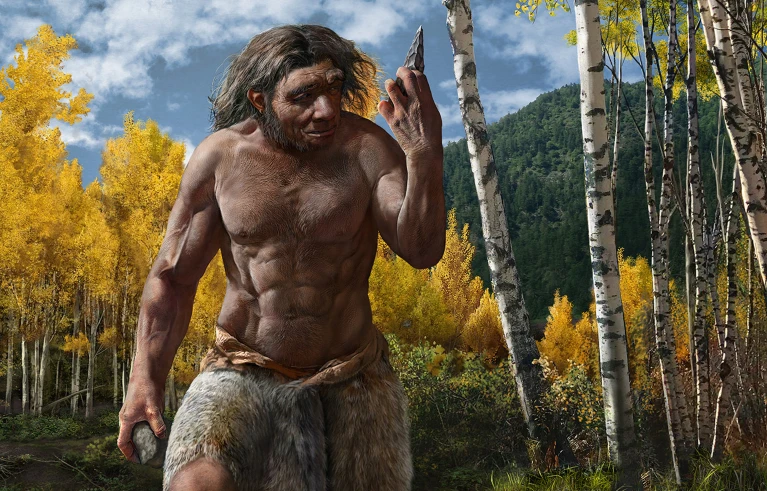

A prominent brow ridge with a brain as large as modern humans and Neanderthals — that’s what the archaic human group, the Denisovans, looked like, according to work published this week in Cell and Science.

A major new study led by Dr Aurélie Manin from the School of Archaeology at the University of Oxford has traced the incredible journey of humankind’s best friend across the Americas, showing how dogs slowly spread southward alongside early farming societies – mirroring the rhythms of human migration, agriculture and cultural change.
A small pilot study published in the journal Psychedelic Medicine suggests that psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy might help reduce depressive symptoms in people with bipolar II disorder who have not responded to conventional treatments.

Looking around, you could easily assume this cold and barren high country was too difficult for people to spend time in. But our new research, published today in Nature Human Behaviour, indicates Dargan Shelter was occupied as early as the last Ice Age and repeatedly visited during this cold period.

This rare find, dating back to a 5,300- to 4,150-year-old mega-village, is the first of its kind ever recorded in Late Prehistoric Iberia, according to findings published in PLOS One.








