Space news stories
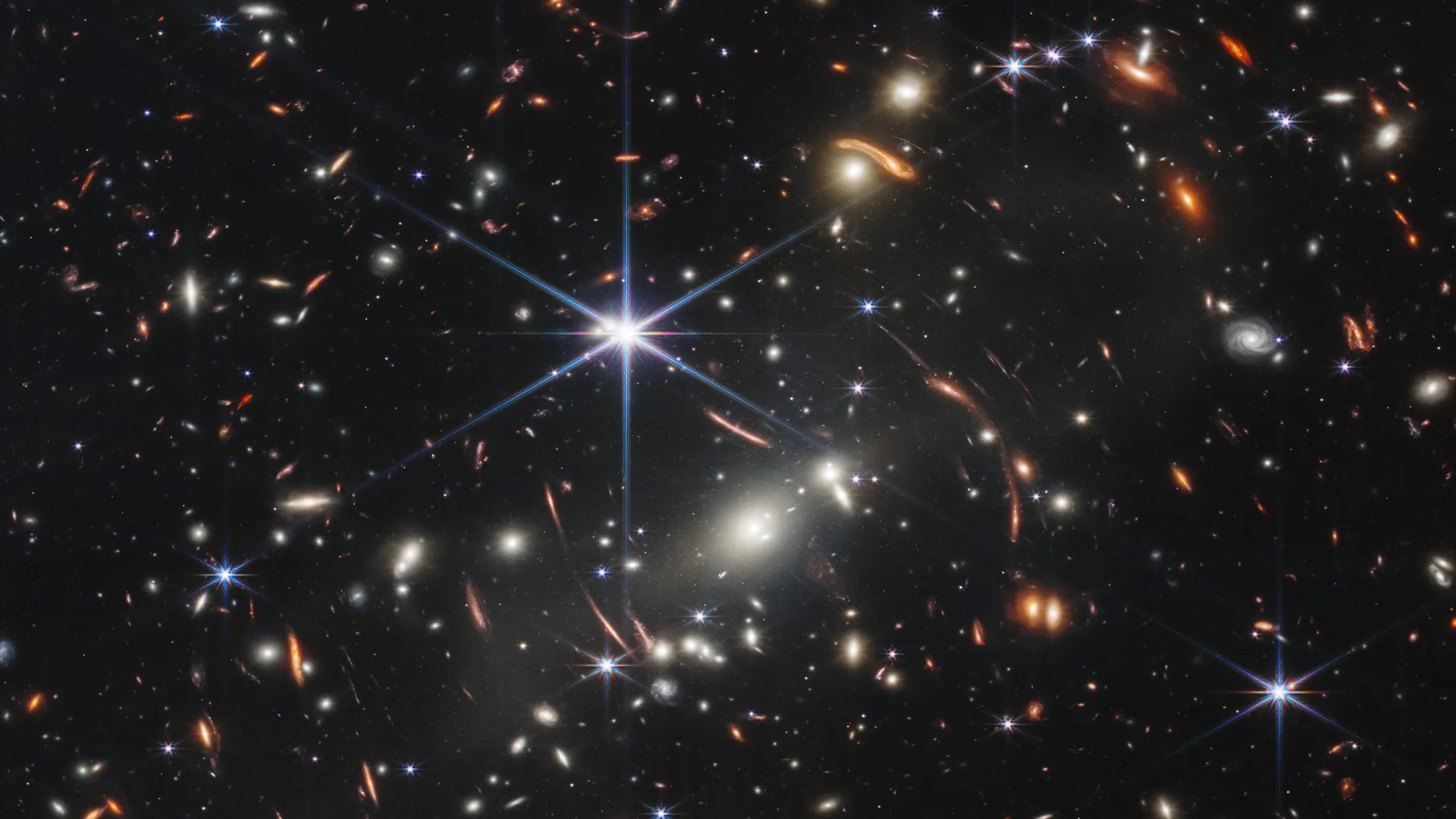

Now, there’s more research to back up the Big Bang. Recently, researchers took a more careful look at the data and determined that the distant galaxies discovered by the James Webb Space Telescope are, indeed, perfectly compatible with our modern understanding of cosmology.
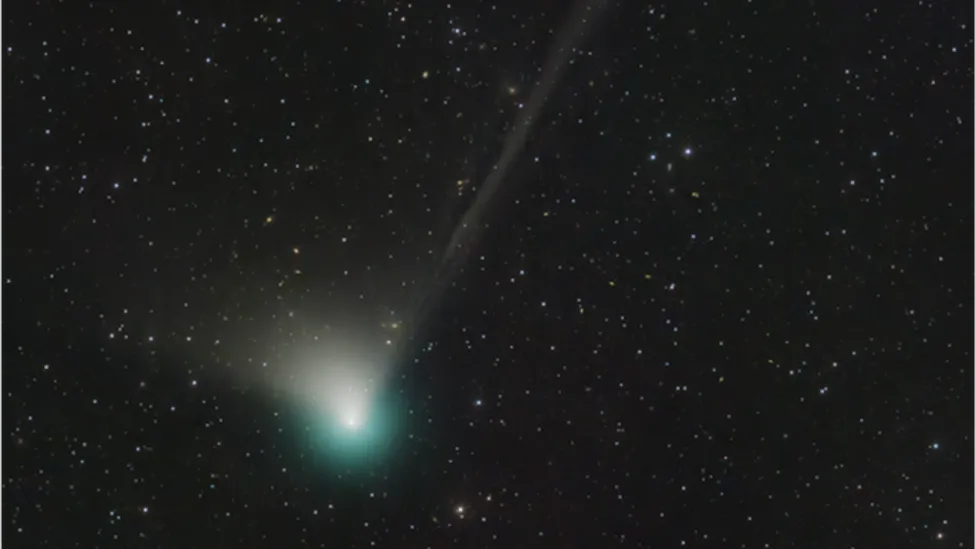

A newly discovered comet will make its closest approach to our planet on Wednesday.Astronomers say the object’s journey toward us took around 50,000 years.
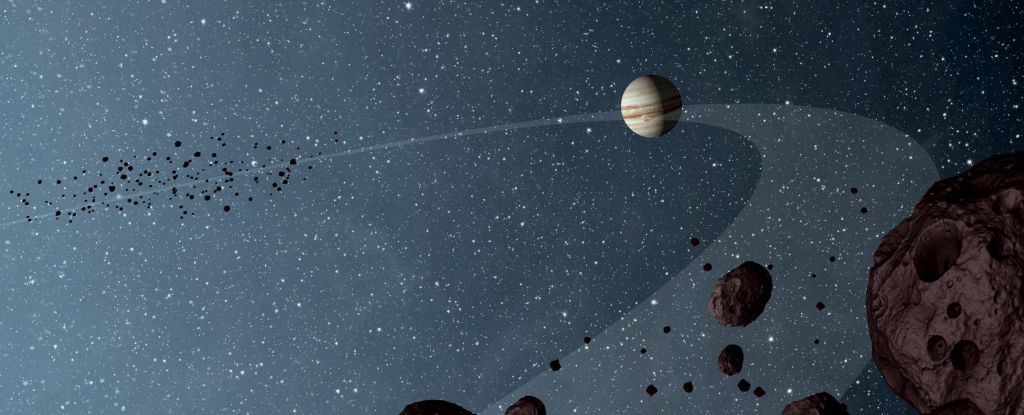

Jupiter isn’t alone along its orbital path around the Sun. Two giant swarms of asteroids have been snared in the gravitational interaction between the gas giant and our star, leading and trailing Jupiter as it treads its cosmic measure.
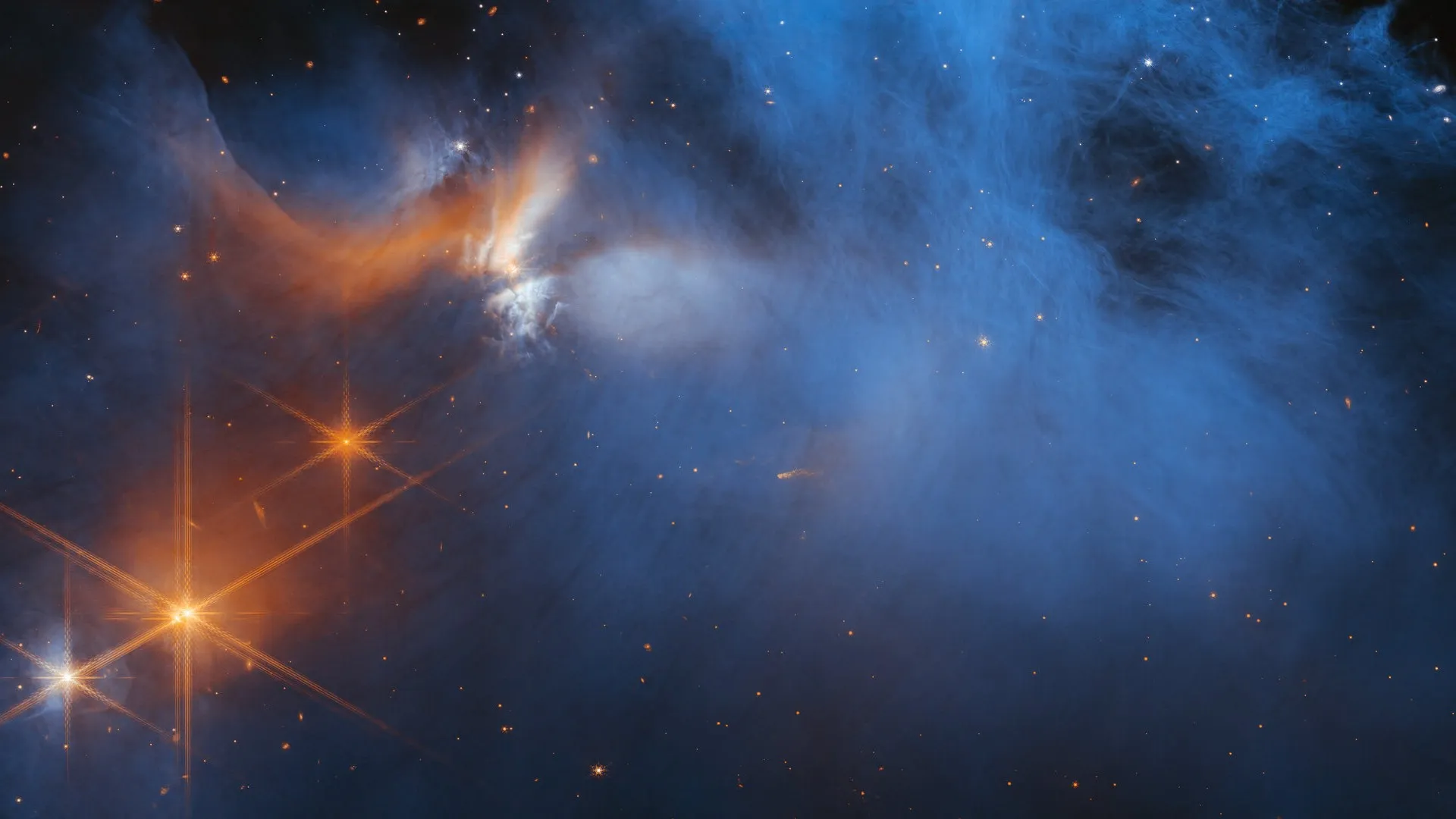

The James Webb Space Telescope’s latest observations of icy molecules will help scientists understand how habitable planets form.
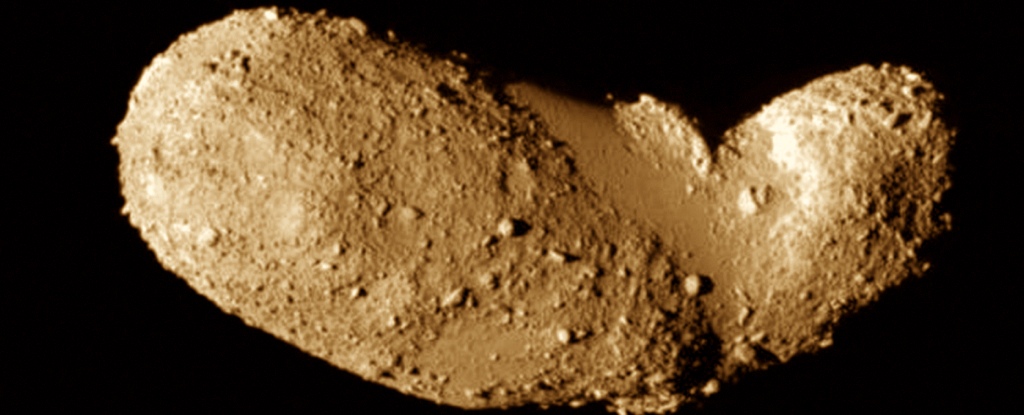
A new study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences discovered that rubble pile asteroids are an extremely resistant type of asteroid and hard to destroy by collision.

A new study shows that the Milky Way is too big for its “cosmological wall”, something yet to be seen in other galaxies. The new research is published in Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
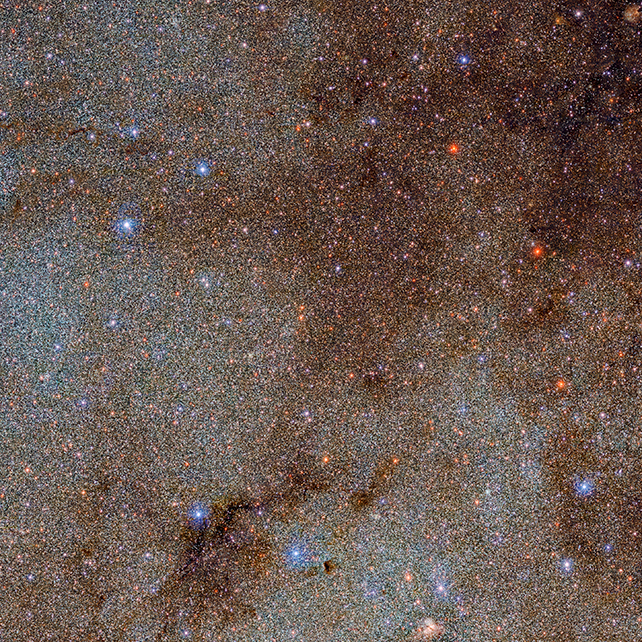

We have the Dark Energy Camera (DECam) to thank for this beautiful shot of space, part of the Víctor M. Blanco 4-meter Telescope at the Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory (CTIO), some 2,200 meters (7,218 feet) above sea level in Chile.
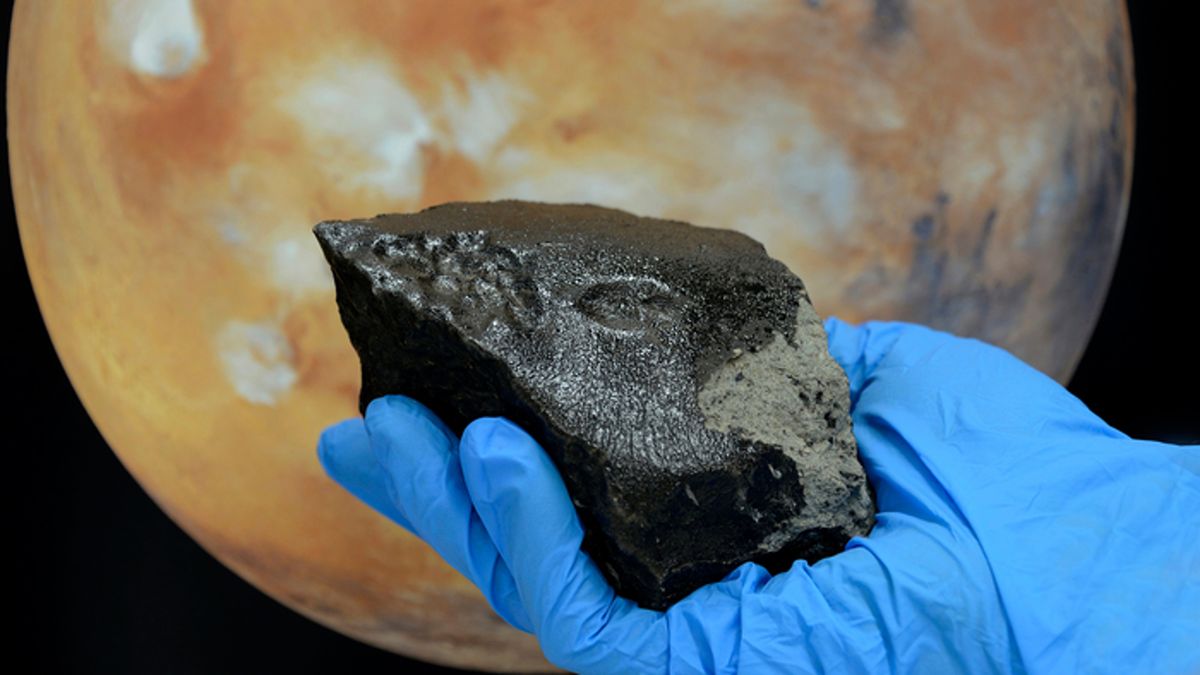

A new study into the Tissint meteorite, which crash-landed in Morocco in 2011, revealed a wide array of organic compounds hidden in the rare space rock.
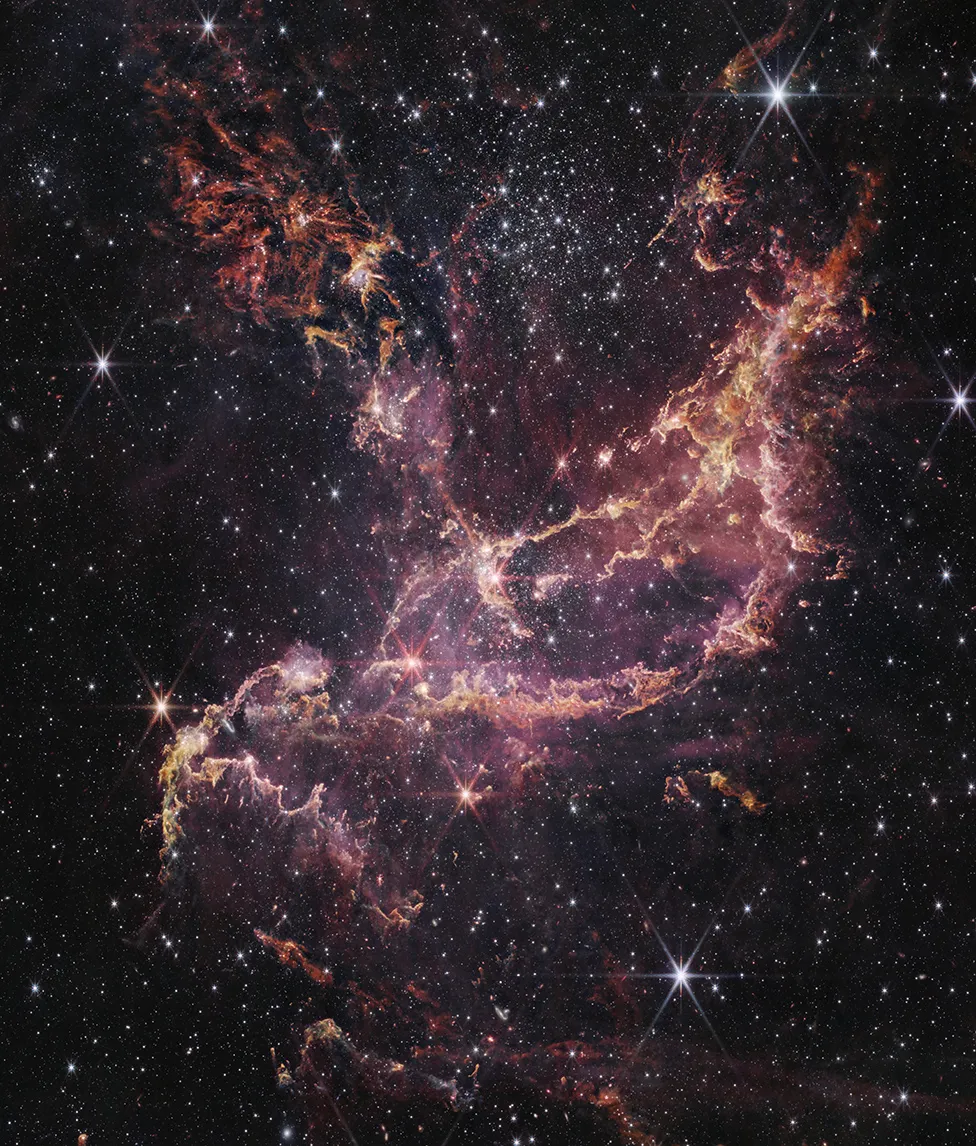

It’s another stupendous image from the new superspace telescope James Webb.The picture shows NGC 346, a region about 200,000 light years from Earth where a lot of stars are being created.

Inside your brain there is a map of every bedroom you’ve slept in. Every kitchen you’ve cooked in. Every city you’ve worked in, every country you’ve holidayed in. There’s even a threadbare map of every Universe you’ve dreamt in
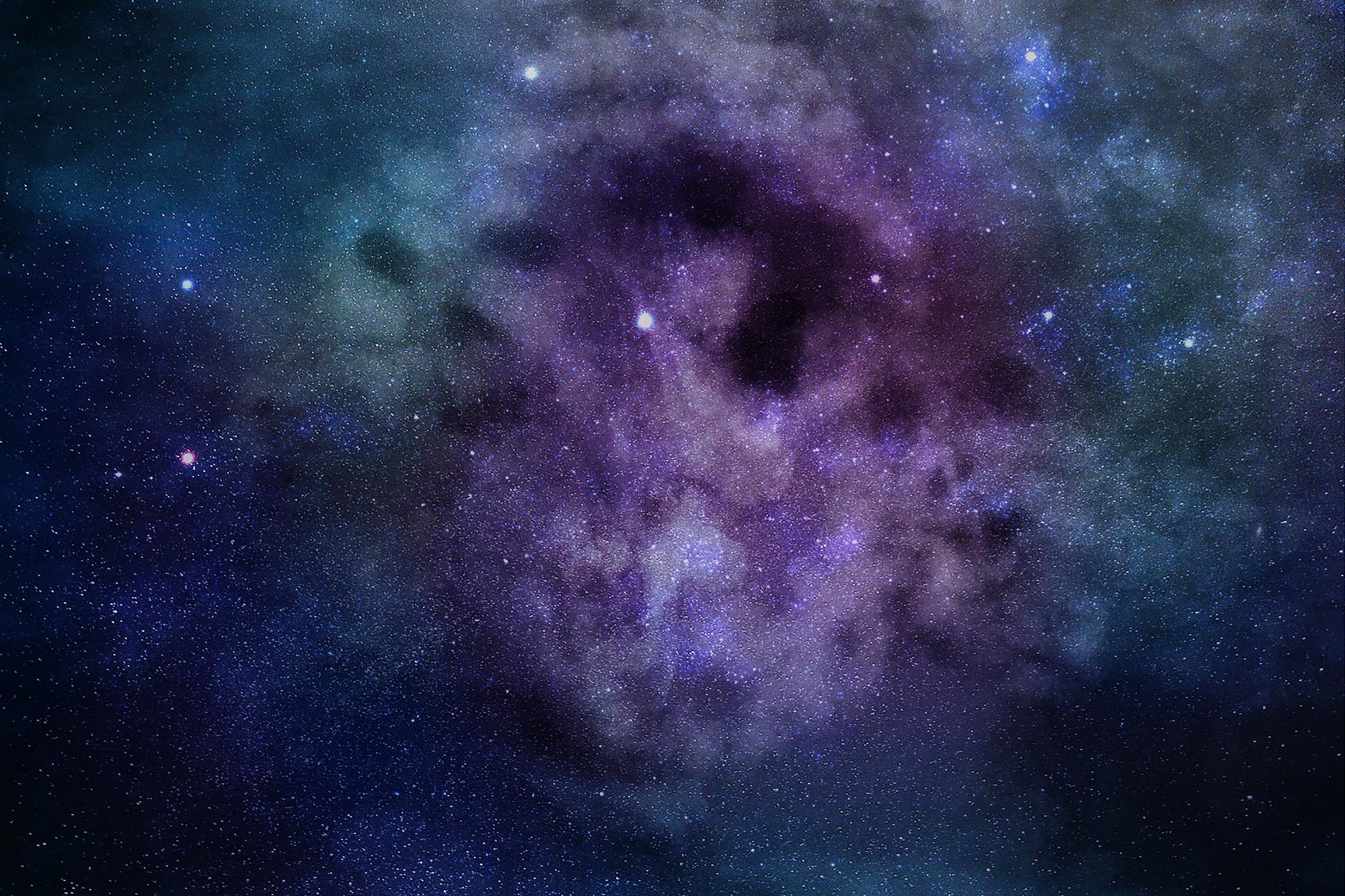

In giant clusters of hundreds or thousands of galaxies, innumerable stars wander among the galaxies like lost souls, emitting a ghostly haze of light. These stars are not gravitationally tied to any one galaxy in a cluster.
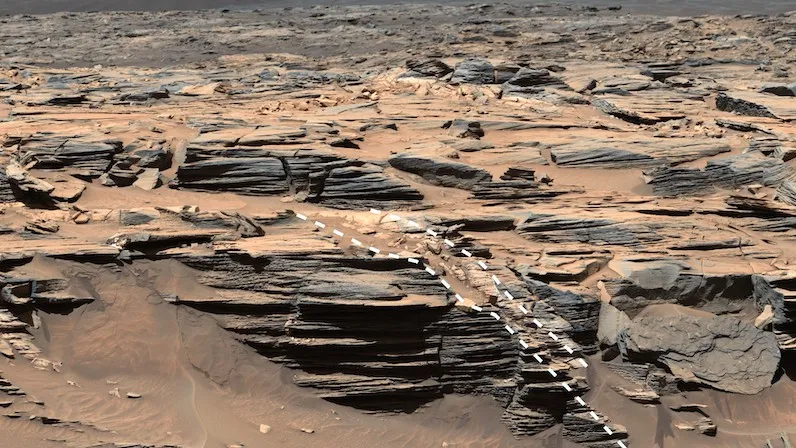

Mysterious “halos” of rock surrounding cracks in a Martian crater may be made of water-rich opal gemstones, a new study suggests.
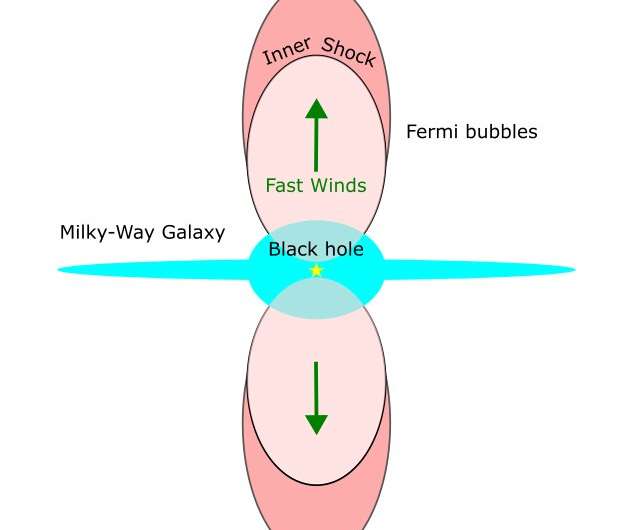
A scientist from Tokyo Metropolitan University has shown that large gamma-ray-emitting bubbles around the center of the Milky Way were produced by fast, outward-blowing winds and an associated “reverse shock.”
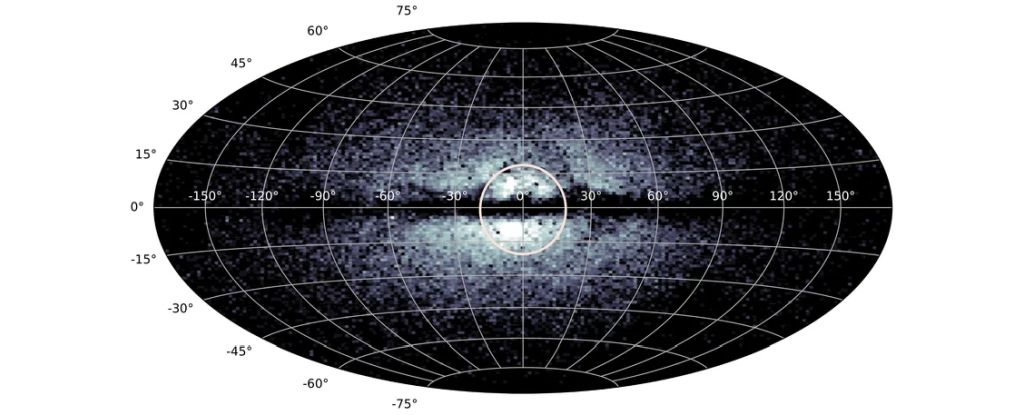
A smattering of stars scattered throughout the center of the Milky Way is the remnants of the ancient galactic core, when our galaxy was still new.
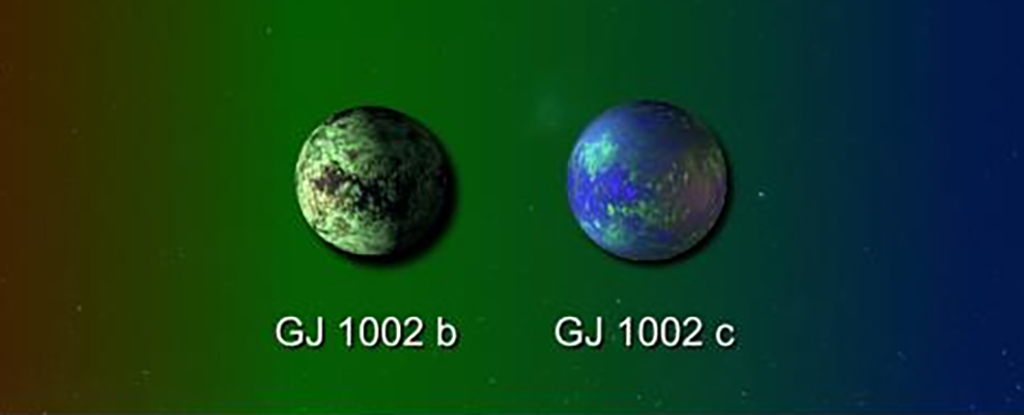

In the search for life on other planets, a couple of promising leads have just opened up: Astronomers have identified two worlds with Earth-like masses, sitting in the habitable zone around a red dwarf star called GJ 1002.
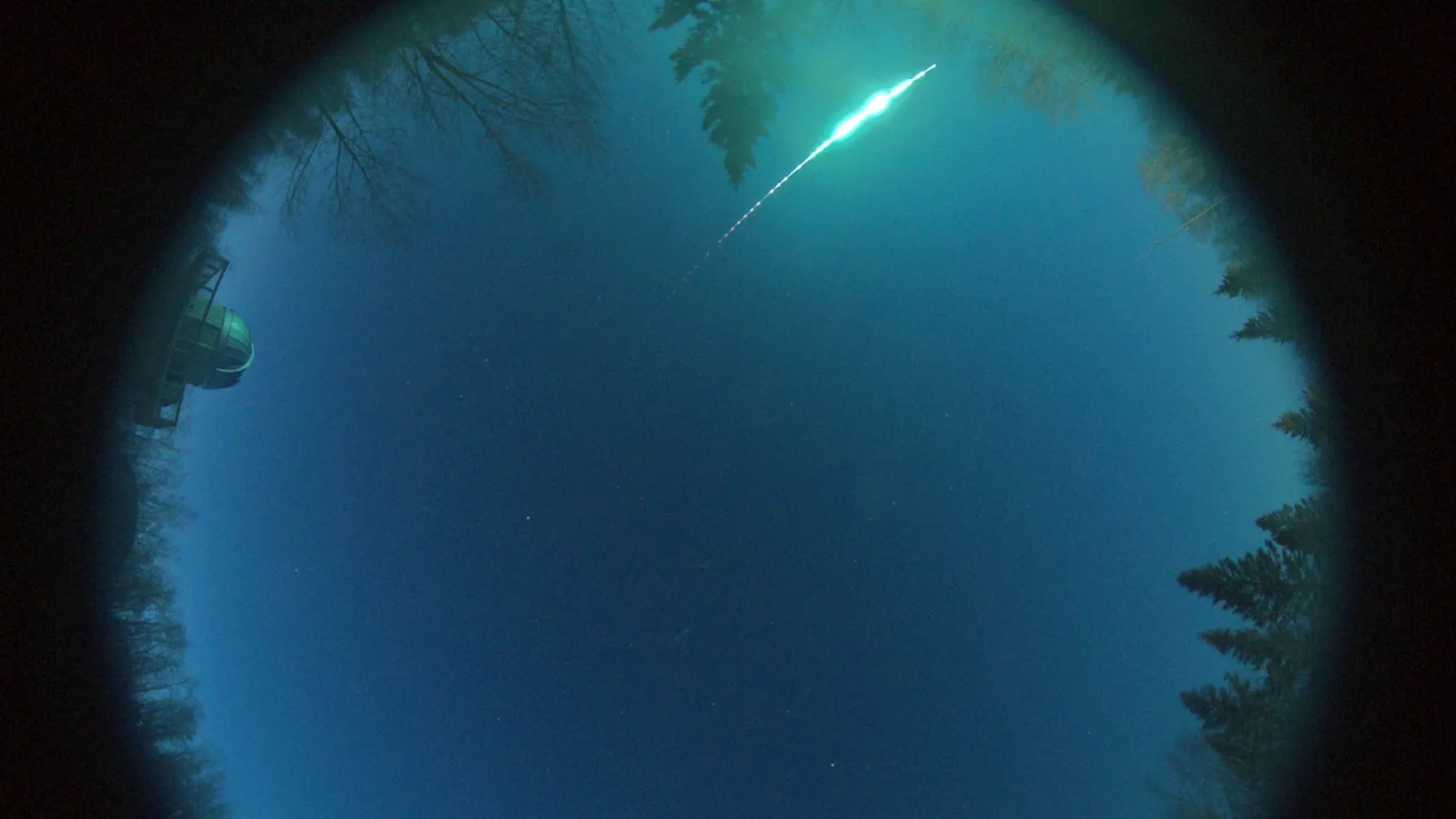

A dazzling fireball that ended its cosmic journey over central Alberta, Canada could change astronomers’ understanding of how the solar system formed 4.5 billion years ago.








