Humans news stories
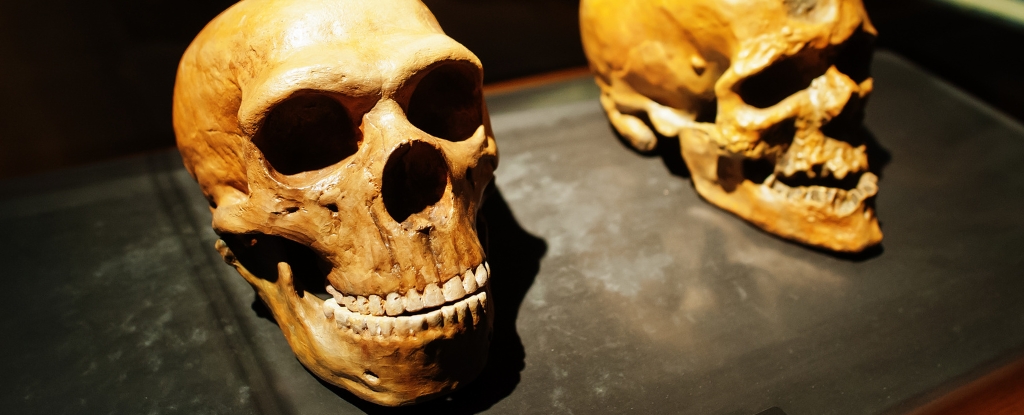

University of Cambridge researchers have now uncovered an estrangement in our family tree, which began with a population separation 1.5 million years ago and a reconciliation just 300,000 years ago. The research was published in Nature Genetics.

Few plants are more celebrated in Egyptian mythology than the blue lotus, a stunning water lily that stars in some of archaeology’s most significant discoveries.

Near the local storefronts lies the site of an excavation that unearthed stone tools from 150,000 years ago—the earliest sign ever of humans inhabiting a tropical forest…”The results represent the oldest yet known clear association between humans and this habitat type,” they wrote in their paper, published in the journal Nature last month after years of research.

The ancestors of all modern humans split off from a mystery population 1.5 million years ago and then reconnected with them 300,000 years ago, a new genetic model suggests. The unknown population contributed 20% of our DNA and may have boosted humans’ brain function.

The red tape of government bureaucracy spans more than 4,000 years, according to new finds from the cradle of the world’s civilisations, Mesopotamia.
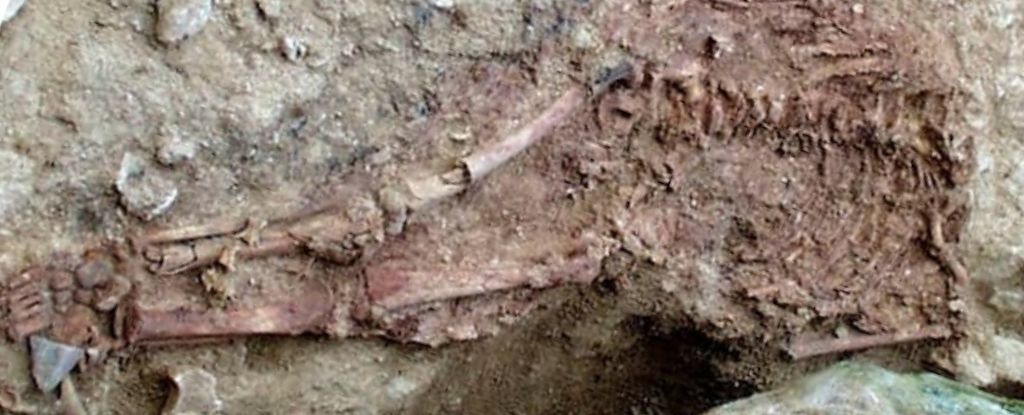
Many years after the Lapedo child’s discovery, some of the same researchers who first excavated the child have confirmed that this strange-looking human lived tens of thousands of years after Neanderthals went extinct.

It is a deep question, from deep in our history: When did human language as we know it emerge? A new survey of genomic evidence suggests our unique language capacity was present at least 135,000 years ago. Subsequently, language might have entered social use 100,000 years ago.
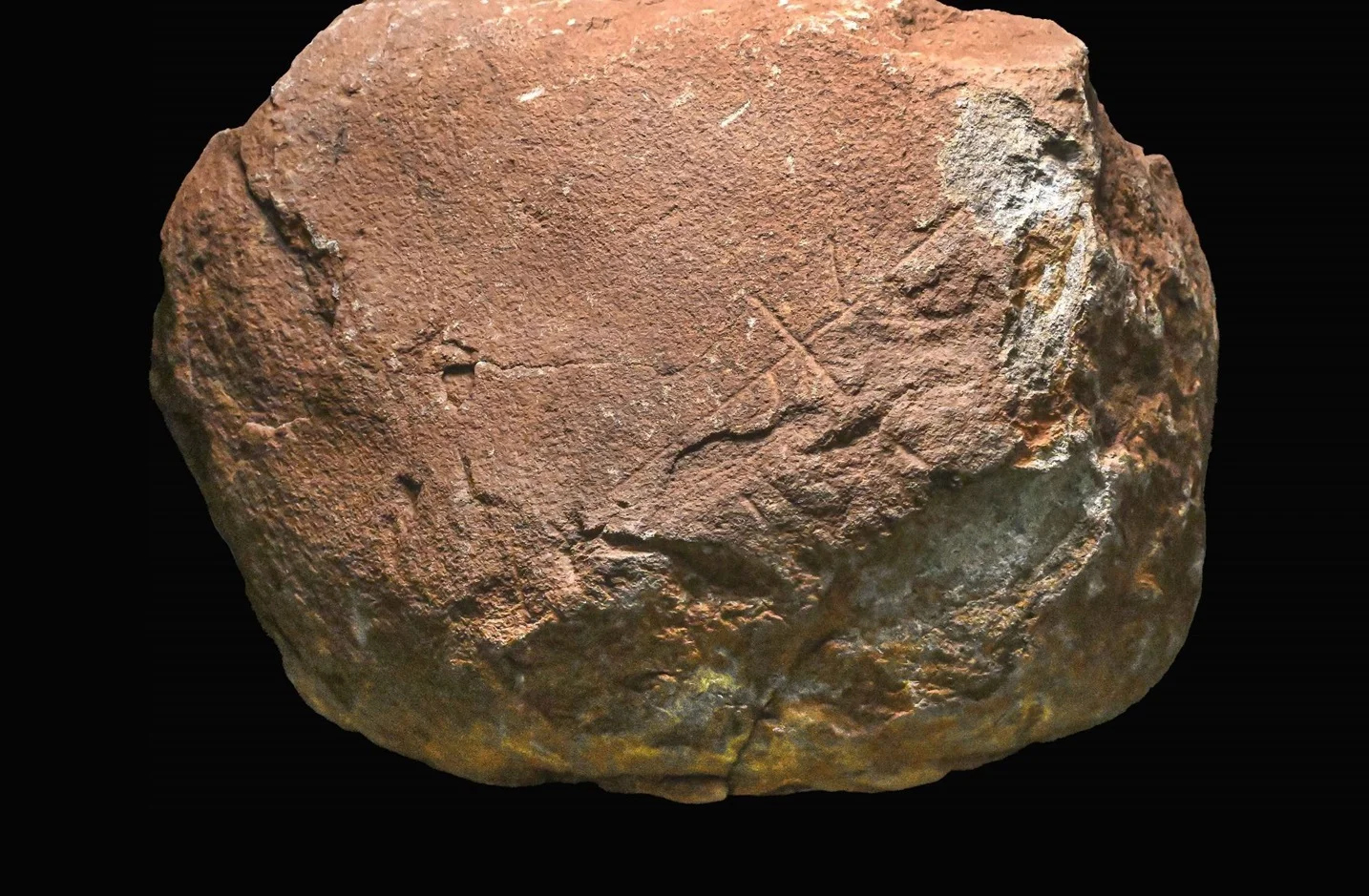

The Department of Culture, Education, and Historical Heritage has announced the discovery of carvings on a gabbro stone block which could date from 200,000-years-ago.

The Neolithic period began in southwest Asia around 12,000 years ago. It marked a major shift in human history as societies transitioned from hunting and gathering to farming. This sparked migrations across Europe and dramatically reshaped the continent’s gene pool. The study was published in Nature.
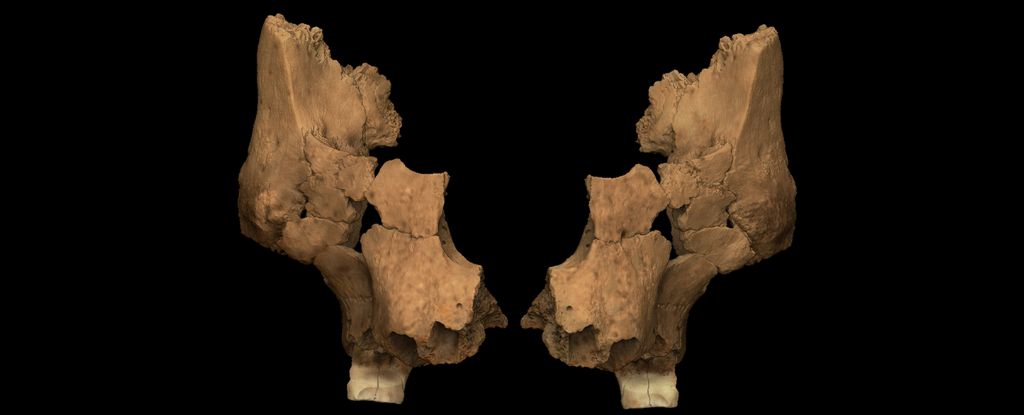
Scientists have put a face, but not an official name, to the earliest human ancestor ever found in Western Europe. This recently discovered hominin is a “new actor in the story of human evolution,” says excavation coordinator Rosa Huguet, from the Catalan Institute of Human Paleoecology and Social Evolution in Spain. The study was published in Nature.

The first-ever published research on Tinshemet Cave reveals that Neanderthals and Homo sapiens in the mid-Middle Paleolithic Levant not only coexisted but actively interacted, sharing technology, lifestyles, and burial customs. This research was published in Nature Human Behavior.
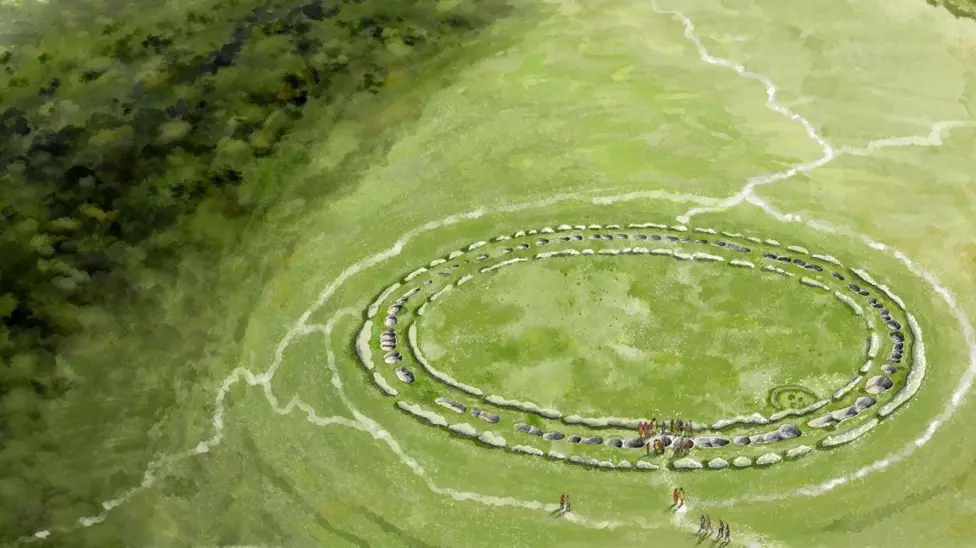

An ancient burial site has been revealed to be the earliest known large circular enclosure in Britain. Archaeological research by the University of Exeter and Historic England has shed new light on the origins of the prehistoric Flagstones monument located near Dorchester, Dorset, during the Neolithic period.

The child’s remains were discovered 27 years ago in a rock shelter called Lagar Velho in central Portugal. The nearly complete skeleton was stained red, and scientists think it may have been wrapped in a painted animal skin before burial. See the study here.
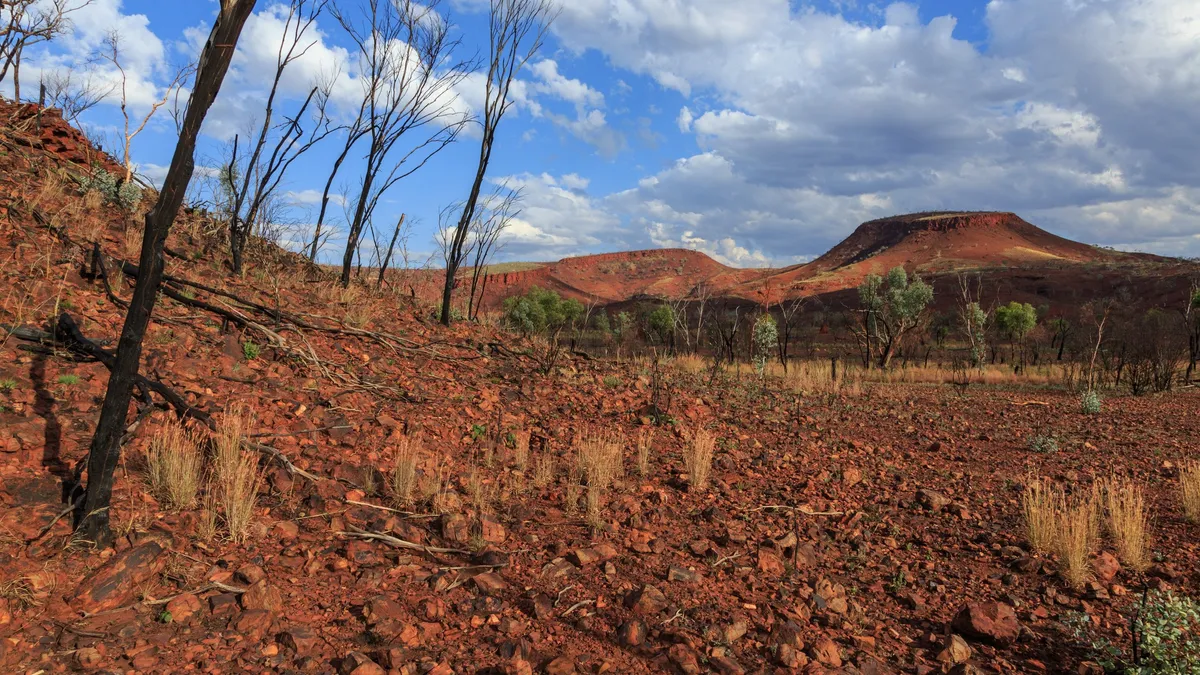

Researchers say they have found “unequivocal evidence” that a meteorite smashed into Earth 3.47 billion years ago, potentially affecting plate tectonics and creating conditions for life. The study was published Thursday (March 6) in the journal Nature Communications.
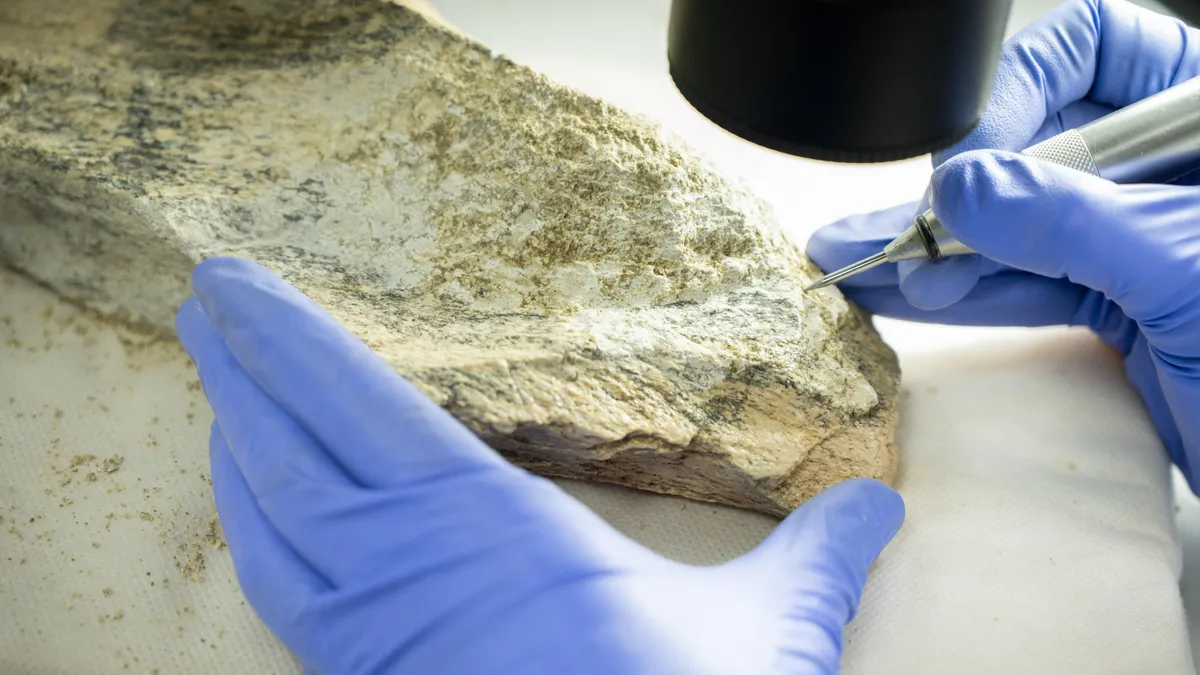

The oldest human-crafted bone tools on record are 1.5 million years old, a finding that suggests our ancestors were much smarter than previously thought, a new study reports. They published their findings Wednesday (March 5) in the journal Nature.
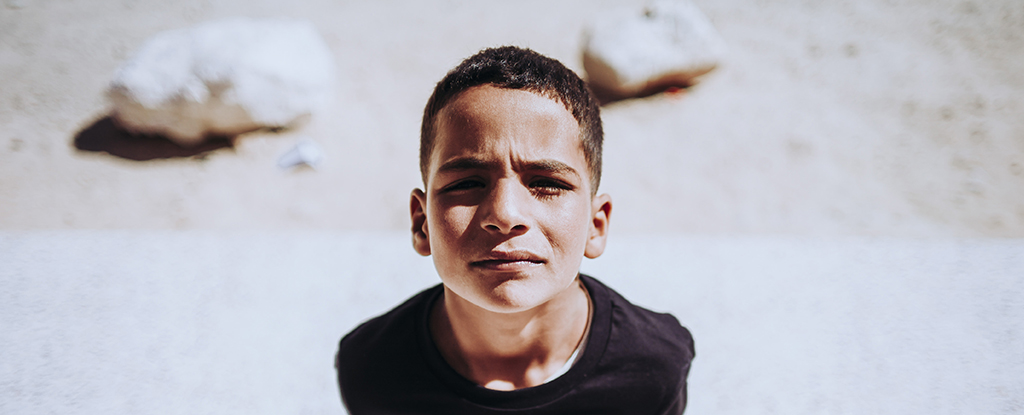

A stressful life can leave marks on our genetic code, some of which can even be passed on to our children. A study now reveals how the biological impact of trauma on a mother persists long after the violent acts themselves have passed.








