Ancient news stories

Homo sapiens who reached Europe around 54,000 years ago introduced bows and arrows to that continent, a new study suggests.
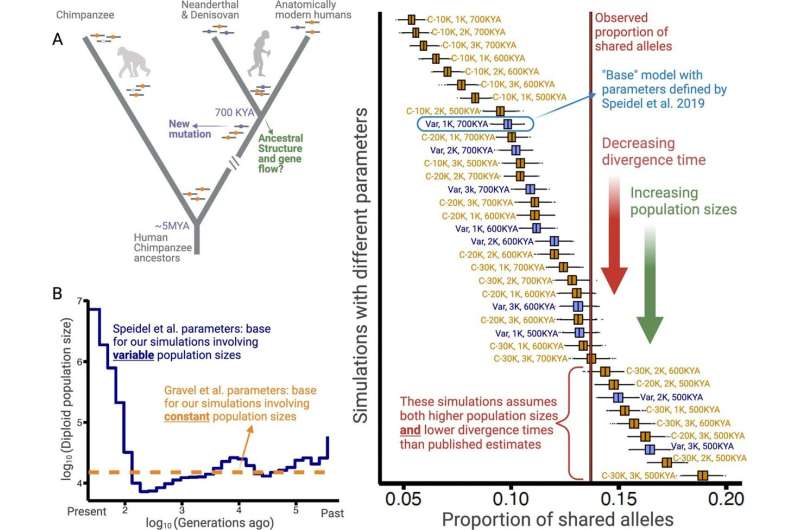
The theory behind these evolutionary trade-offs is called balancing selection. A University at Buffalo-led study published in eLife explores this phenomenon by analyzing thousands of modern human genomes alongside ancient hominin groups, such as Neanderthal and Denisovan genomes.

The cryptic language of the Book of Revelation — famous for its exotic imagery, including a red beast with seven heads and a symbolic female figure likened to the evils of Babylon — is deliberately similar to language used in ancient Roman “curse tablets,” according to new research.

While excavating two large buildings in the ruins of the palace in the city of Yueyang, the researchers from the Institute of Archaeology at the China Academy of Social Sciences were surprised to make the discovery.
It is called Radiocarbon 3.0: it is the newest method developments in radiocarbon dating, and promises to reveal valuable new insights about key events in the earliest human history, starting with the interaction between Homo Sapiens and Neanderthals in Europe.
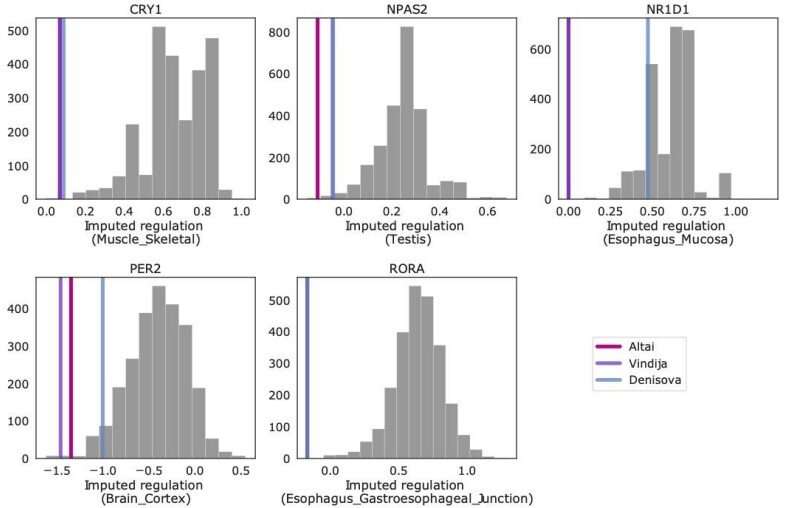
A team of epidemiologists and geneticists from Vanderbilt University, the University of Pennsylvania and the University of California has found evidence that suggests modern humans mating with Neanderthals may have gained an ability to adapt to differences in the amount of daylight hours in Eurasia.
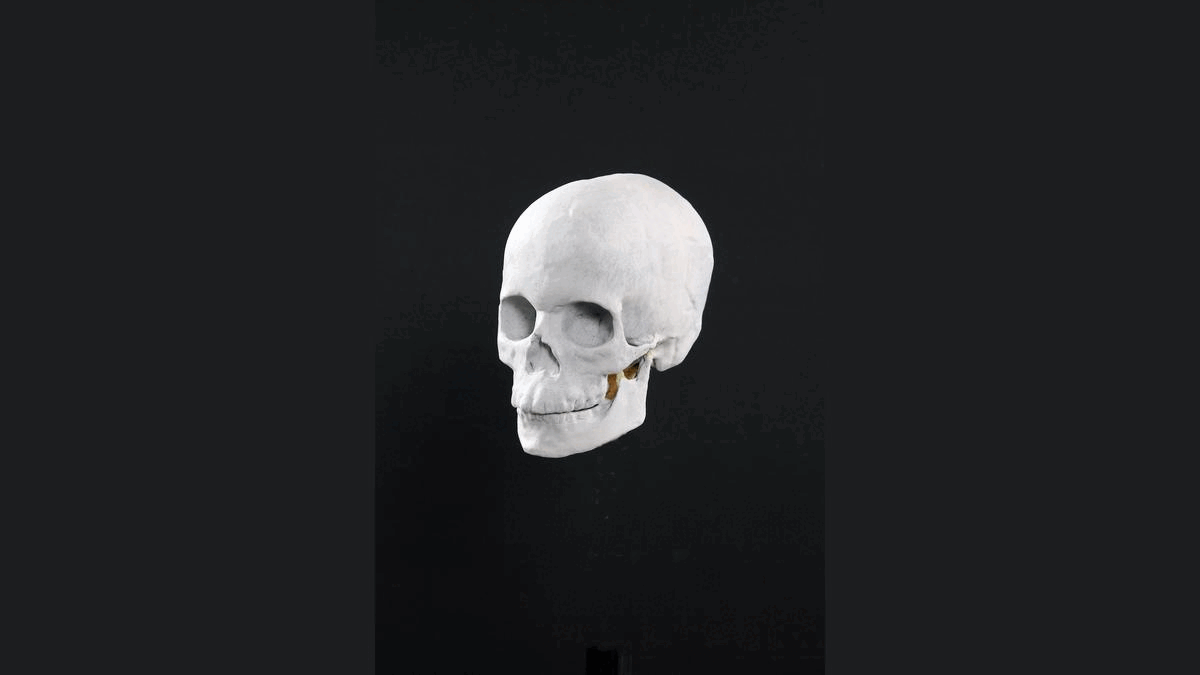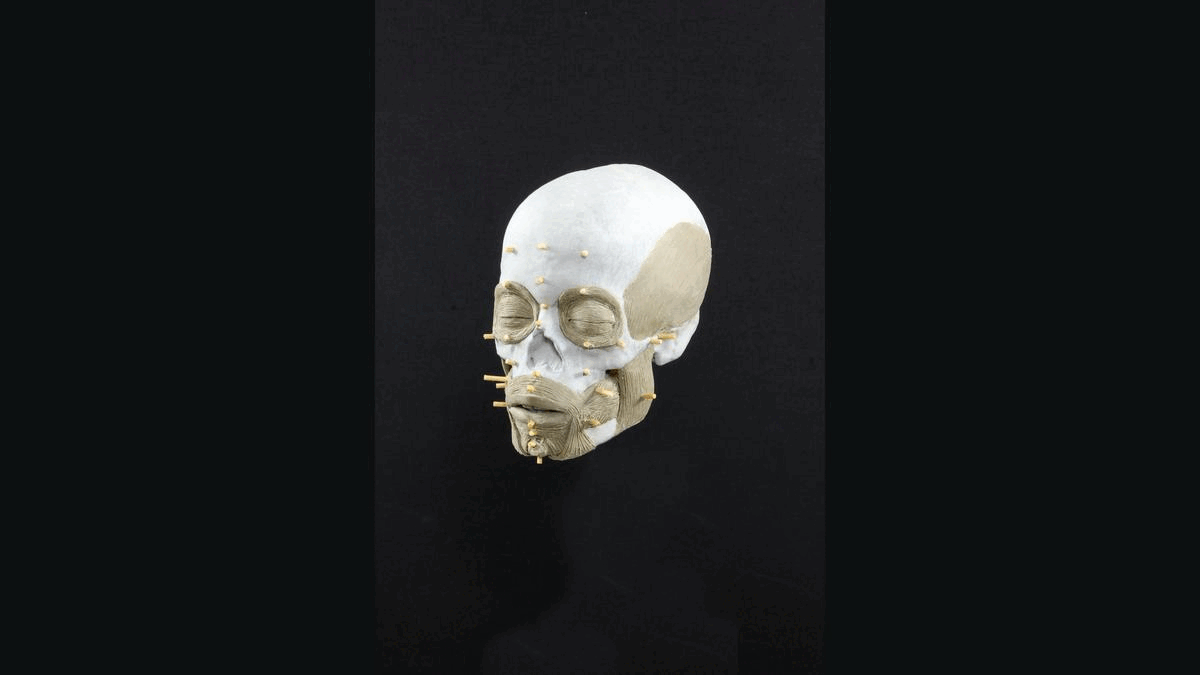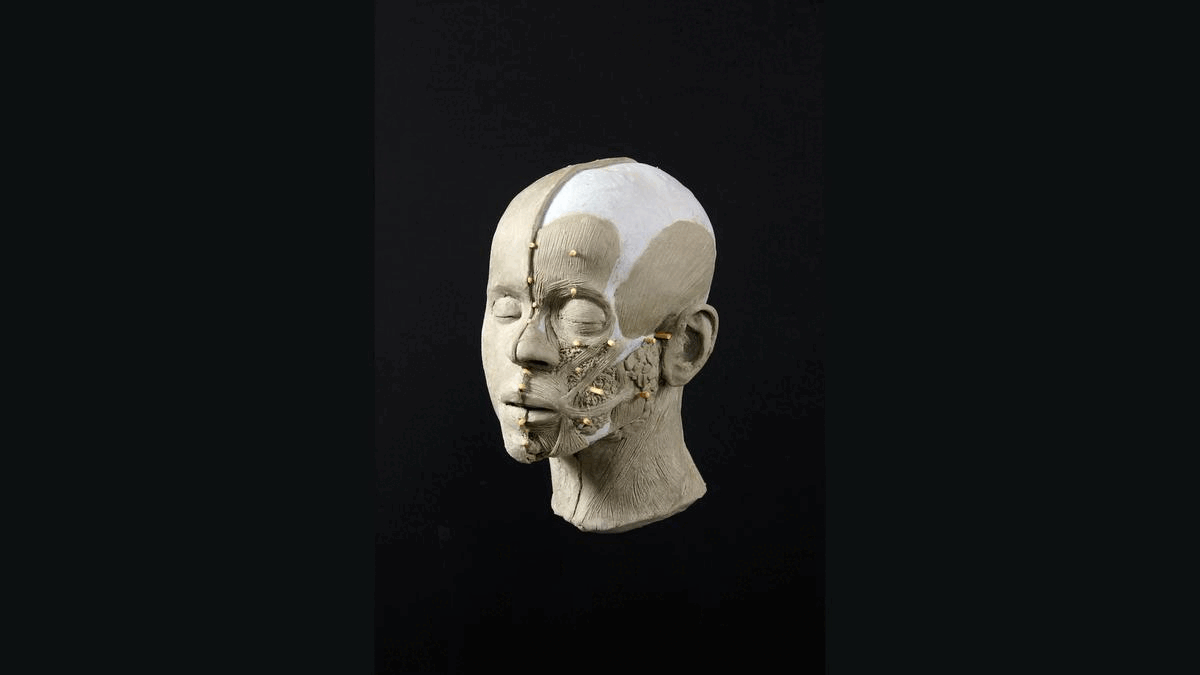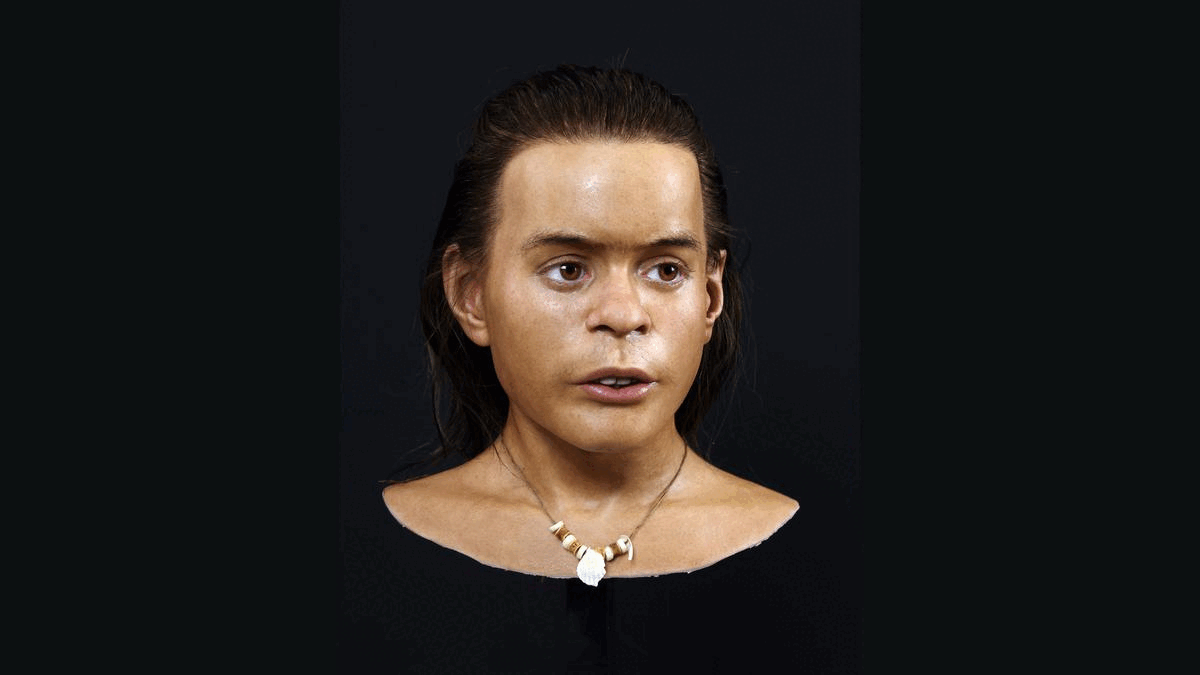
About 8,300 years ago, a teenage boy with an unusual skull and short stature may have scampered along the rocky coast of what is now Norway, pausing to regain his balance as he clutched a fishing rod.
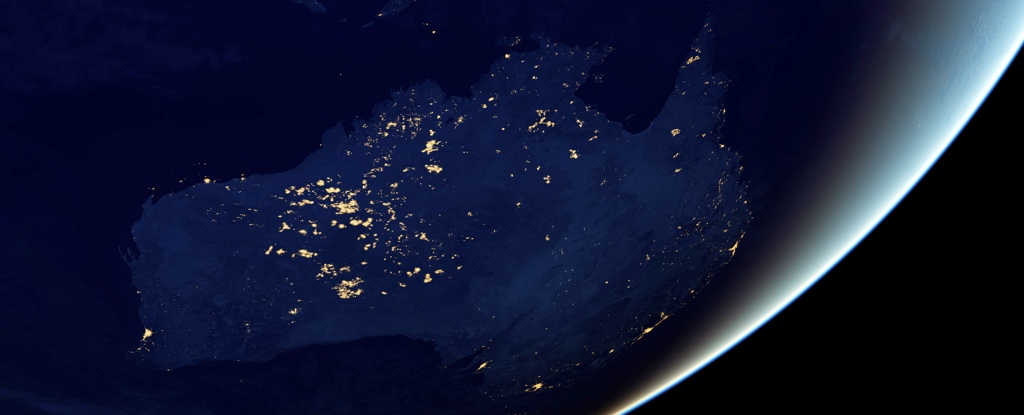

Between 75,000 and 50,000 years ago, humans began to make their way across the megacontinent of Sahul, a landmass that connected what is now Australia, Tasmania, New Guinea, and the Aru Islands.
DNA reveals previously unknown degree of mixture between Japan, North America and the Eurasian mainland. See study here.
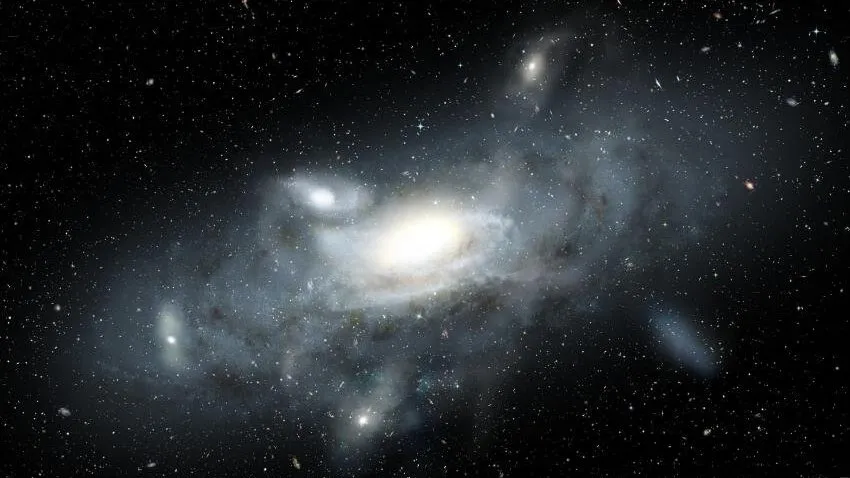

A sparkling cannibal galaxy discovered by the James Webb Space Telescope appears to be a “very early” mirror image of the Milky Way, and it could help astronomers understand how our galaxy took shape, a new study has revealed.
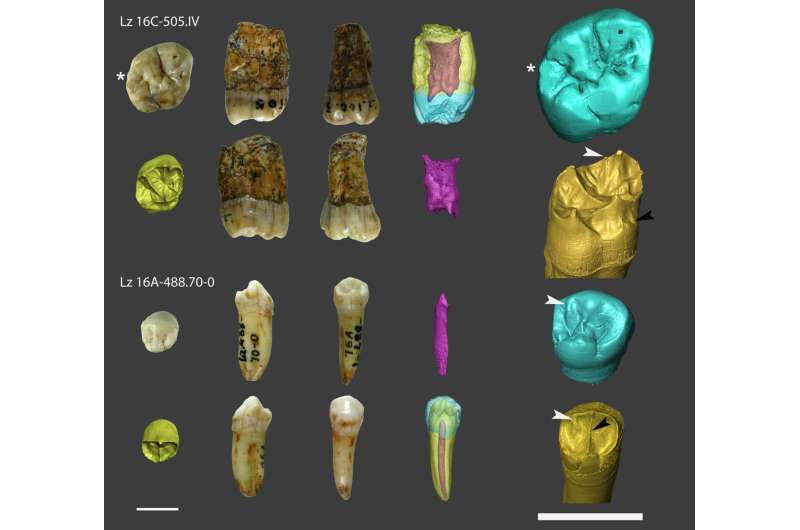
A new analysis of the teeth remains found at the Lezetxiki site confirm that they belonged to Neanderthal individuals. The study, which… has been published in American Journal of Biological Anthropology, confirms a late presence of Neanderthals in the north of the Iberian Peninsula.
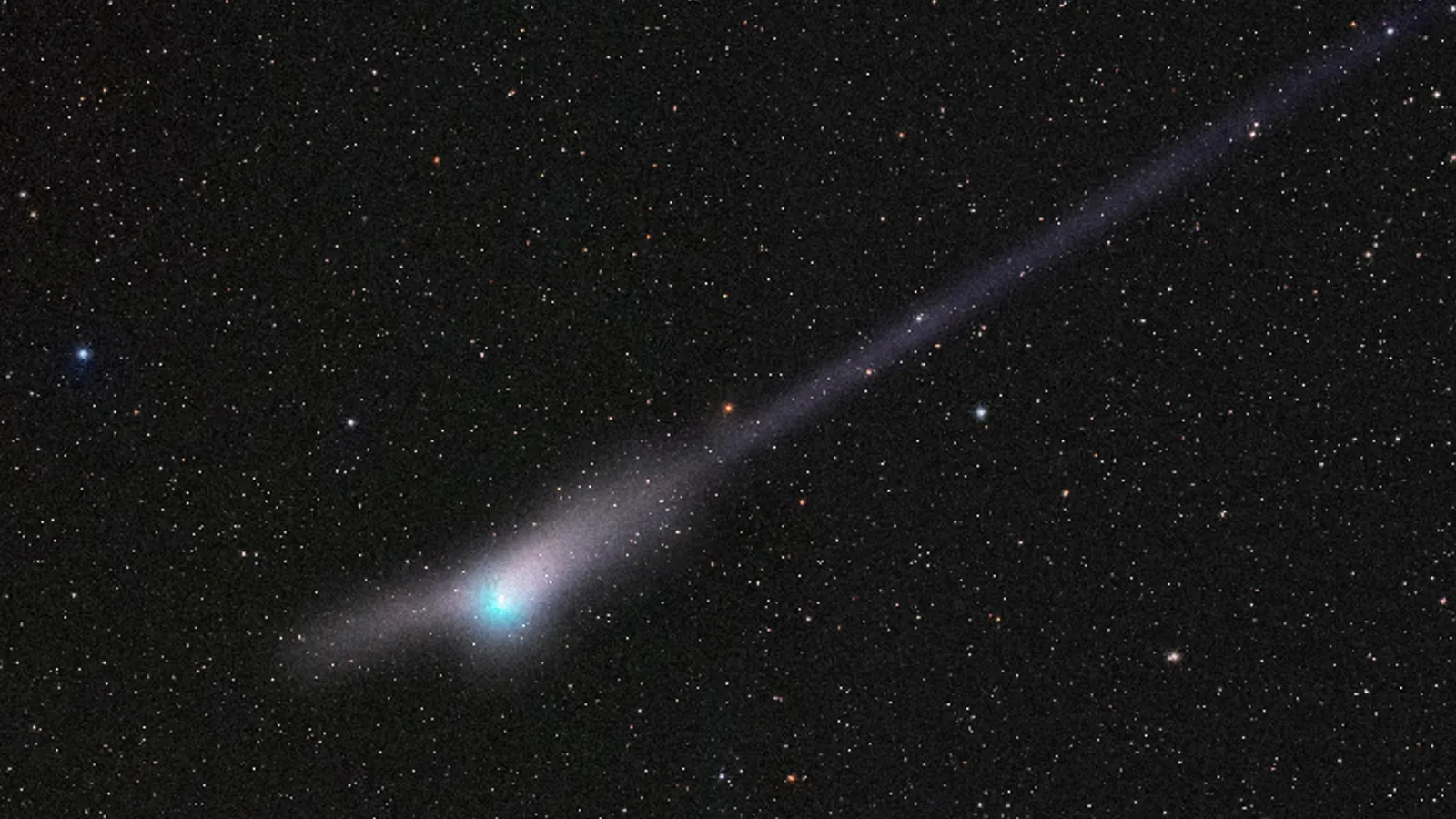

A rare green comet zipping by Earth for the first time since the Stone Age is about to pass right next to Mars this week, and the once-in-a-lifetime cosmic pairing could be visible through a simple pair of binoculars.
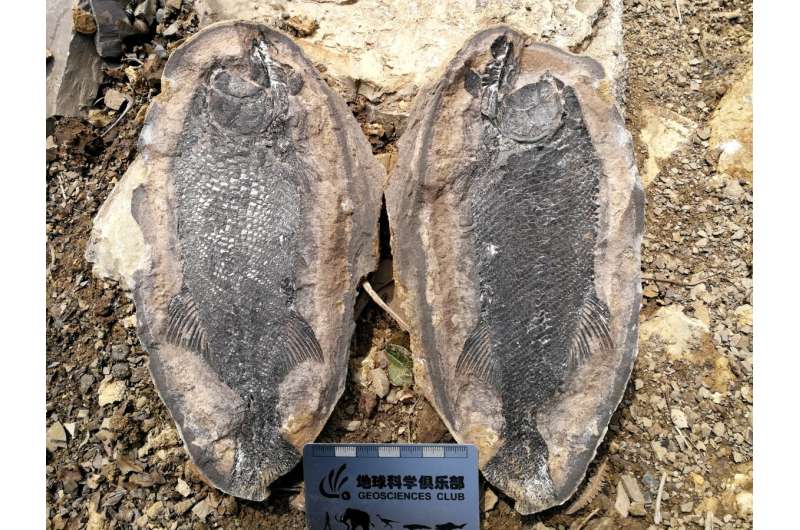

About 250 million years ago, the Permian-Triassic mass extinction killed over 80% of the planet’s species. In the aftermath, scientists believe that life on Earth was dominated by simple species for up to 10 million years before more complex ecosystems could evolve. Now this longstanding theory is being challenged by a team of international researchers. See paper here.
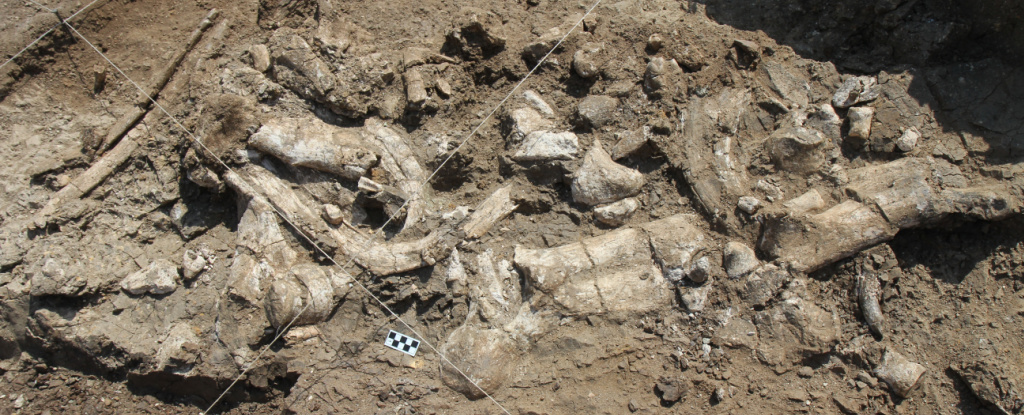

Archaeologists have revealed what could be the oldest stone tools ever found, and they think someone other than our closest Homo ancestors may have made them. See paper here.
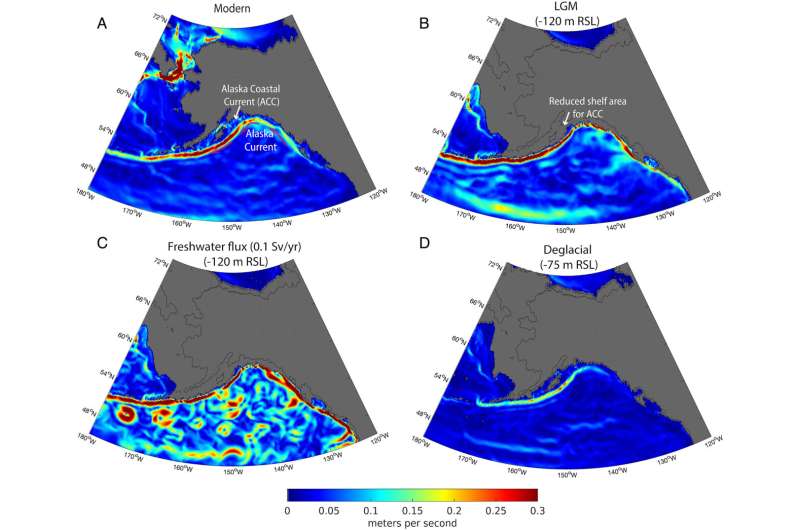
Researchers have pinpointed two intervals when ice and ocean conditions would have been favorable to support early human migration from Asia to North America late in the last ice age, a new paper published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences shows.
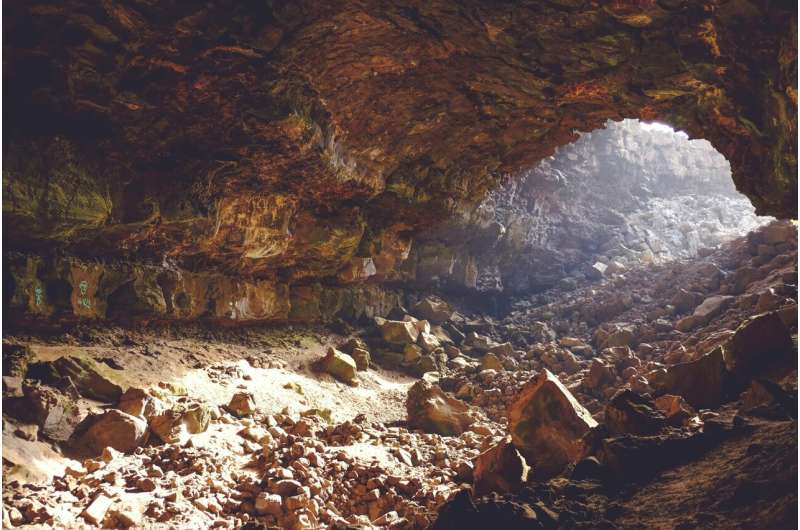

A study published in Frontiers in Environmental Archaeology shows that 90,000 years ago, these Neanderthals were cooking and eating crabs.








