News Desk

A study led by Prof. Amos Frumkin from the Hebrew University of Jerusalem sheds new light on one of humanity’s most significant turning points: the Neolithic Revolution. Published in the Journal of Soils and Sediments, the study presents compelling evidence that catastrophic wildfires and soil erosion—driven by natural climate shifts—may have sparked the first widespread transition from hunting and gathering to farming in the southern Levant over 8,000 years ago.
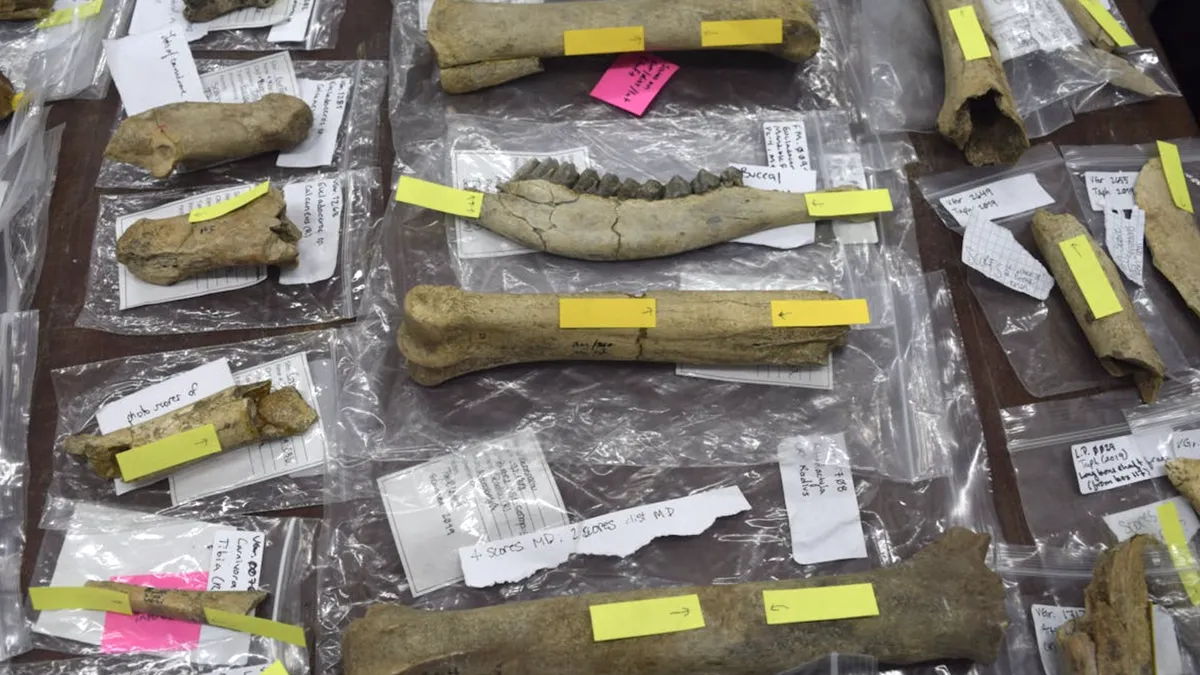
Researchers reexamining fossils identified telltale marks made by human ancestors cutting meat from bones. The discovery pushes back the date hominins started living in Europe by 200,000 years. The research was published in Nature Communications.

Thought to be more than 2,000 years old, the Antikythera mechanism is widely considered the first computer in history, an analog calculator that was way ahead of its time… or was it? The research has yet to be peer-reviewed or published in a journal, but is available on the preprint server arXiv.
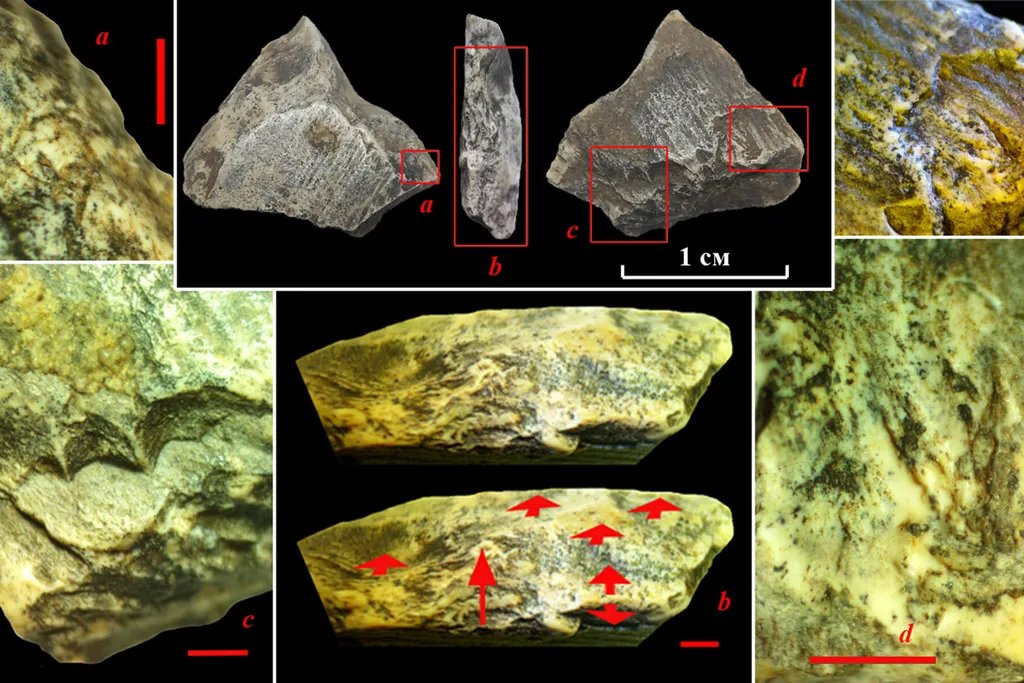

Archaeologists have unearthed mysterious 400,000-year-old artifacts made from mammoth tusks that may be the oldest human-made ivory objects ever found. They describe their findings in a recent paper published in the International Journal of Osteoarchaeology.
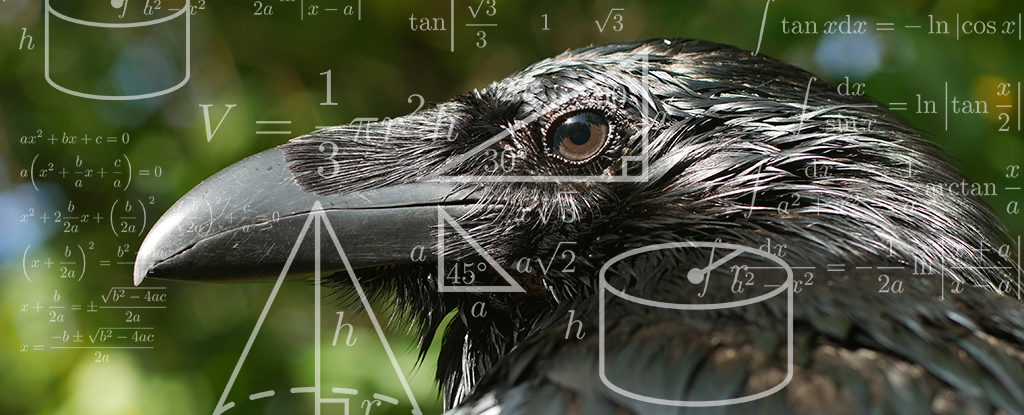
Crows have a sense of geometric intuition much like our own, a new study reveals. The research was published in Science Advances.

Extraterrestrial rocks, recently delivered by a space probe, could answer the big questions about alien lifeforms and human existence

A study by Dr. Matthew S. Taylor, published in the Journal of Osteoarchaeology, reports on the reanalysis of modified human bones discovered at several prehistoric South Texas archaeological sites.
Scientists have cooked up a non-hallucinogenic version of LSD, which they say has “extremely high therapeutic potential” for conditions like schizophrenia.
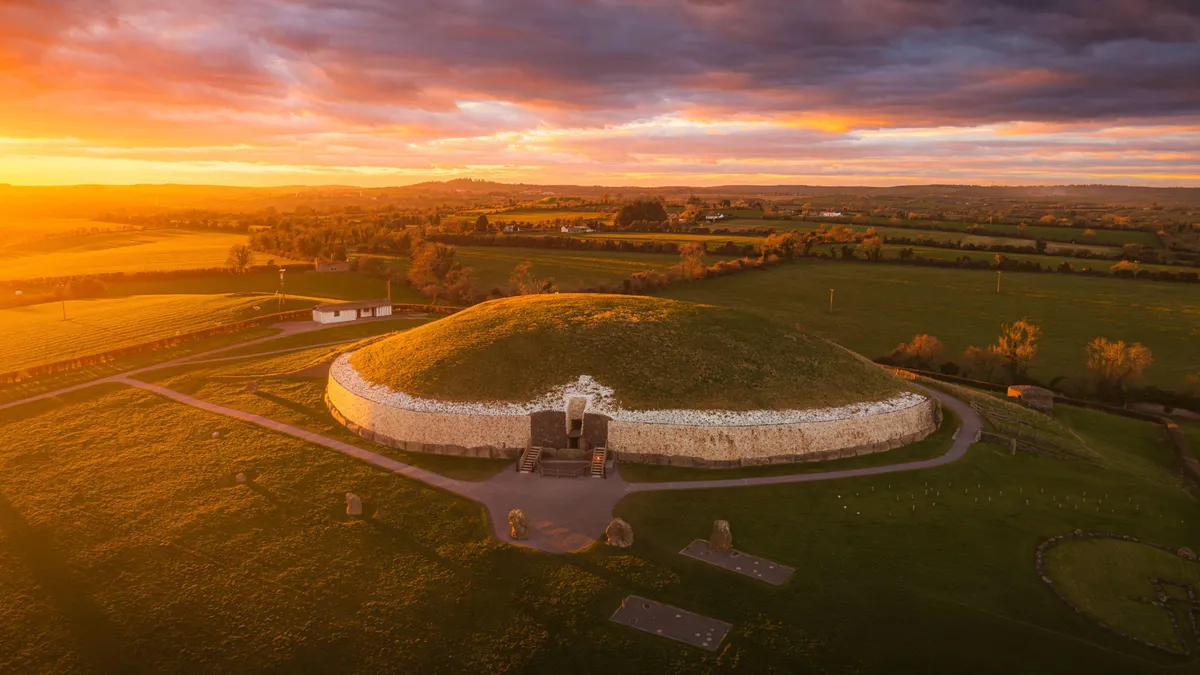

Archaeologists have long assumed that Stone Age tombs in Ireland were built for royalty. But a new analysis of DNA from 55 skeletons found in these 5,000-year-old graves suggests that the tombs were made for the community, not for a ruling dynasty. The study was published April 2 in the Cambridge Archaeological Journal
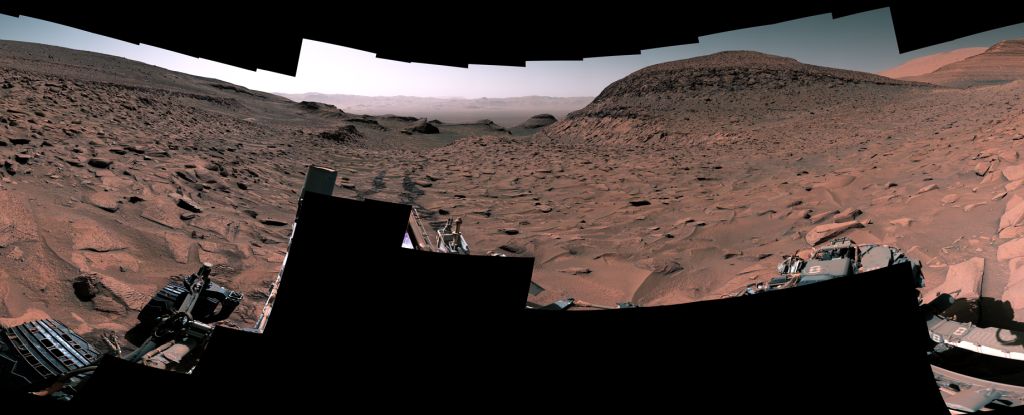

A surprise discovery in Gale Crater is the component that was missing in the puzzle of Mars’s climate history. The findings have been published in Science Advances.
Researchers have revealed the Arabian Peninsula’s green past. Though a desert today, ancient Arabia had lakes and rivers due to high rainfall. Results of the expeditions are published in the Communications Earth & Environment journal.

In a study published in the Journal of Paleolithic Archaeology, researchers analyzed these stone tools and discussed how the different techniques used to make them hint at the ways that prehistoric people traveled, interacted, and shared their craft.
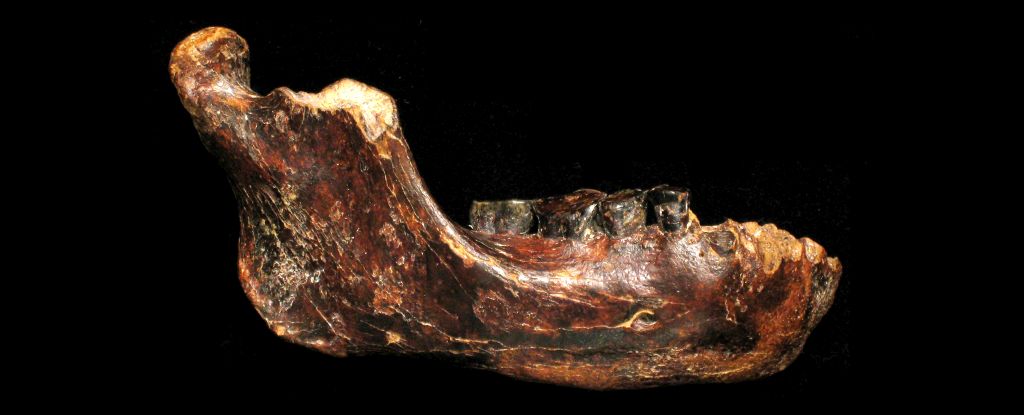
Analysis of a perfect jawbone found in Taiwan has given us new clues to the Denisovans, an enigmatic people with whom our ancestors had relations. The research has been published in Science.

Seafaring hunter-gatherers were accessing remote, small islands such as Malta thousands of years before the arrival of the first farmers, a new international study has found. The findings, “Hunter-gatherer sea voyages extended to remotest Mediterranean islands,” have been published in Nature.
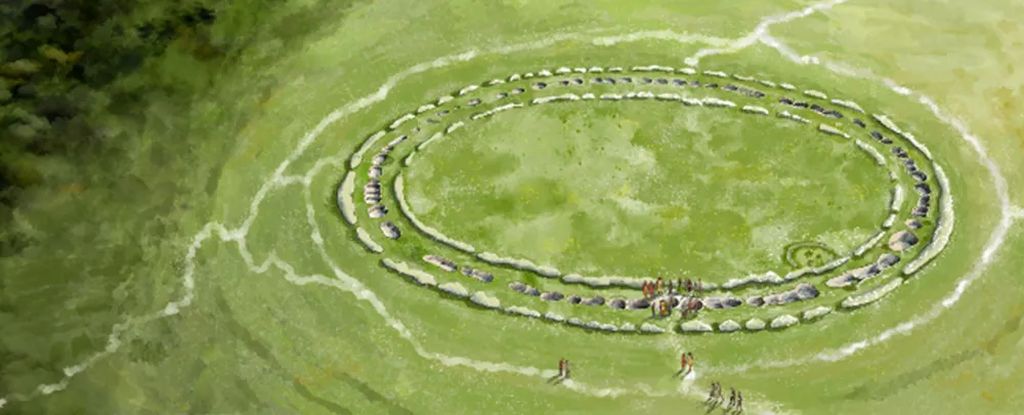

At a newly dated 5,200 years old, the Flagstones monument in southern England is now the oldest known large stone circle in Britain. The research has been published in Antiquity.

Scientists claim they have resurrected the dire wolf using ancient DNA, cloning and gene-editing technology. The species of wolf, which died out some 12,500 years ago, is the “world’s first successfully de-extincted animal”, according to Dallas-based biotech company Colossal Biosciences.








