News Desk
A recent study published in Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging has revealed that psilocybin can induce a state of hyperconnectivity in the brain. This heightened brain connectivity is linked to profound changes in perception and a sense of unity with the universe, which many users describe as mystical experiences.
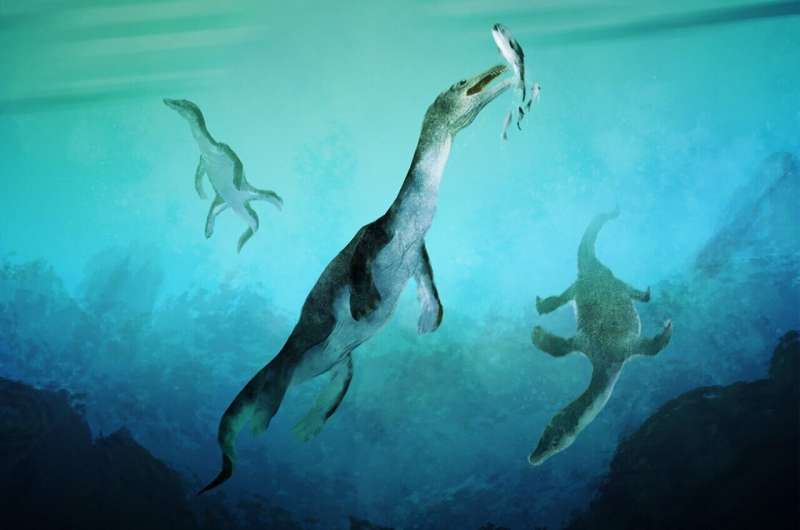

An international team of scientists has identified the oldest fossil of a sea-going reptile from the Southern Hemisphere—a nothosaur vertebra found on New Zealand’s South Island. 246 million years ago, at the beginning of the Age of Dinosaurs, New Zealand was located on the southern polar coast of a vast super-ocean called Panthalassa.
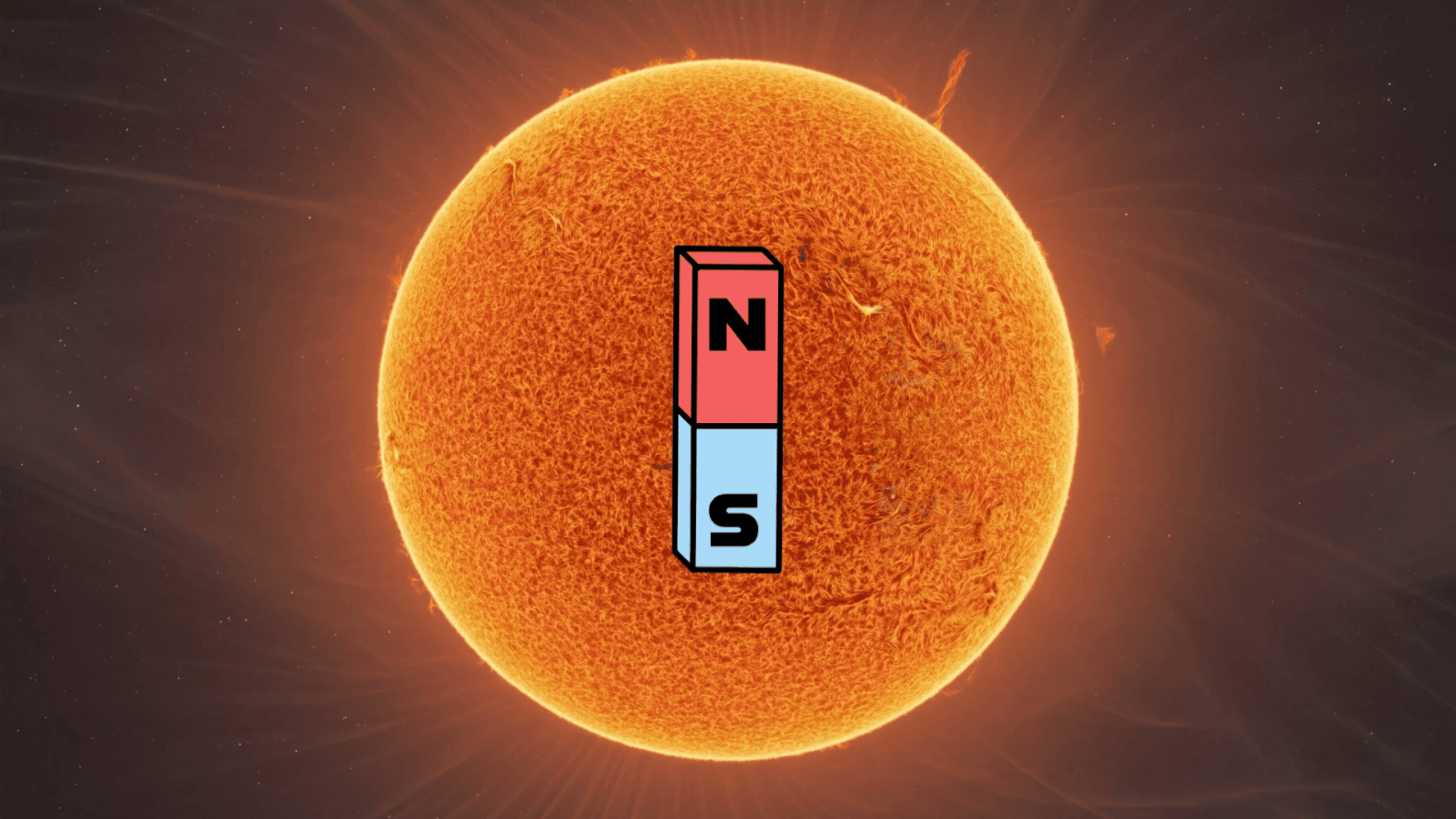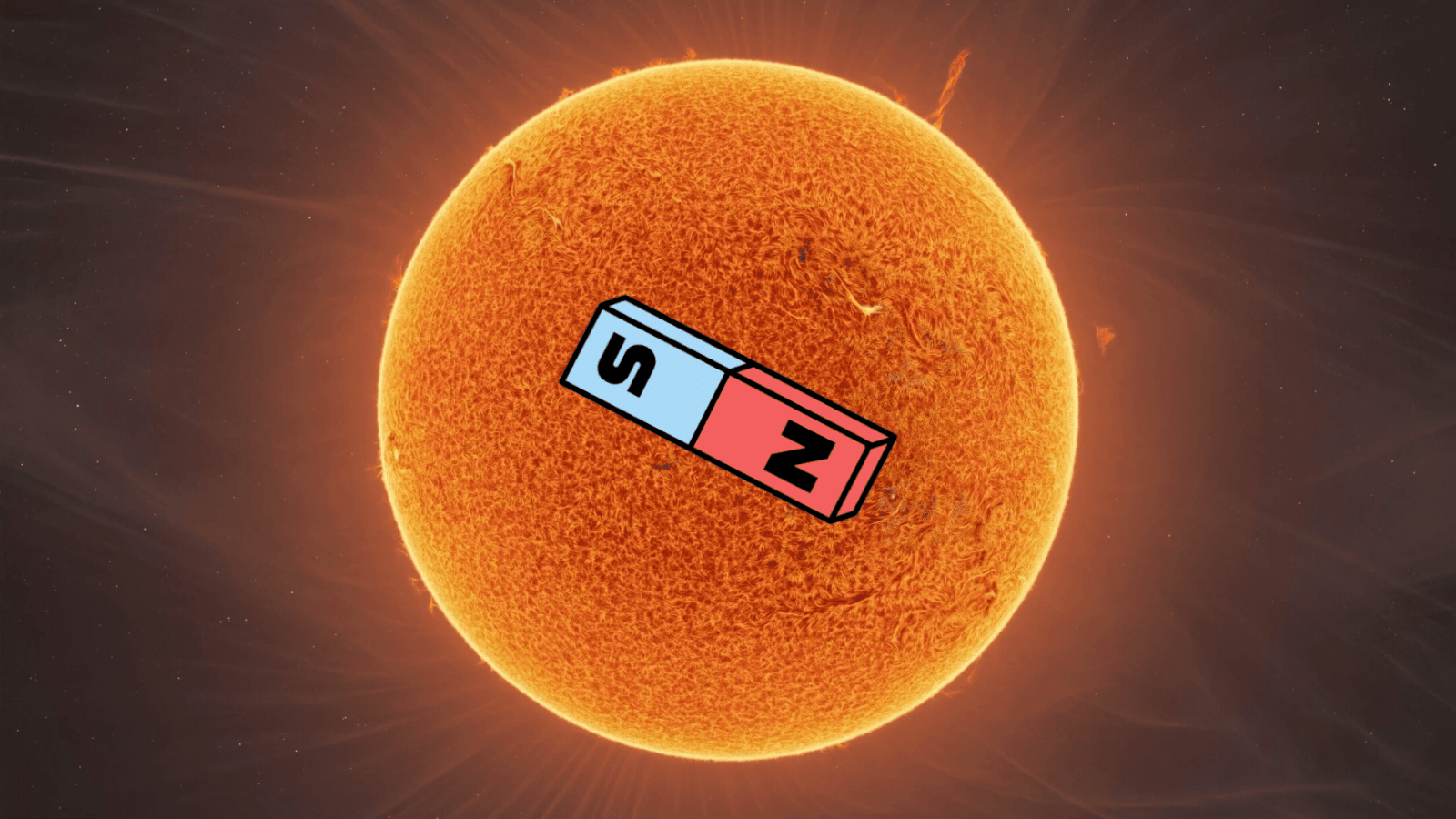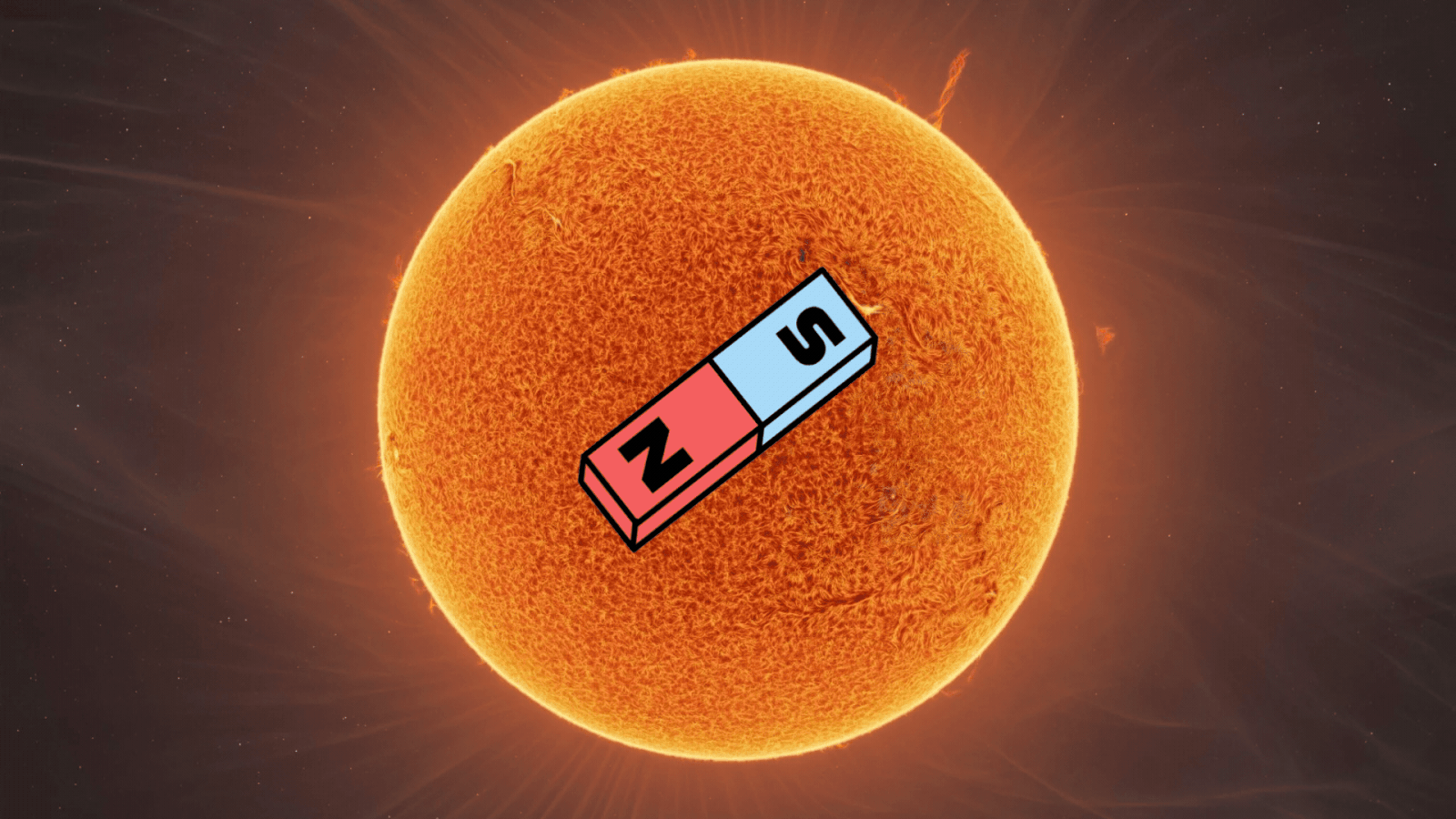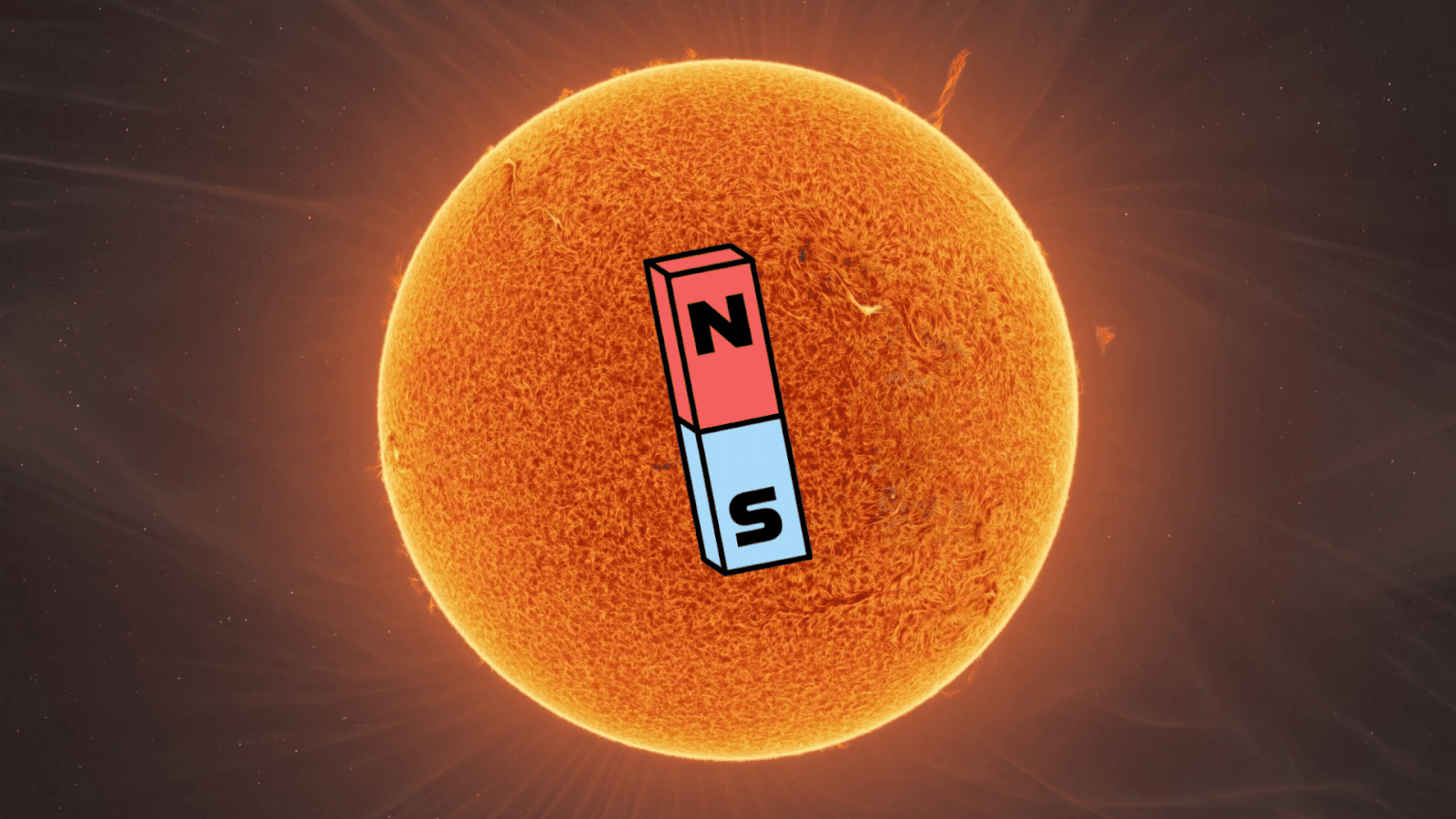
This phenomenon happens roughly every 11 years and marks an important stage in the solar cycle. The shift in polarity indicates the halfway point of solar maximum, the height of solar activity, and the beginning of the shift toward solar minimum.
Older individuals who have used psychedelics tend to exhibit better cognitive functioning and fewer depressive symptoms compared to those who have not, according to new research published in Gerontology & Geriatric Medicine. However, psychedelic usage was not linked to improvements in episodic memory.

Charles Darwin enjoys a near god-like status among scientists for his theory of evolution. But his ideas that animals are conscious in the same way humans are have long been shunned. Until now.
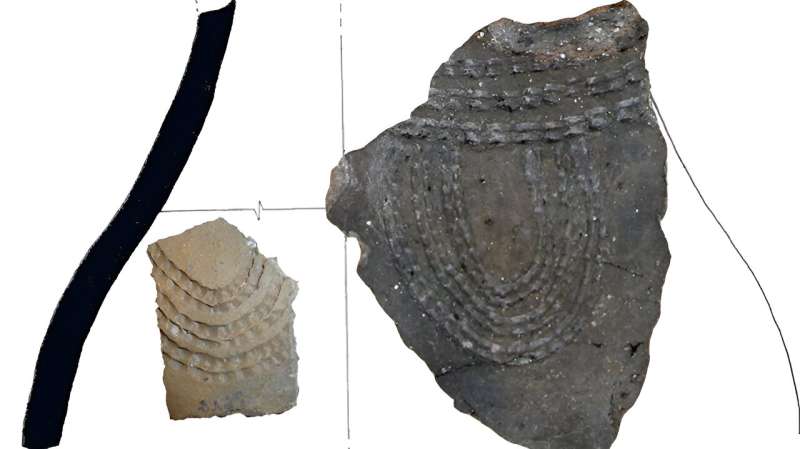

A joint study…yields the first direct proof of the consumption and processing of dairy products in the Pyrenees already at the start of the Neolithic period, approximately 7,500 years ago, as well as the consumption of pig. The results lead to doubts about the belief that these products were first used much later in the Pyrenean mountain range.

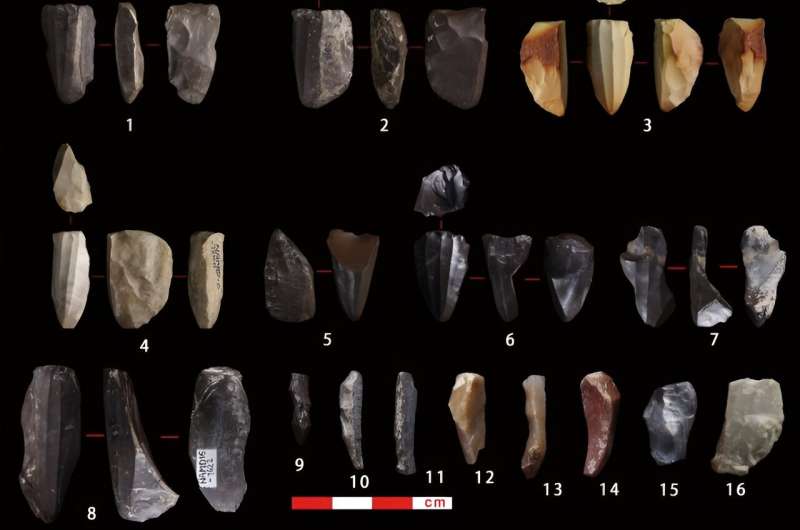
A leap in stone tool complexity in the fossil record suggests hominin knowledge underwent a sudden increase around 600,000 years ago, helping explain how modern humans and our ancestors became expecially proficient at adapting to new environments. This research was published in PNAS.
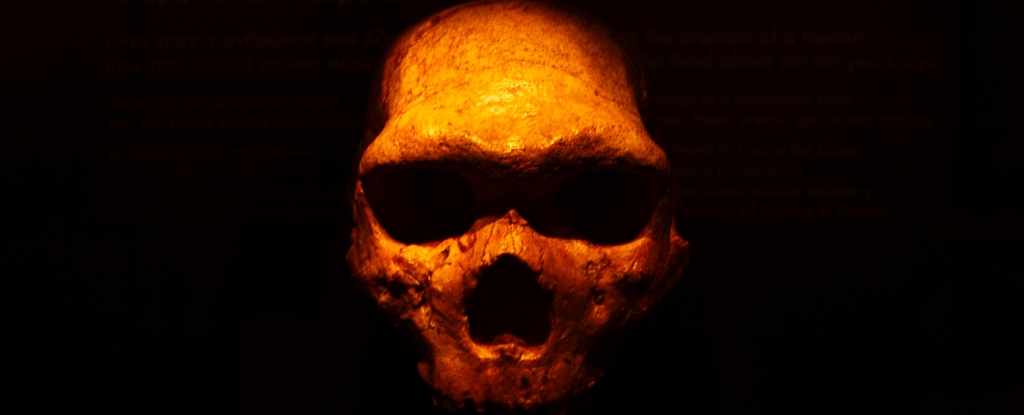
Genetic studies are revealing ever more about the links between modern humans and these long-gone relatives – most recently that a rush of interbreeding between our species occurred in a relatively short burst of time around 47,000 years ago. But one mystery still remains.

Excavation of the layered sediments at Avon Downs reveals a long history of raw stone extraction and tool making. In the short period of our study, we recorded about 1,500 stone artifacts on the surface and under the ground. Details of the findings can be found d here in the newly published research.
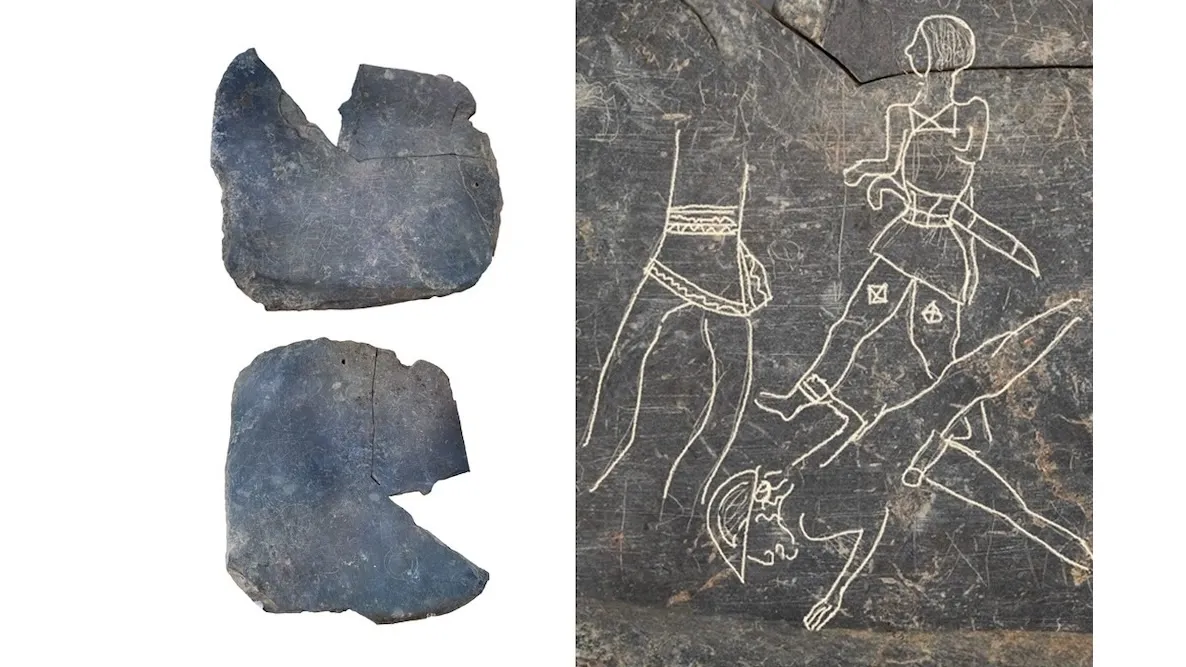

Archaeologists in Spain have discovered a unique tablet containing ancient drawings that depict Tartessian battle scenes and an alphabet.
A recent study published in iScience suggests that psilocybin does not impair learning and may enhance exploratory behavior. The study marks the first investigation into how psilocybin influences reinforcement learning, a type of learning based on rewards and cues.
A research team led by Prof. Zhang Xiaoling from the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology (IVPP), Chinese Academy of Sciences, published a paper entitled “The Earliest Evidence for a Microblade Adaptation in the Remote, High Altitude Regions of the Tibetan Plateau” in Science China Earth Sciences.
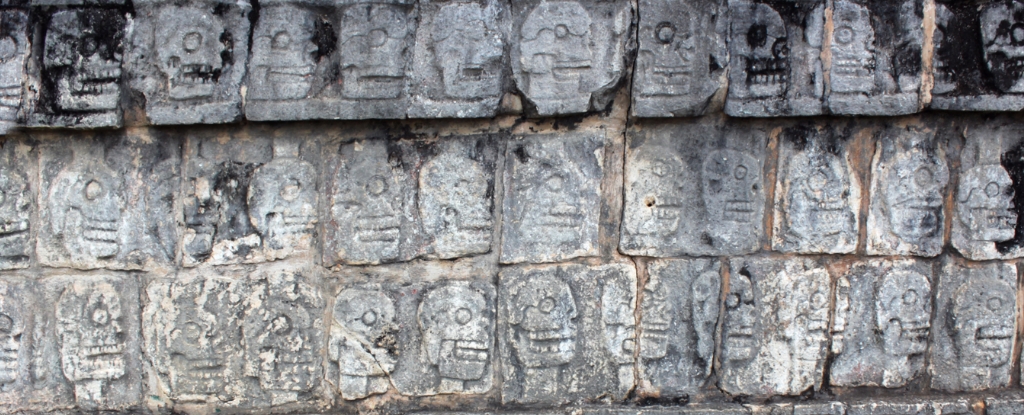

According to a new analysis of ancient DNA led by researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology, the chosen victims have something in common.
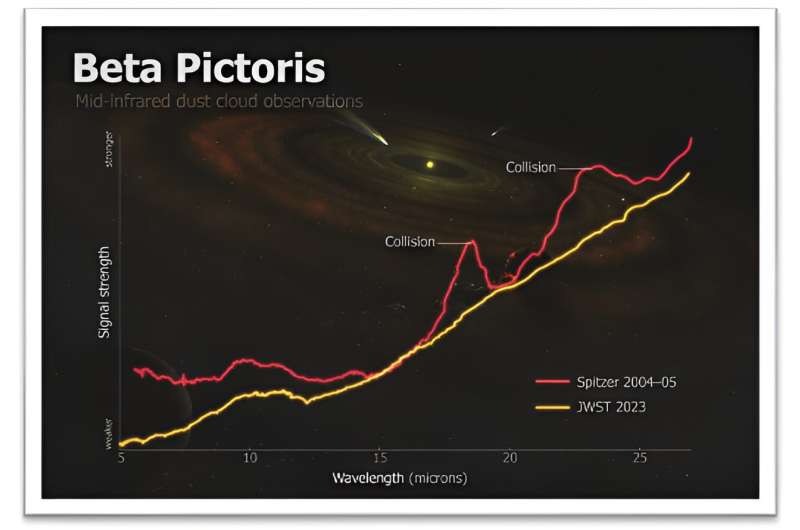
Astronomers have captured what appears to be a snapshot of a massive collision of giant asteroids in Beta Pictoris, a neighboring star system known for its early age and tumultuous planet-forming activity.
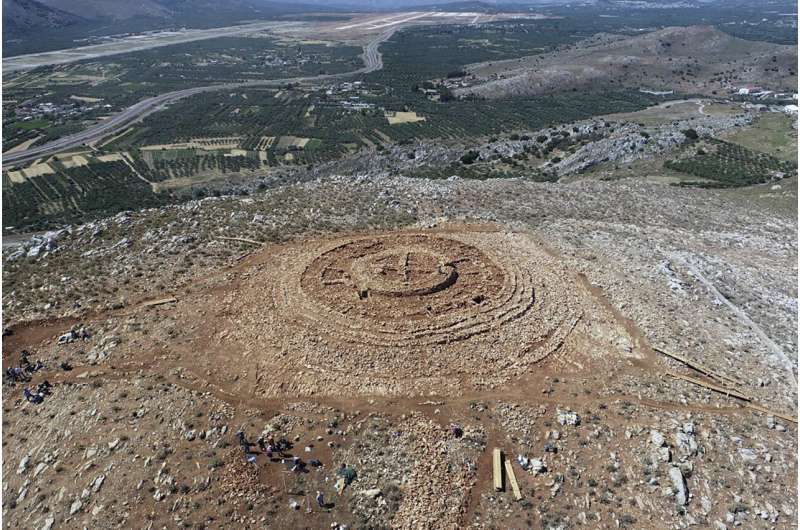

Greece’s Culture Ministry said Tuesday that the structure is a “unique and extremely interesting find” from Crete’s Minoan civilization, famous for its sumptuous palaces, flamboyant art and enigmatic writing system.
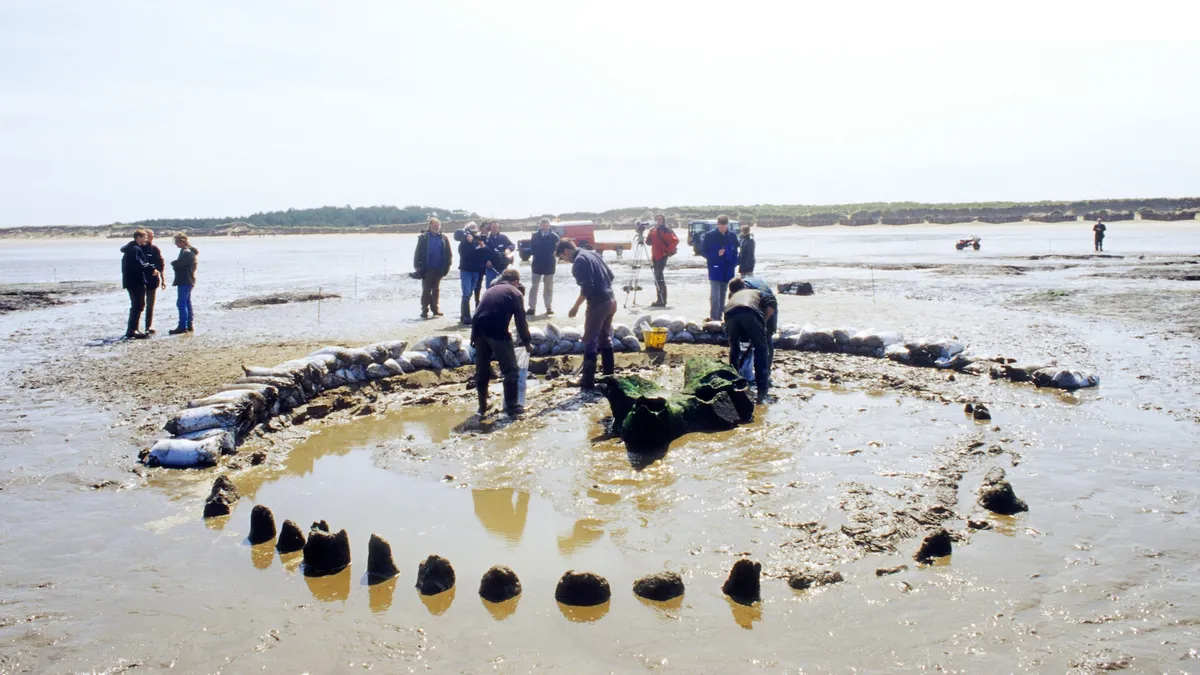

A mysterious Bronze Age wooden circle known as “Seahenge” on England’s east coast was built more than 4,000 years ago in an effort to bring back warmer weather during an extreme cold spell, a new study suggests.








