News Desk

According to the researchers, several symbols engraved on stone “cylinder seals” were developed into signs used in “proto-cuneiform,” an early version of the cuneiform script used in southern Mesopotamia, now southern Iraq. The researchers reported their findings in a study published Tuesday (Nov. 5) in the journal Antiquity.
A recent study published in AJOB Neuroscience found that a majority of Americans support psilocybin, a psychedelic compound from certain mushrooms, for supervised medical treatment and well-being enhancement. This strong bipartisan approval highlights public openness to legalized and controlled use of the drug for both medical and personal enhancement purposes, though with caution for future policy.

Scientists say there has been an alarming lack of progress in saving nature as the UN biodiversity summit, COP 16, draws to a close…Representatives of 196 countries have been meeting in Cali, Colombia, to agree on how to halt nature decline by 2030.

The devastation of a giant meteorite impact on early Earth may have allowed life to flourish, new research suggests. The study was published Oct. 21 in the journal PNAS.
The region is known as one of the earliest places people practiced animal husbandry. The new study adds insight into how this developed. The study, published in Nature, spans nearly 6,000 years of genetic data in the region.

Prehistoric Polynesian seafarers were highly skilled and undertook some of the longest and most technically demanding voyages in prehistory—but did they ever sail into very high latitudes with landfall in Antarctica, as some scholars have argued? An international team of archaeologists and paleoecologists seeking an answer to this question…Their study is published in the journal Archaeology in Oceania.

A small 4,400-year-old town in the Khaybar Oasis of Saudi Arabia hints that Bronze Age people in this region were slow to urbanize, unlike their contemporaries in Egypt and Mesopotamia, finds a new study published Wednesday (Oct. 30) in the journal PLOS One.
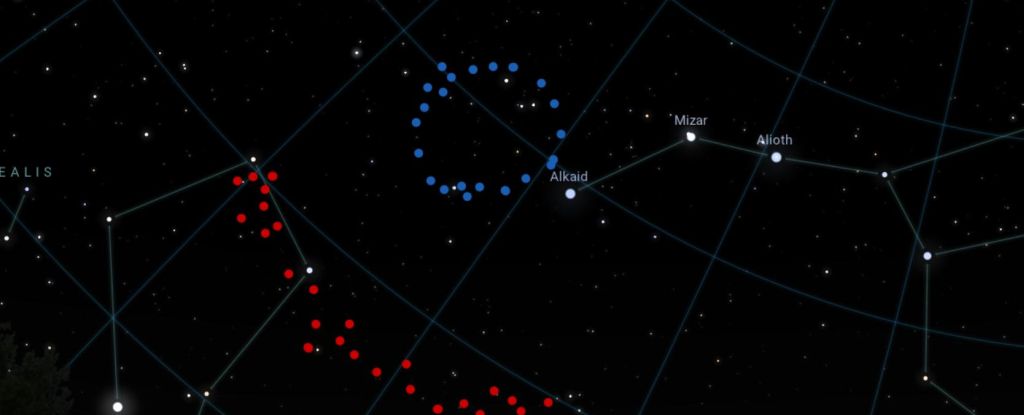
The discovery, led by astronomer Alexia Lopez of the University of Central Lancashire, was presented at the 243rd meeting of the American Astronomical Society in January, and has been published in the Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics.
Scientists have been trying to figure out where kissing came from for a long time. New research suggests that the answer is to be found in the behaviour of ancient ape ancestors of humans…

A study published in L’Anthropologie by Professor Ella Been from Ono Academic College and Dr. Omry Barzilai from the University of Haifa sheds new light on the burial practices of Homo sapiens and Neanderthals in the Levant region during the Middle Paleolithic (MP).

The city contains up to 6,674 structures, including pyramids like the ones at Chichén Itzá and Tikal, according to a study published Tuesday (Oct. 29) in the journal Antiquity. The researchers used previously created lidar (light detection and ranging) maps, which are created by shooting laser pulses at the ground, to reveal the potentially 1,500-year-old site.

According to a new study published in the journal Fungal Ecology, fungi may have their own unique measure of intelligence, making them capable of basic shape recognition and decision-making throughout the networks they build.
Palaeontologists studying fossils of corals and algae from 385 million years ago have found a symbiotic relationship between the organisms today was present in the ancient past as well. The research was published in Nature.

A new study published in iScience on October 25 describes how researchers used ancient DNA to corroborate the events of the saga and discover details about the “Well-man,” blending history and archaeology with science and setting a precedent for future research on historical figures.
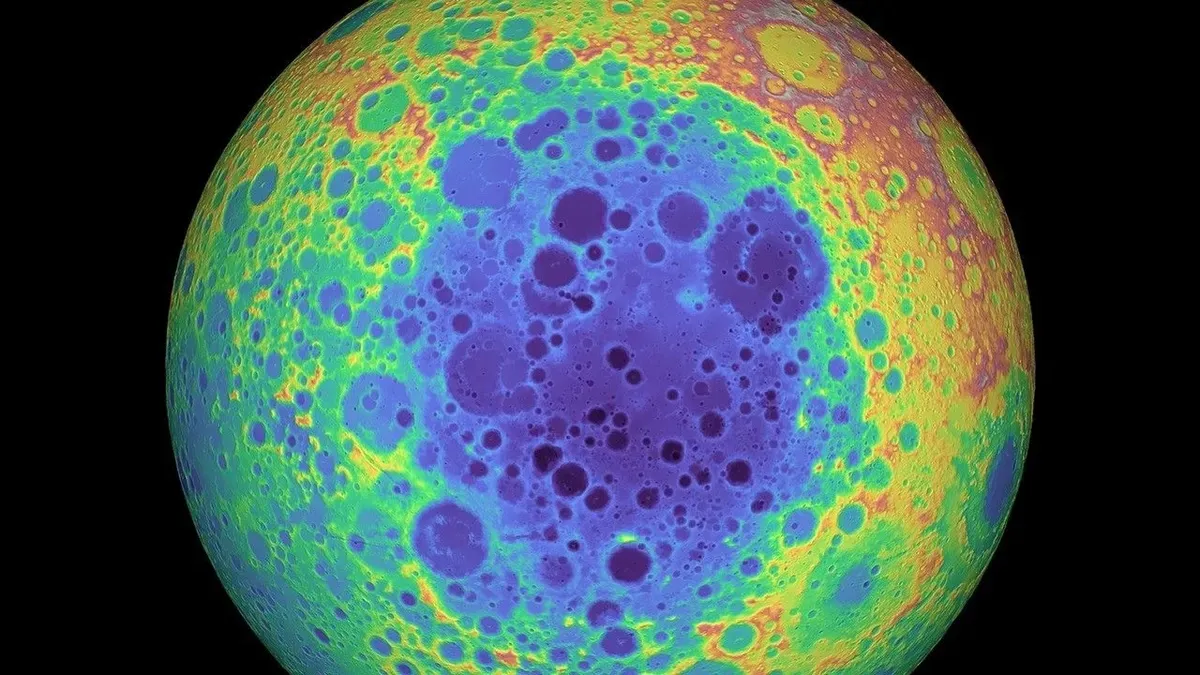
The largest and oldest-known impact site on the moon is the South Pole-Aitken basin. Thanks to new research, scientists have dated the basin to the period between 4.32 and 4.33 billion years ago.

‘Bricks’ of DNA, some of which have chemical tags, could one day be an alternative to storing information electronically.








