News Desk
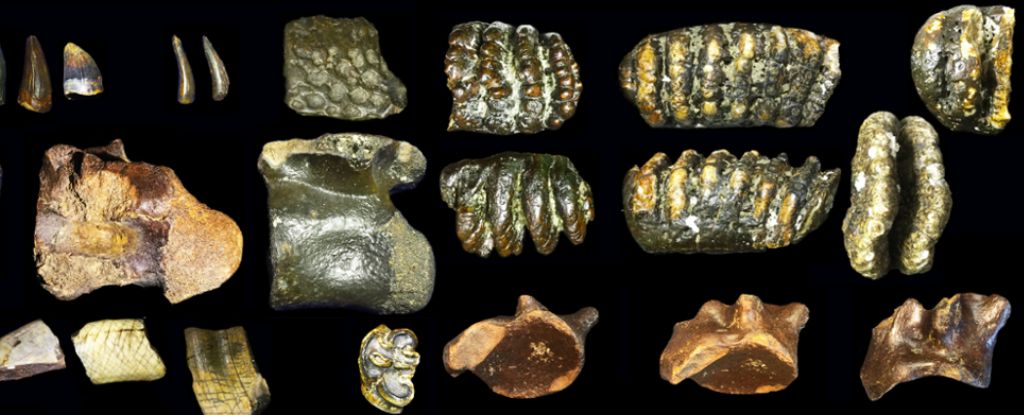
Better understanding species distribution through time could help determine why the megafauna vanished between 50,000 and 10,000 years ago. This in turn could give crucial insight into prehistoric ecosystems and help understand and even prevent future extinctions.
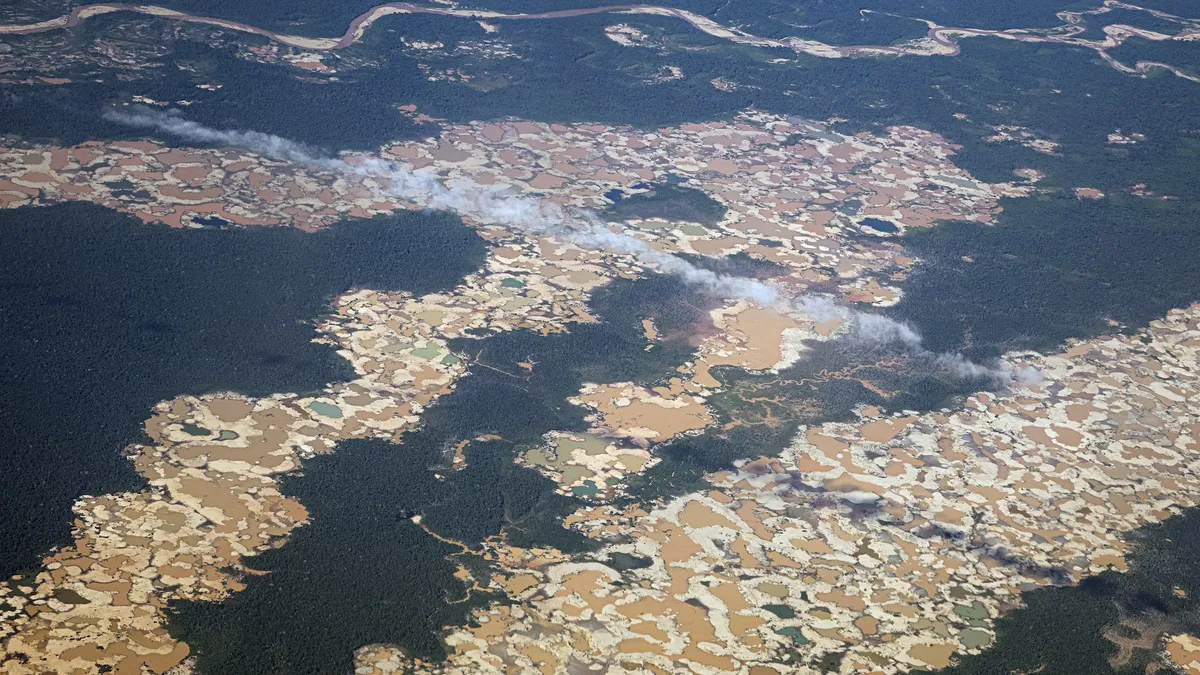

Gold mining is literally sucking the Amazon rainforest dry, creating an environment where trees cannot grow, according to a new study.
A significant fossil puzzle piece in the evolution of the first vertebrate animals to leave Earth’s ancient seas and walked on land was discovered in Scotland more than 40 years ago. But it has only just been accurately aged—and the results have left palaeontologists stunned. The results are published in the journal PLOS One.
The new study published in the journal Geoarchaeology shows that geophysical imaging methods can be useful to find other artefacts in open air sites outside caves and rock shelters.

Recent genetic analysis of seven individuals from the area, including a potential royal and a sacrificial burial, revealed that the people of classic Copán had genetic similarities with late archaic (5,600–3,700 years ago) populations, later Maya groups, and modern Maya communities in Mexico. This study published in Current Biology found signs of a dramatic decline—but not complete disappearance—of the Maya population.
DNA records reveal a fascinating timeline, including the existence of an ancient population with genetics unrelated to any modern descendants – a group of people who may have been some of the earliest settlers in South America, but who subsequently disappeared completely. The research has been published in Science Advances.
Pacific island researchers believe that ceremonial drinking of kava—a plant-based beverage with calming properties— combined with talanoa, a form of open, respectful dialogue, can offer relief to people with PTSD, especially those who haven’t responded well to conventional treatments. They have published their work in Frontiers of Psychology.

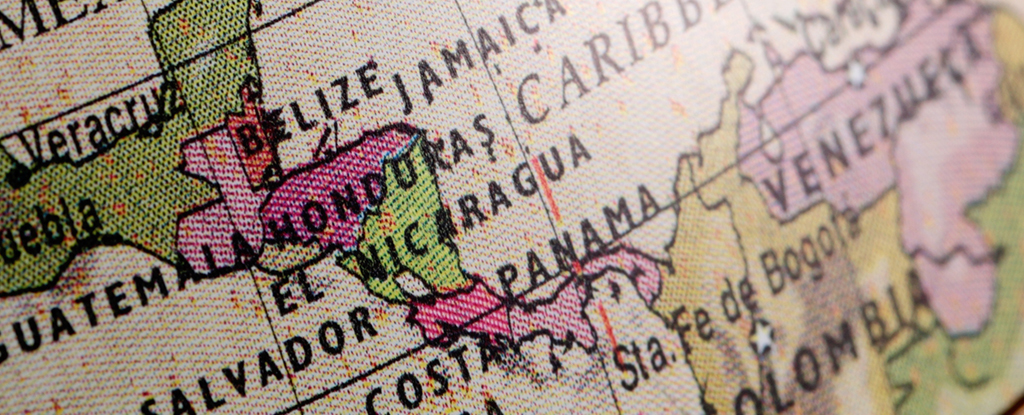
Scientists have identified a new pod of ancient hunter-gatherers who lived near the land bridge between North America and South America about 6,000 years ago. The new study was published Wednesday in the journal Science Advances.
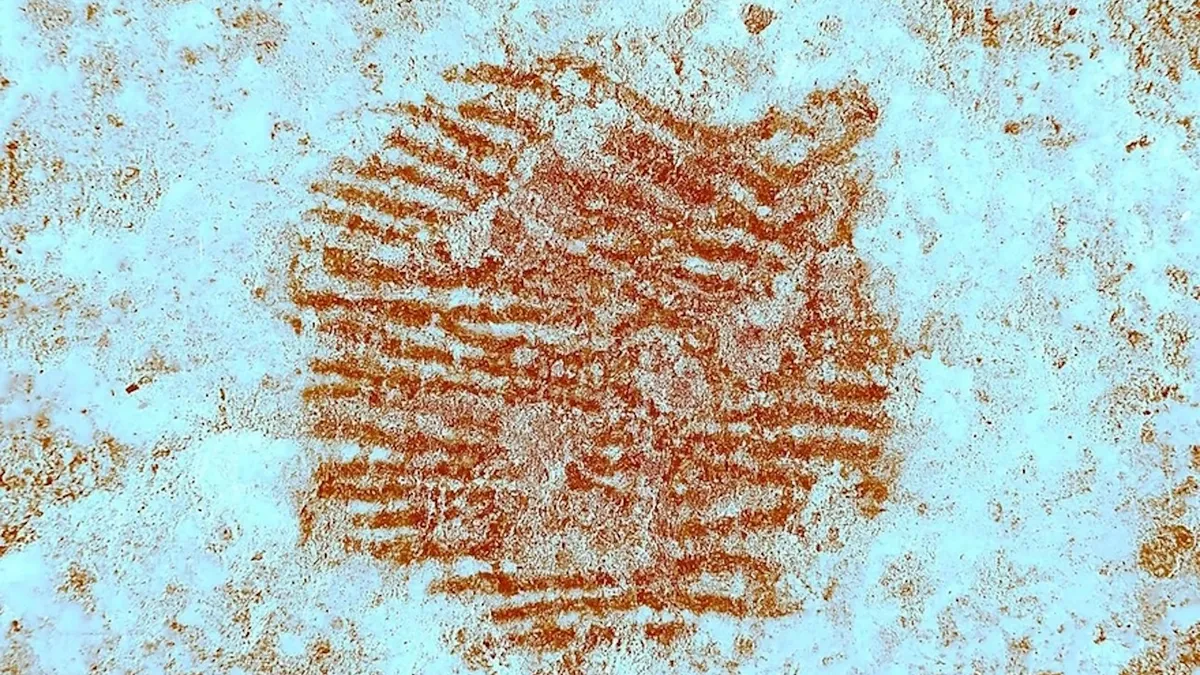

The discovery of a 43,000-year-old fingerprint in Spain is challenging the idea that Neanderthals were not capable of symbolic art.
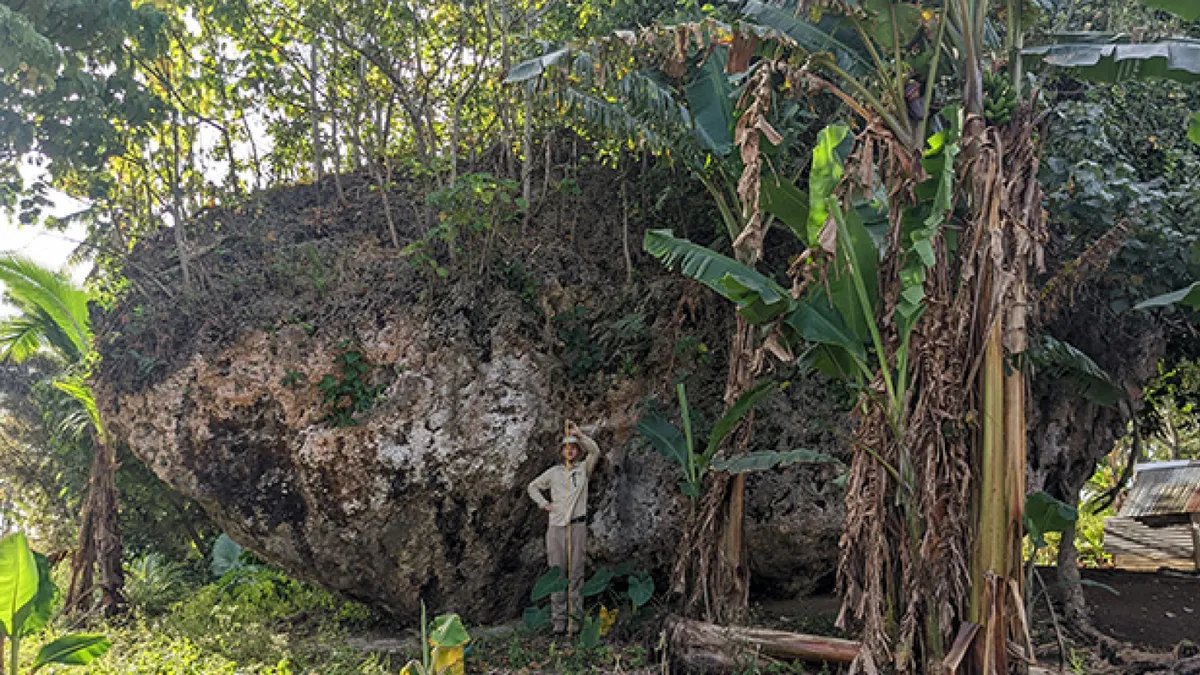

According to a new study published online on 21 April in the journal Marine Geology, the boulder — named Maka Lahi, which is Tongan for “big rock” — may have been deposited in its unlikely home by a huge tsunami that struck the island around 7,000 years ago.
A new study published in Molecular Psychiatry provides preliminary evidence that cannabidiol, a compound derived from cannabis, may reduce cognitive decline and brain pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease.

Data and findings are not always shared openly in science. Sometimes, researchers hoard those data and provide little to no access to colleagues from their field…The so-called “Gollum effect” hampers collaborations and harms the careers of less established researchers, claims the team.Their results are published in the journal One Earth.

A recent study by Dr. Georges Mouamar and his colleagues investigated the largest assemblage of securely identified rattles in the Near East. The findings are published in the journal Childhood in the Past.

New research published in Communications Biology has uncovered the earliest known use of the medicinal and psychoactive plant Peganum harmala, commonly known as Syrian rue or harmal, in fumigation practices and inhaled as smoke.
New research into the hand structures of different ancient human relatives found in modern South Africa reveals varying levels of dexterity and climbing ability, offering new clues into the evolution of humans.









