Humans news stories
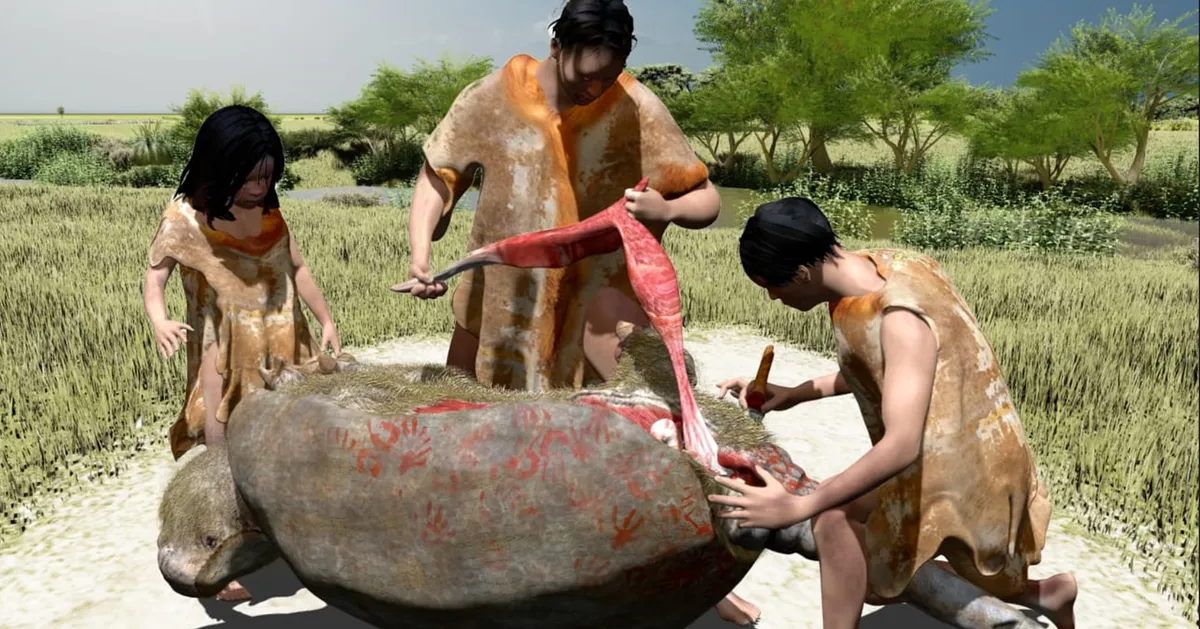

The discovery of butchered bones belonging to a glyptodont, a giant relative of the armadillo, suggests that humans were living in Argentina 20,000 years ago. See the study here.
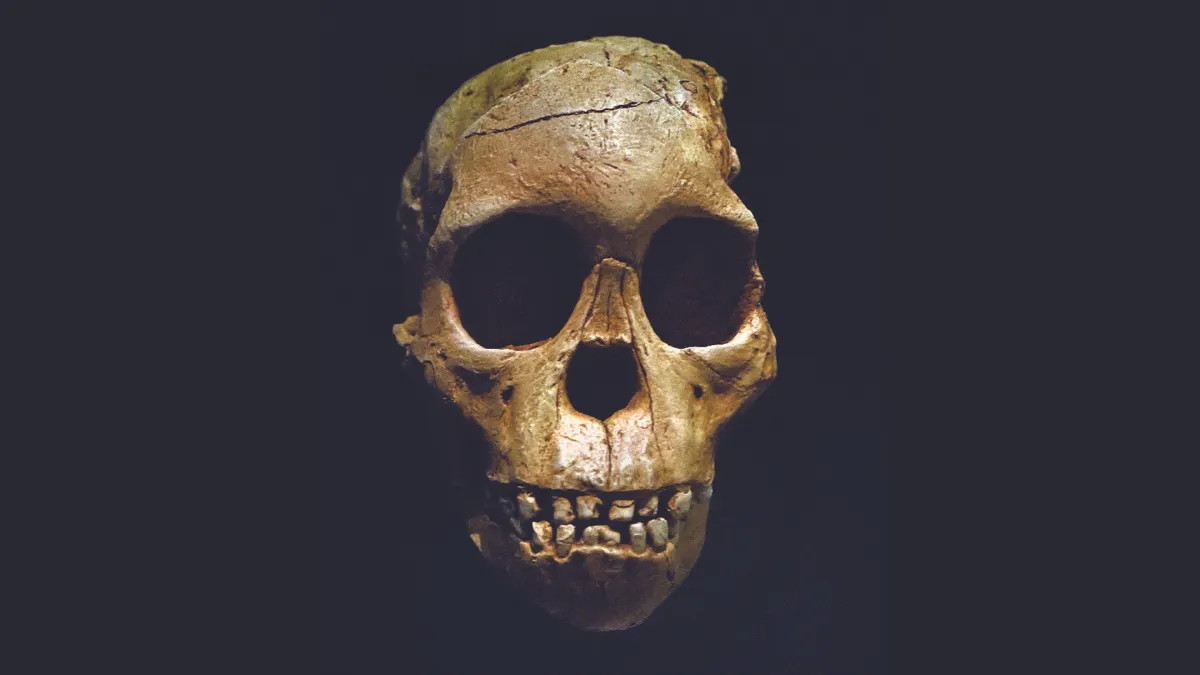

A new study examines fossil teeth of the Taung Child to hone in on its age…In the century since the Taung Child was found and described, a great debate has developed about the geological ages of the Australopithecus fossils found at Sterkfontein as well as those from Taung and a third site, Makapansgat.

In 2029, an asteroid larger than the Eiffel Tower will skim past Earth in an event that until recently scientists had feared could foreshadow a catastrophic collision. Now, researchers hope to scrutinise 99942 Apophis as it makes its close encounter in an effort to bolster our defences against other space rocks
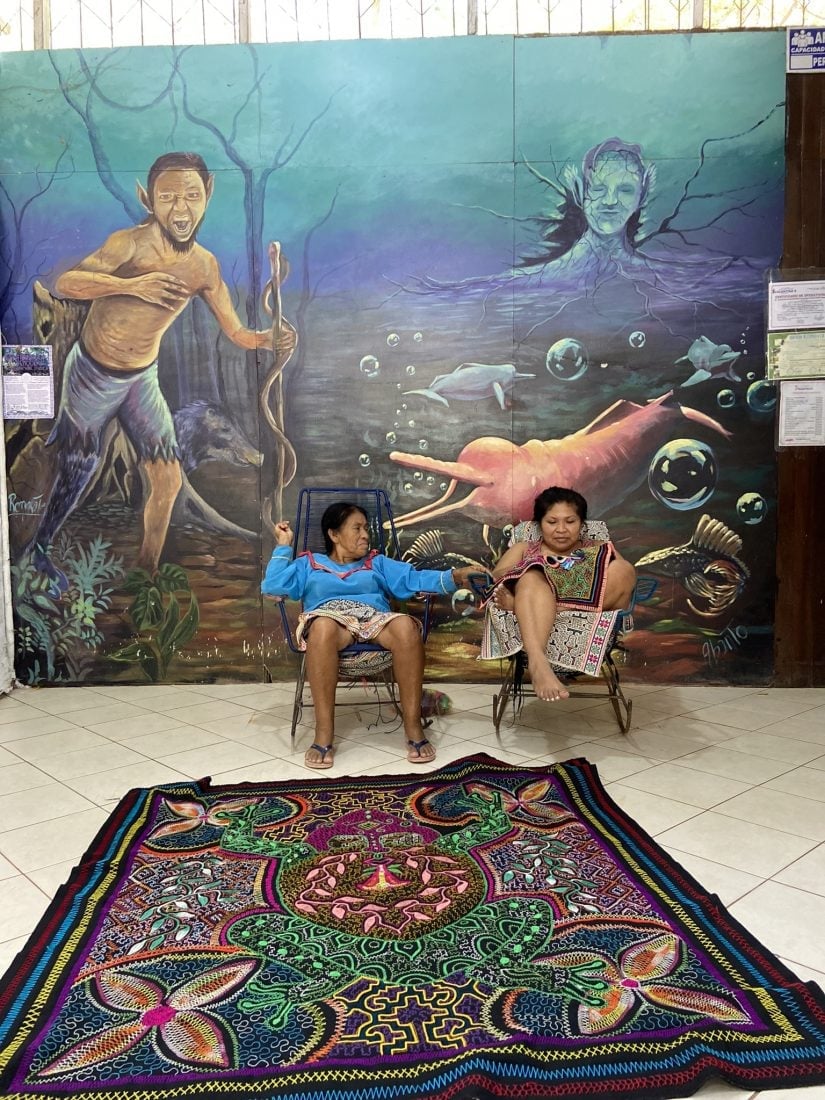

Indigenous leaders denounce a “spiritual extractivism” of the psychedelic plant taking place and warn about the impacts of its exploitation on the forest and traditional knowledge.

The hunt for alien civilisations may be entering a new era, researchers believe. Scientists with Breakthrough Listen, the world’s largest scientific research programme dedicated to finding alien civilisations, say a host of technological developments are about to transform the search for intelligent life in the cosmos.
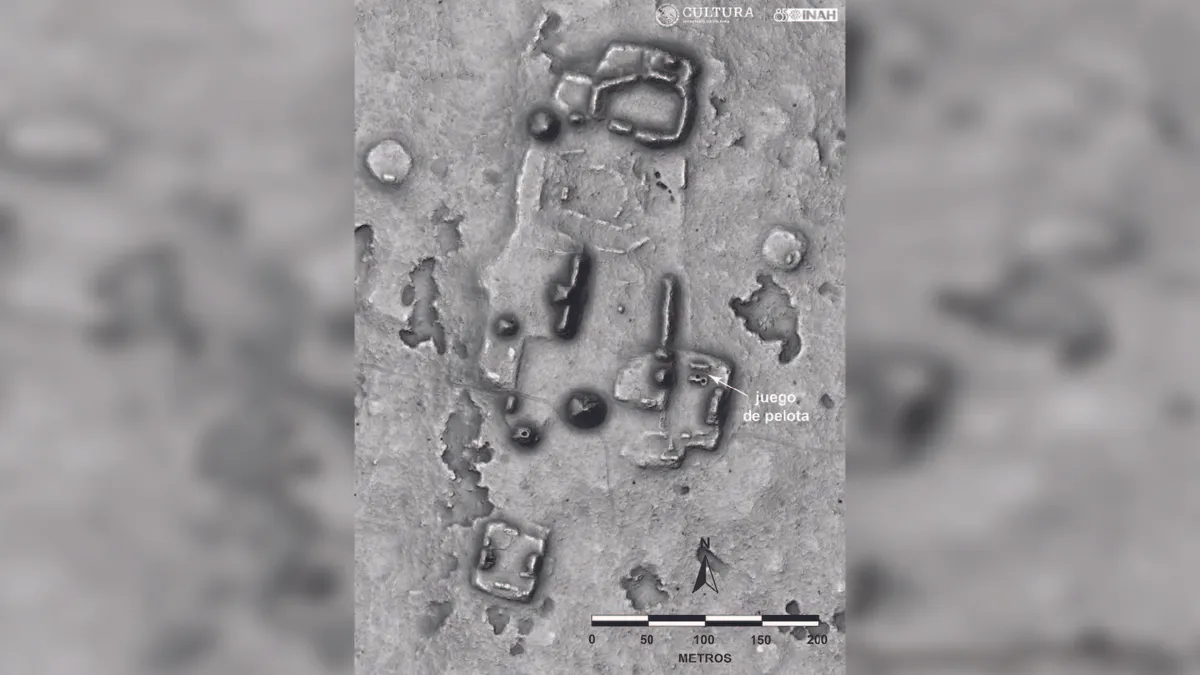

Archaeologists in Campeche, Mexico, have found an underground structure beneath a Maya ball court, as well as offerings on top of a Maya pyramid at another site.
In a new study published in the journal Molecular Psychiatry, scientists have used sophisticated imaging techniques to explore the neural underpinnings of these eyes-closed visual experiences, offering new insights into visual perception and imagery.

Archaeologists have uncovered one of the earliest Christian buildings in the Arabian Gulf—the first physical evidence of a long-lost community.
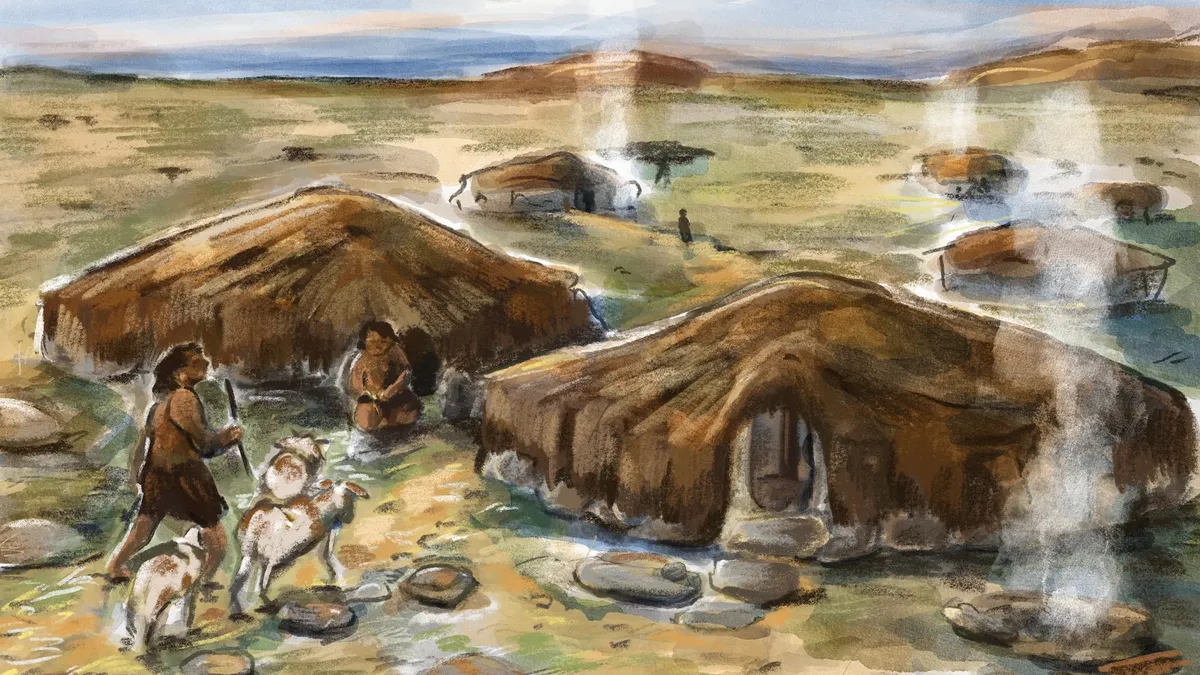

Archaeologists in Saudi Arabia have excavated eight ancient “standing stone circles” that they say were used as homes. About 345 of these structures were identified through aerial surveys across the Harrat ‘Uwayrid, a lava field near the city of AlUla in northwestern Saudi Arabia, the team reported July 2 in the journal Levant.

A study led by researchers from the UAB and the CSIC has revealed that the earliest Neolithic groups to settle some 7,000 years ago in the Pyrenean site of Coro Trasito (Tella, Huesca) used species selection strategies to manufacture their tools made out of bone and chose deer for the projectile tips.
Neanderthals and modern humans had a fascinatingly intertwined past. We know, from studies of our own DNA, that when the paths of the two species crossed, things could get more than a little steamy. The research has been published in Science.

This year, the famous festival Hayes Pavilion showcased seaweed bioplastic, proving biomaterials can create functional, sustainable structures for events and inspire eco-conscious design.
A recent study on mice found that administering cannabidiol helped extinguish the preference for cocaine. It also restored gut microbiota diversity disrupted by cocaine. The research was published in Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry.

This, the team says, opens up a new way to explore the properties of time crystals, as well as phenomena such as quantum fluctuations, correlation, and synchronization – an important factor in designing quantum computers.

Utilizing the in-house developed ArchCUT3-D software, which allows a computational analysis of the three dimensional traits of rock engravings, the research showcases an innovative approach that provides new insights into the production processes and cultural significance of engravings found in Timna Park, southern Israel.
Because of the dramatic shifts in the global climate which led to the thawing at the end of the Ice Age, many scientists have argued that climate change must have been the primary driver of the megafauna extinctions…the authors of the new study say that the climatic impacts can’t account for the scope of the megafauna losses.








