Humans news stories
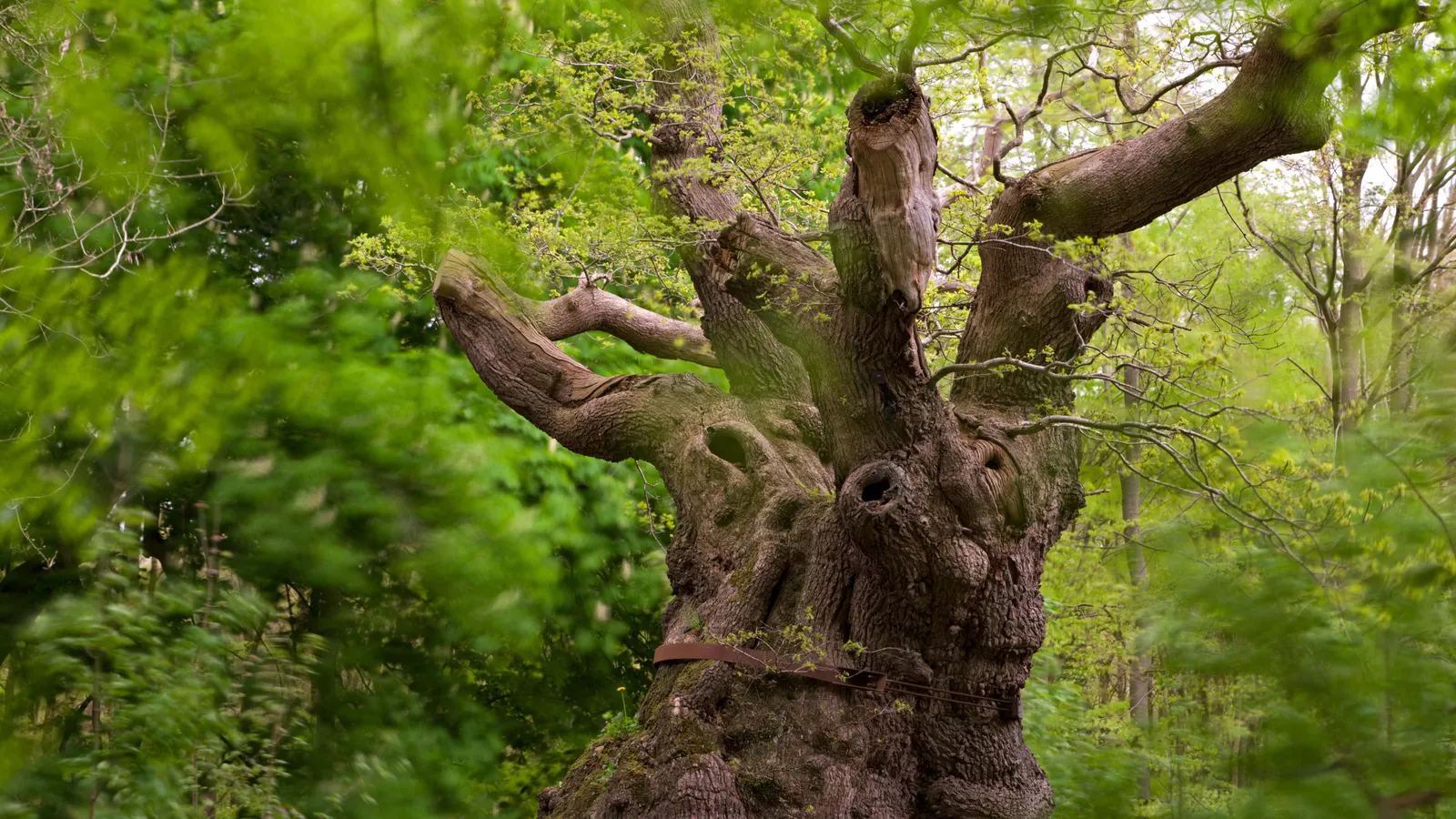

Inside some of our most magnificent trees, miniature worlds are at risk of extinction. The race is on to accelerate trees’ ageing process, so these intricate communities aren’t lost forever

Right now, a spacecraft is carrying a very special delivery to Earth after a years-long voyage to a cosmic destination that can shed light on how life might have first emerged on our planet and how we can protect it from future cosmic hazards.
Image from: asteroidmission.org (Wiki Commons)
The ability of the mind to generate the symptoms of illness is known as the “nocebo” effect. The nocebo effect is the unpopular twin brother of the placebo effect. Whereas the placebo effect alleviates pain and the symptoms of illness, the nocebo effect does the opposite: it generates pain and symptoms.
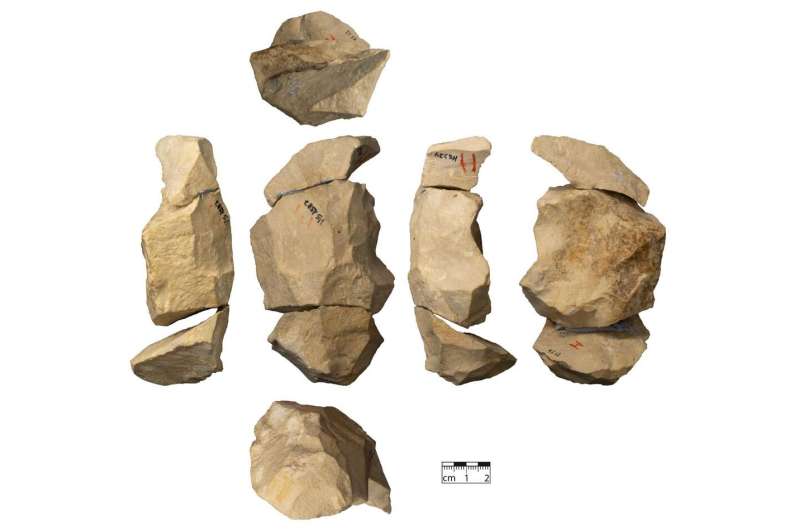

Neanderthals living in the Swabian Jura more than 45,000 years ago used sophisticated techniques with many different production strategies to make stone tools.

The growing legitimacy of psychedelics as therapies promises to transform how we view the extraordinary.

Prof Paul Davies suggests viruses may form vital part of ecosystems on other planets.

A billion years have vanished from the geological record – and over 152 years after this was first discovered, scientists can’t agree on why.
Genetic “dark matter” may drive the emergence of new species, new research finds.
The new research establishes northern Arabia as a critical migration pathway in the storied history of our species.
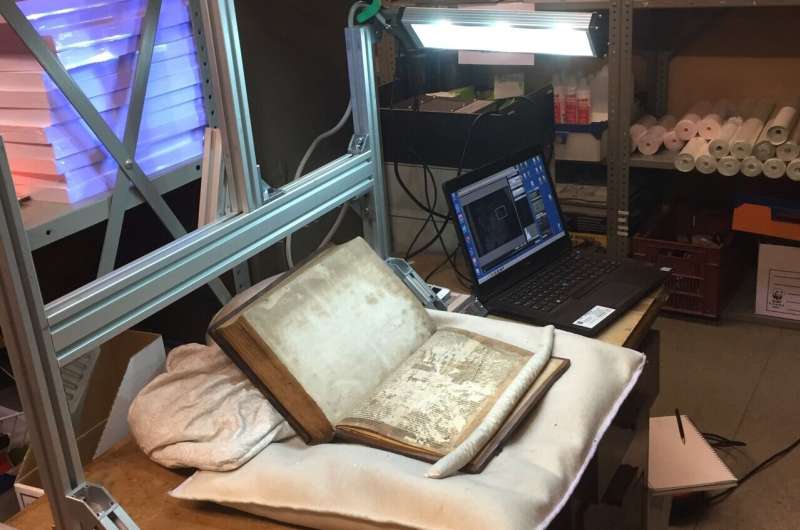

Medieval manuscript fragments discovered in Bristol that tell part of the story of Merlin the magician, one of the most famous characters from Arthurian legend, have been identified by academics from the Universities of Bristol and Durham as some of the earliest surviving examples of that section of the narrative.
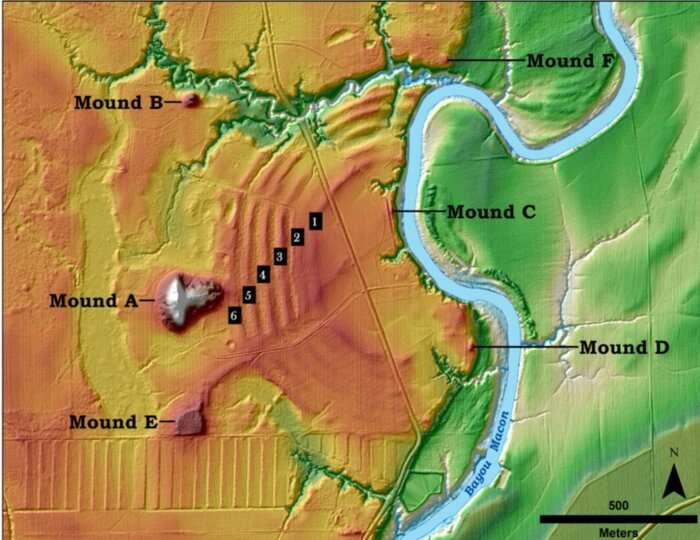
The Native Americans who occupied the area known as Poverty Point in northern Louisiana more than 3,000 years ago long have been believed to be simple hunters and gatherers. But new Washington University in St. Louis archaeological findings paint a drastically different picture of America’s first civilization.
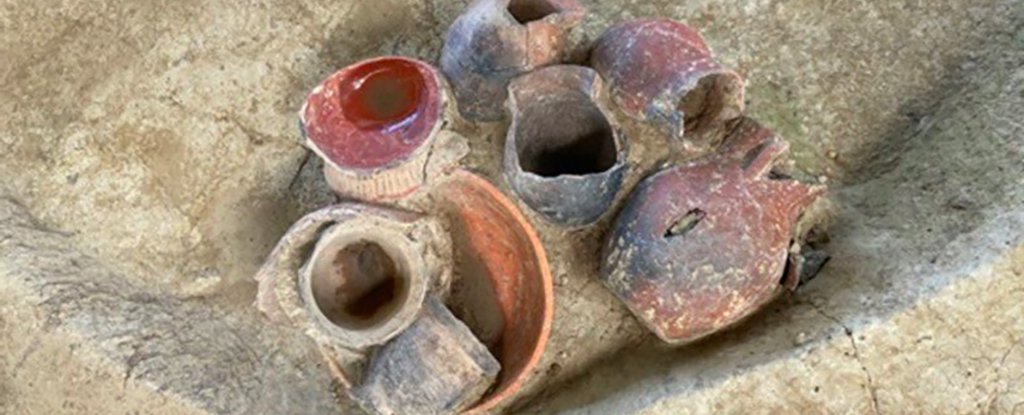

Archaeologists have discovered some of the oldest artifacts ever found to be associated with beer, in a haul from Qiaotou in southern China dating back 9,000 years. However, it appears the ancient drinkers in question weren’t in it simply for a buzz.
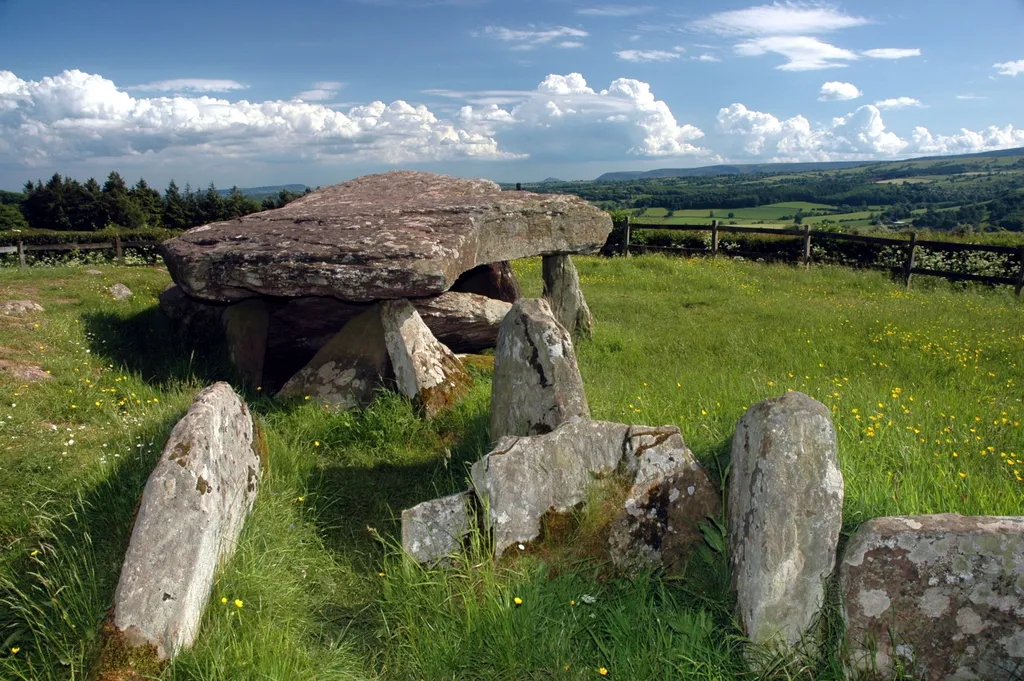

A mysterious stone tomb in western England — known as Arthur’s Stone because of its links to the mythical King Arthur — originated almost 6,000 years ago as part of an elaborate “ceremonial landscape” across the whole area, according to archaeologists.
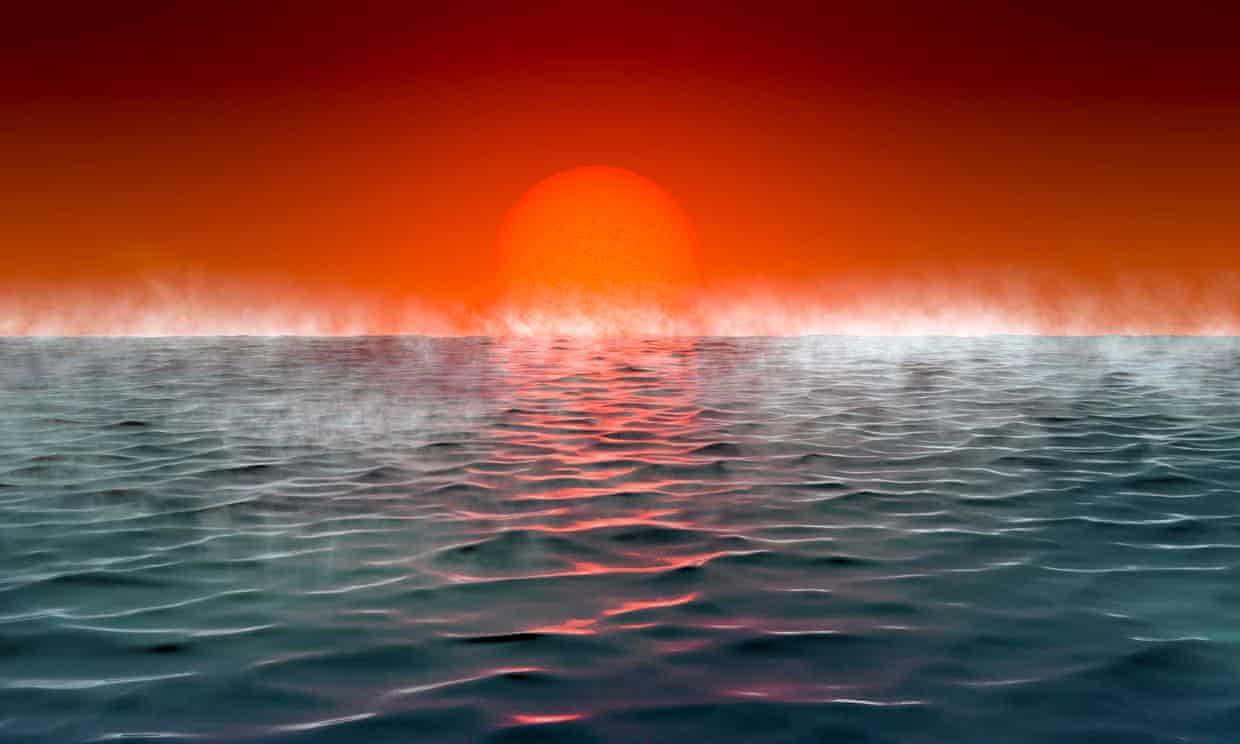

Cambridge astronomers identify new hycean class of habitable exoplanets, which could accelerate search for life.
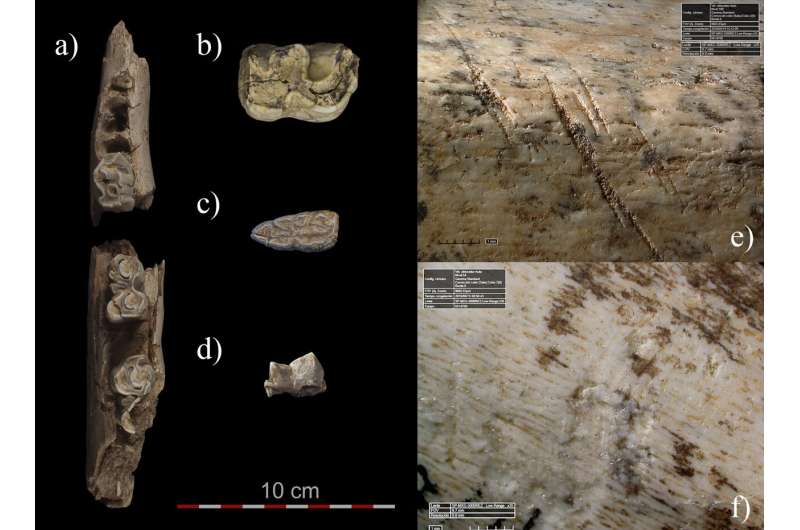

Abel Moclán, a researcher at the Centro Nacional de Investigación sobre la Evolución Humana (CENIEH), is the lead author of a paper published in the journal Quaternary Science Reviews which undertook a zooarchaeological and taphonomic study of the Neanderthal Navalmaíllo Rock Shelter site (Pinilla del Valle, Madrid), some 76,000 years old, whose results indicate that these Neanderthals mainly hunted large bovids and cervids.
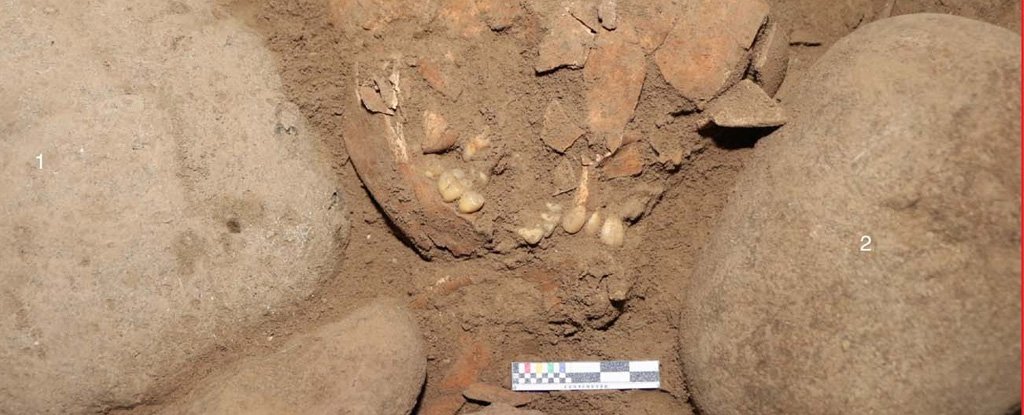

The skeleton of an ancient woman, discovered in an Indonesian cave in 2015, appears to have ancestry unlike any other human found to date.








