Animal Life news stories

A study led by researchers from the UAB and the CSIC has revealed that the earliest Neolithic groups to settle some 7,000 years ago in the Pyrenean site of Coro Trasito (Tella, Huesca) used species selection strategies to manufacture their tools made out of bone and chose deer for the projectile tips.
A chance encounter in remote Australia, and years of painstaking analysis has pushed back evidence for the start of complex life on the planet by 750 million years.
Scientists have found a surprising connection between dinosaurs and ancient grapes. Fossilised seeds found in Central and South America hint that the mass extinction at the end of the “Age of Dinosaurs” might have created the conditions for ancient grapes to spread. See the study published in the journal Nature Plants.

A giant 280m-year-old salamander-like creature that was an apex predator before the age of the dinosaurs has been discovered by fossil hunters in Namibia.
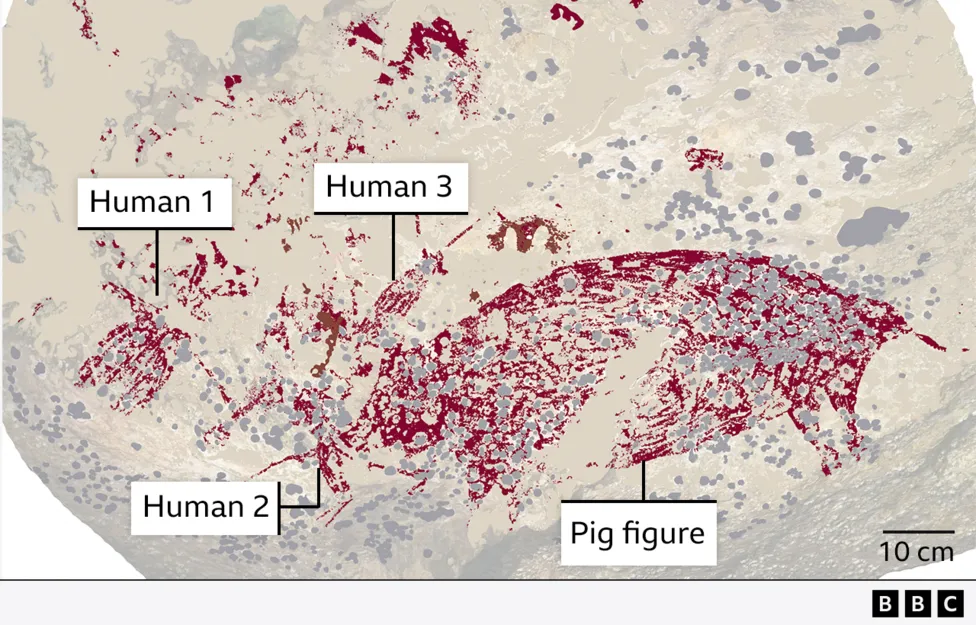

The oldest example of figurative cave art has been discovered in the Indonesian Island of Sulawesi by Australian and Indonesian scientists. The painting of a wild pig and three human-like figures is at least 51,200 years old, more than 5,000 years older than the previous oldest cave art.

It sounds like a scene from a Spielberg film: an injured worker undergoes an emergency amputation, performed by one of her colleagues, allowing her to live another day. But this is not a human story – it is behaviour seen in ants.
A new study challenges the theory that dinosaur fossils inspired the legend of the mythological creature, the gryphon.
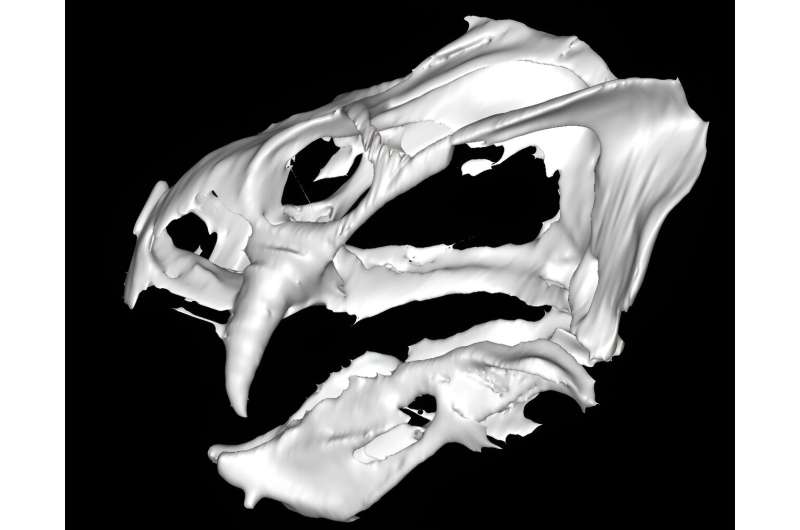
Details of an ancient cousin of modern-day mammals are being revealed for the first time. Hi-tech scanning of an ancient fossil, which was captured in sandstone around 252–254 million years ago, is giving experts valuable insight into the animal’s anatomy and evolution. The study, published in the Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society.
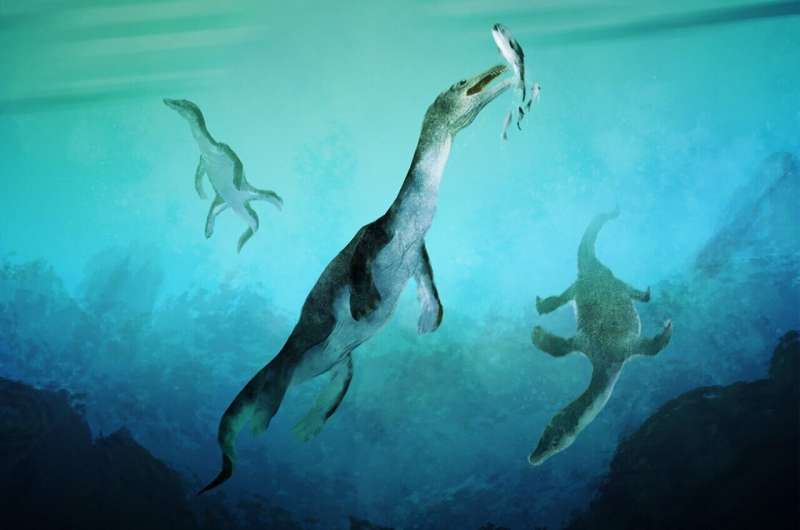

An international team of scientists has identified the oldest fossil of a sea-going reptile from the Southern Hemisphere—a nothosaur vertebra found on New Zealand’s South Island. 246 million years ago, at the beginning of the Age of Dinosaurs, New Zealand was located on the southern polar coast of a vast super-ocean called Panthalassa.

Charles Darwin enjoys a near god-like status among scientists for his theory of evolution. But his ideas that animals are conscious in the same way humans are have long been shunned. Until now.
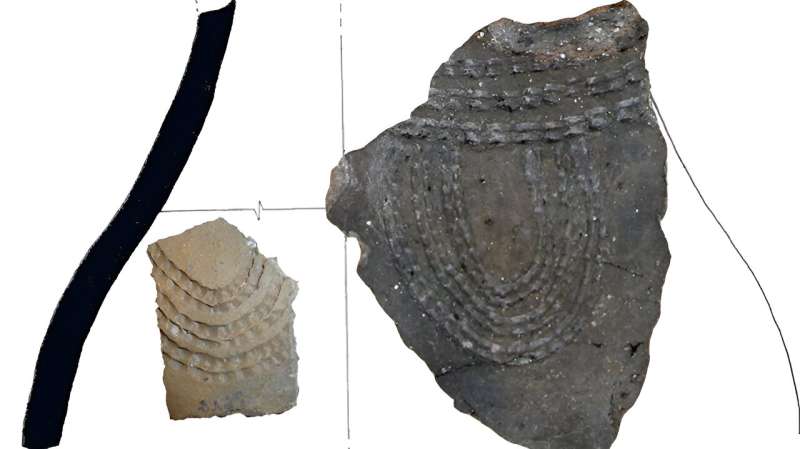

A joint study…yields the first direct proof of the consumption and processing of dairy products in the Pyrenees already at the start of the Neolithic period, approximately 7,500 years ago, as well as the consumption of pig. The results lead to doubts about the belief that these products were first used much later in the Pyrenean mountain range.
The universal equation has been shown to accurately predict the flapping frequency of birds, insects and even long-extinct prehistoric creatures like the flying reptiles, pterosaurs. It even translates to the flapping flippers of swimming creatures like whales and penguins. The study is published in the open-access journal PLOS ONE.
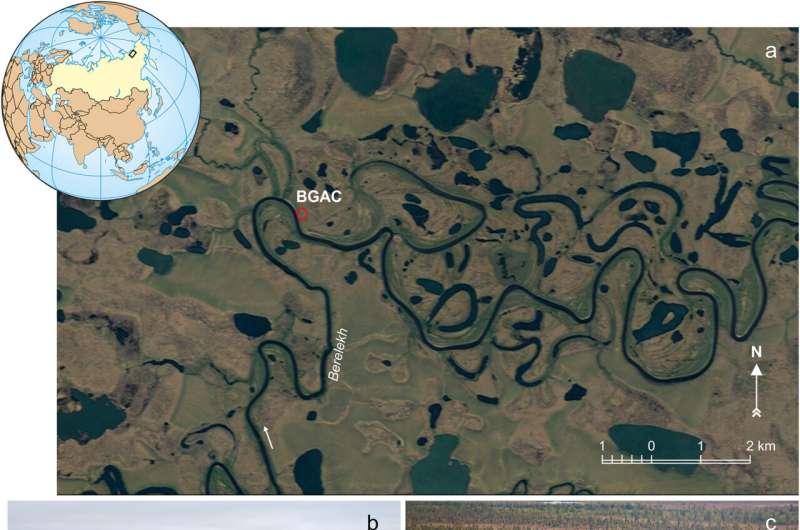
In the East Siberian Arctic (>70 °N), there is not only evidence of significant woolly mammoth populations, but also how humans interacted with them, the focus of new research in Quaternary Science Reviews.

Elephants call out to each other using individual names that they invent for their fellow pachyderms, a study said on Monday.

Earth’s largest remaining tract of tropical rainforest is kept alive by a complex water cycle that we’re only just beginning to understand. Yet our activities are changing it before we can see the full picture, a new report finds.
New research led by geologists at Western Australia’s Curtin University provides evidence that fresh water emerged on Earth about 4 billion years ago – half a billion years earlier than previously thought. The study is published in the journal Nature Geoscience.








