Animal Life news stories
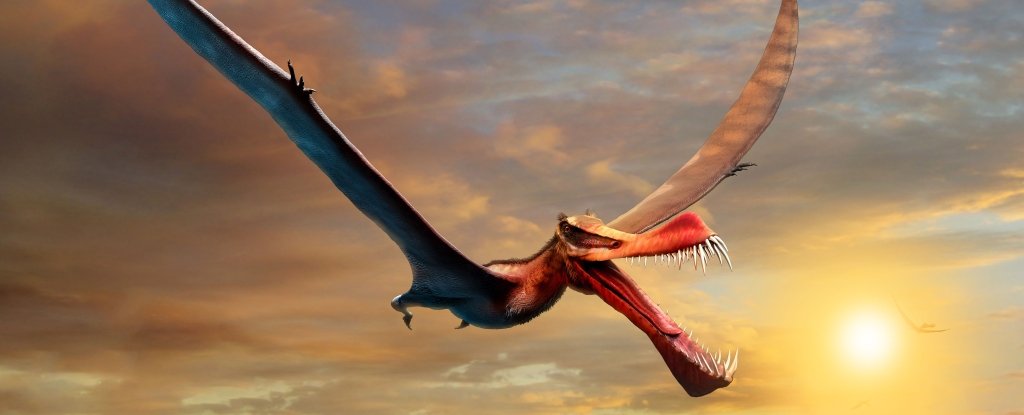

With a seven-meter wingspan, and a mouth bristling with fangs, a newly discovered pterosaur would have ruled the skies over Australia’s northeast around 110 million years ago.
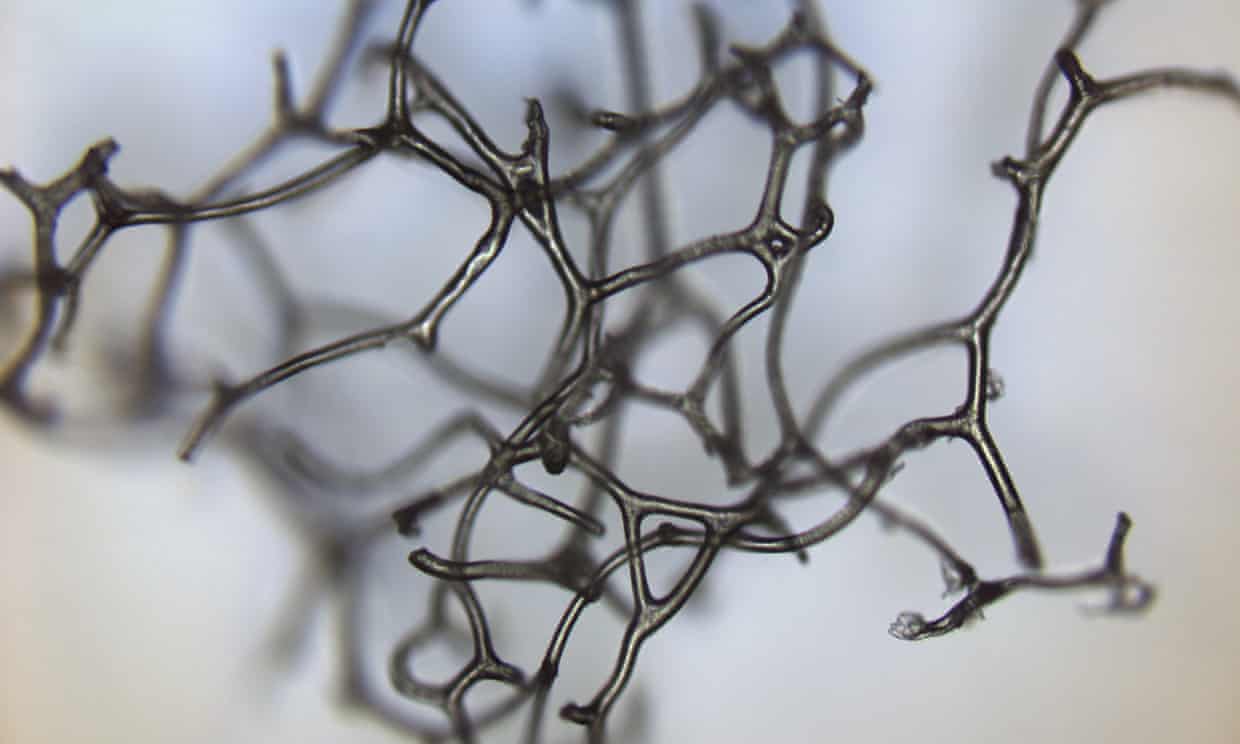
Intricate patterns of tubular structures discovered in giant ancient reefs may be the remnants of prehistoric horny sponges and the oldest known fossils of animal life on Earth.
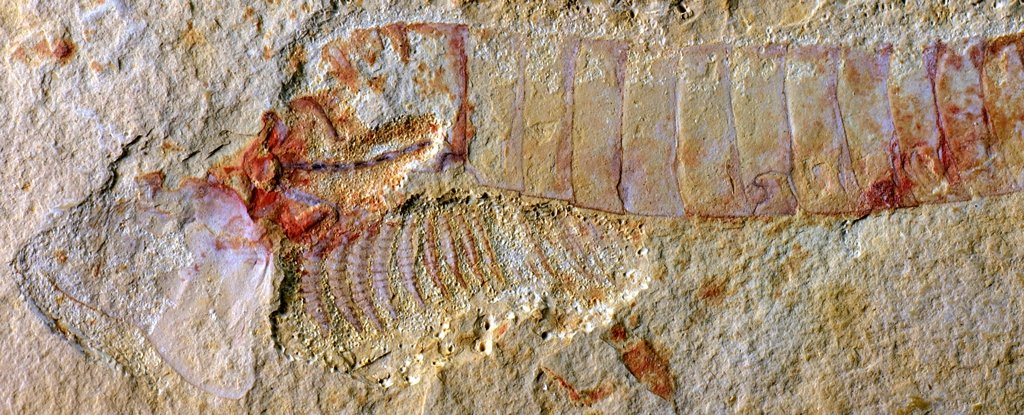

Charles Darwin famously discussed the “imperfections” of the geological record in his book On The Origin of Species. He correctly pointed out that unless conditions are just right, it’s unlikely for organisms to be preserved as fossils, even those with bones and shells.

Researchers exploring the Indian Ocean have discovered the remains of a collapsed underwater volcano with an uncanny resemblance to the all-seeing “Eye of Sauron” from J.R.R. Tolkien’s famous fantasy series “The Lord of the Rings,” as well as two other seafloor structures named after places in Tolkien’s Middle-earth.
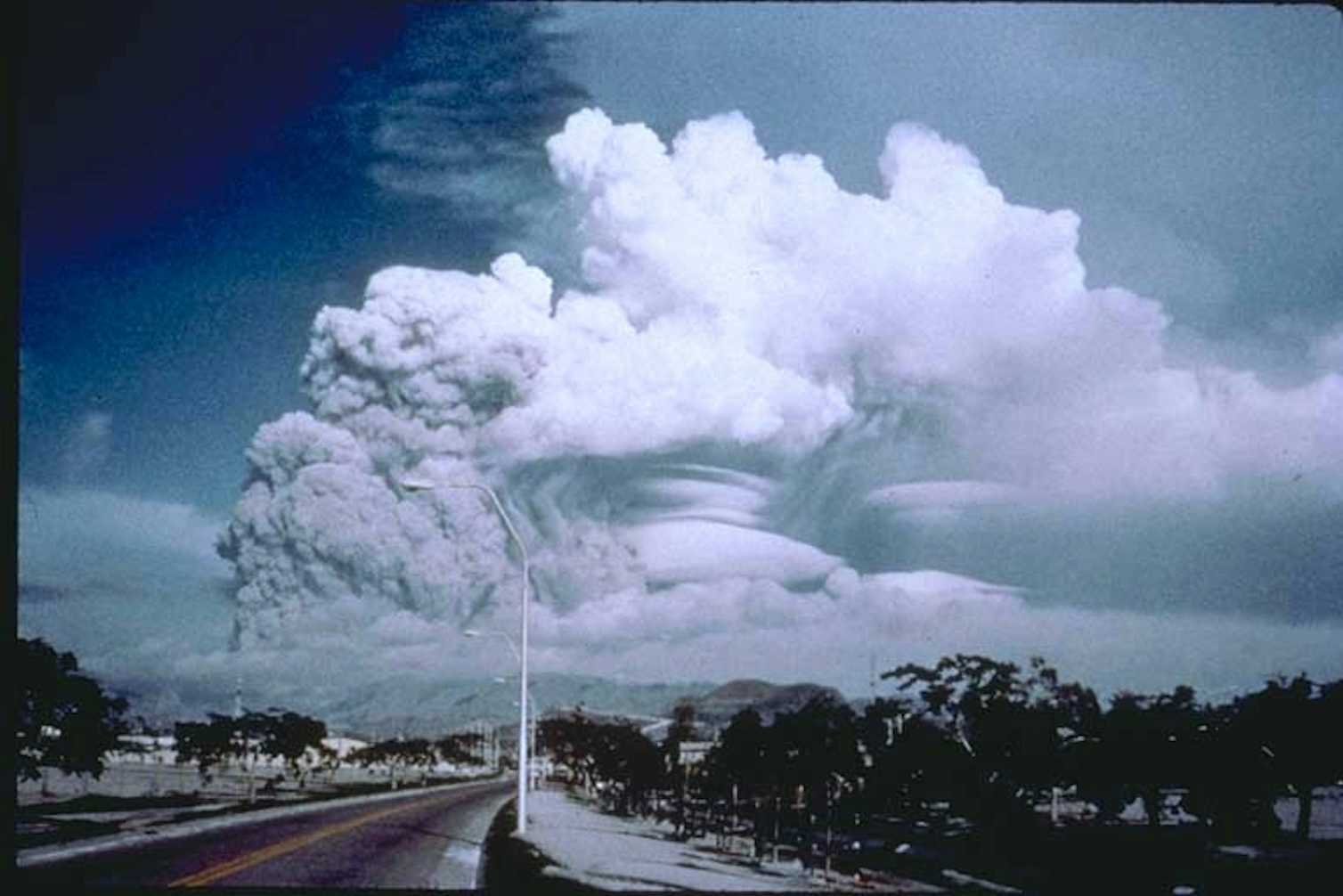

Around 74,000 years ago, a “supereruption” on the island of Sumatra, Indonesia, blasted out an estimated 5,000 cubic kilometres of magma.
Researchers have discovered the fossilised remains of 3.4-billion-year-old methane-cycling microbes that lived in a hydrothermal system beneath the ancient seafloor – the oldest microfossils of this type found to date.
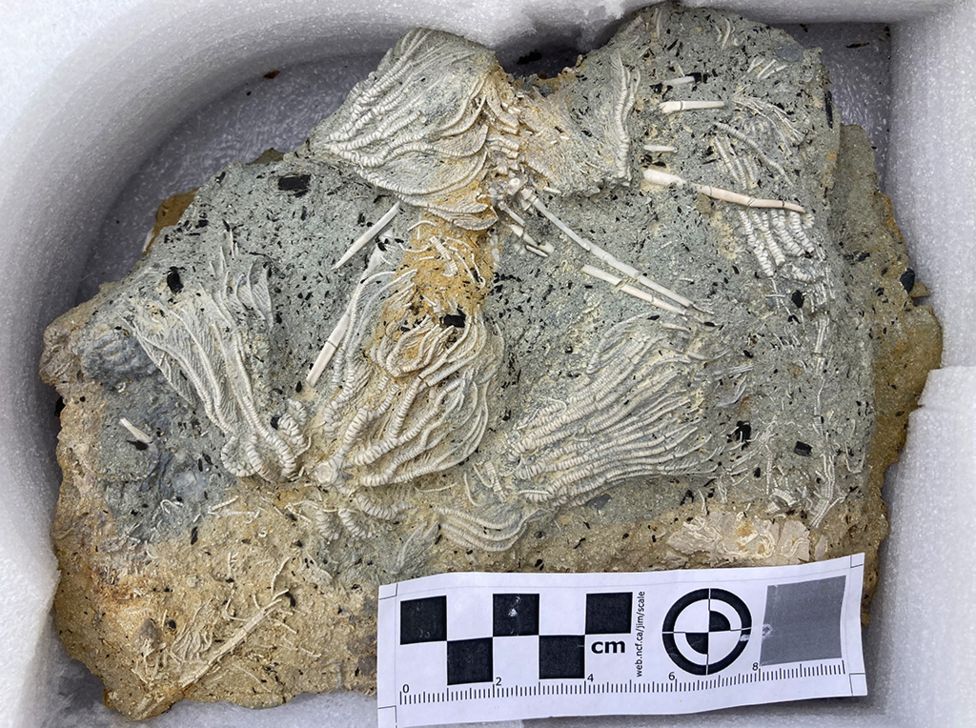

Palaeontologist Tim Ewin is standing in a quarry, recalling the calamity that’s written in the rocks under his mud-caked boots.
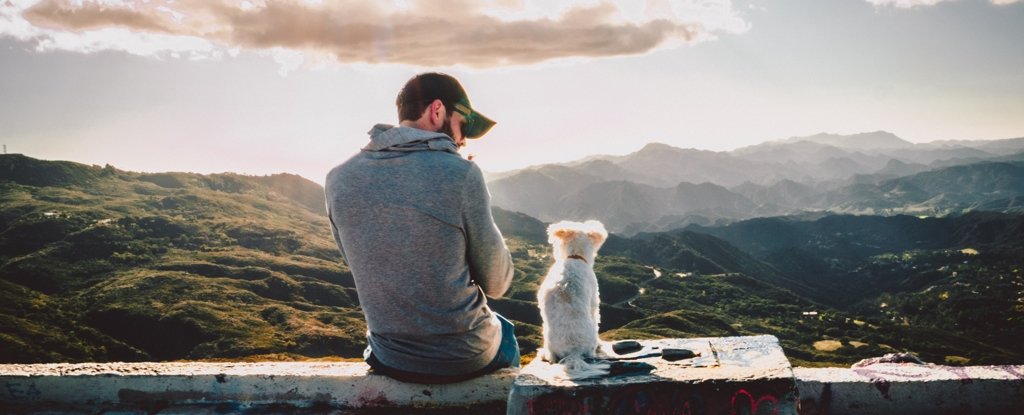

Dogs are born with an innate ability to read human gestures that is not apparent in their closest relative, wolves.
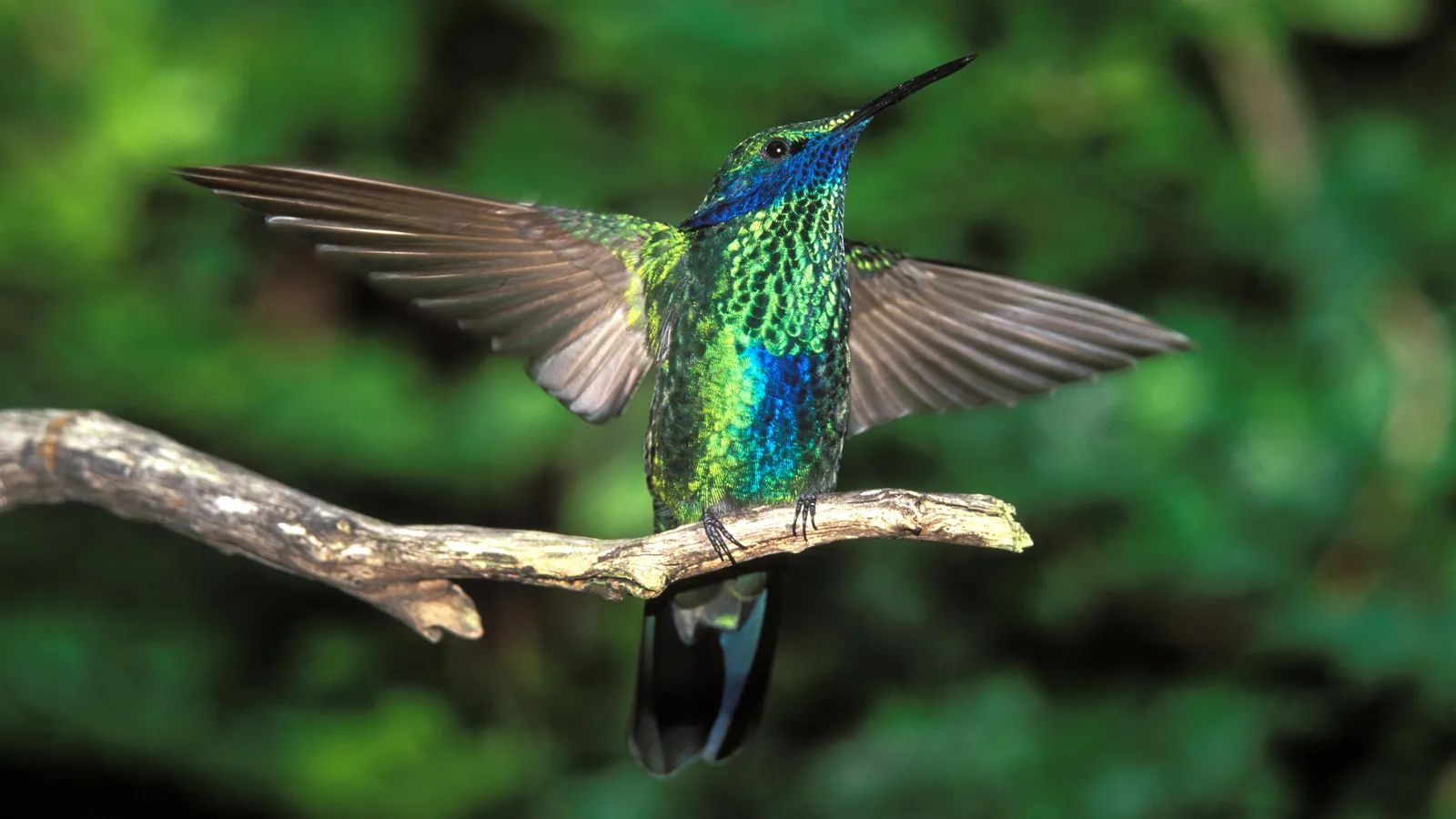

The stories of enigmatic birds told in indigenous folklore aren’t just fascinating tales, they may be a way to preserve languages and cultures at risk of extinction.
Large coastal sharks engage in ‘shift work’ to share their resources, according to a new study from Murdoch University’s Harry Butler Institute.
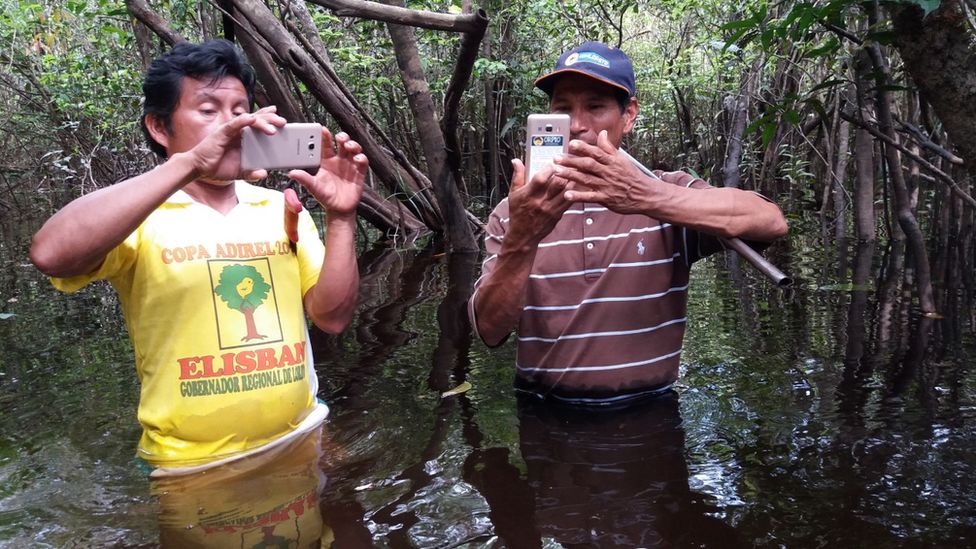

Technology can help indigenous communities to significantly curb deforestation, according to a new study. Indigenous people living in the Peruvian Amazon were equipped by conservation groups with satellite data and smartphones.

For almost 2 decades, genomes isolated from fossils have galvanized the study of human evolution. Yet despite vast improvements in retrieving and analyzing that DNA, researchers have deciphered whole genomes from just 23 archaic humans, 18 of them Neanderthals. This week, however…

Scientists at the University of Southampton have discovered that changes in Earth’s orbit may have allowed complex life to emerge and thrive during the most hostile climate episode the planet has ever experienced.
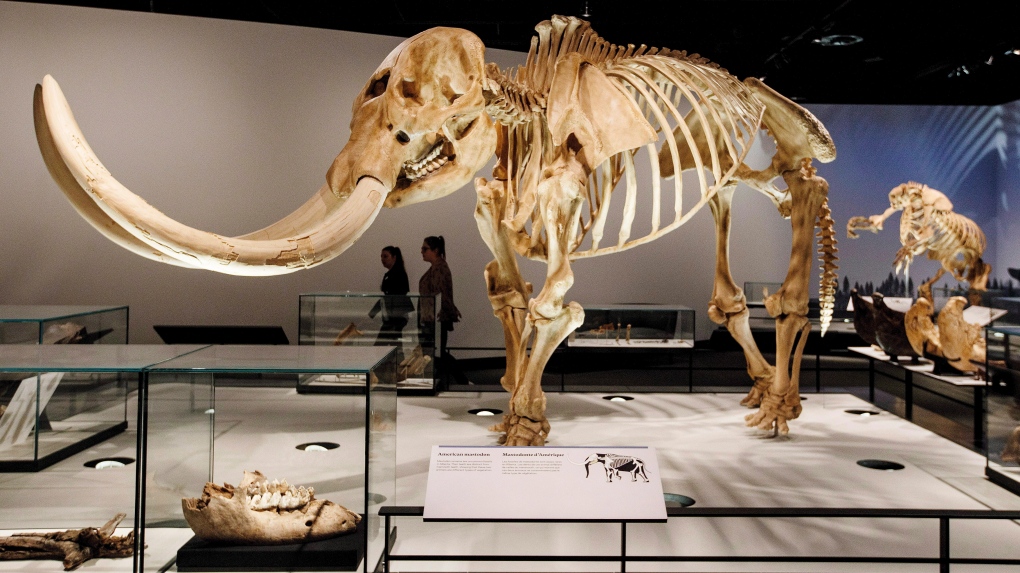

A new study suggests that prehistoric elephants like the mastodon and woolly mammoth were wiped out by waves of extreme global environmental change, rather than being hunted to extinction by early humans.

Dinosaurs were facing a crisis even before the asteroid hit, with extinctions outpacing the emergence of new species — a situation that made them “particularly prone to extinction,” a new study suggests.
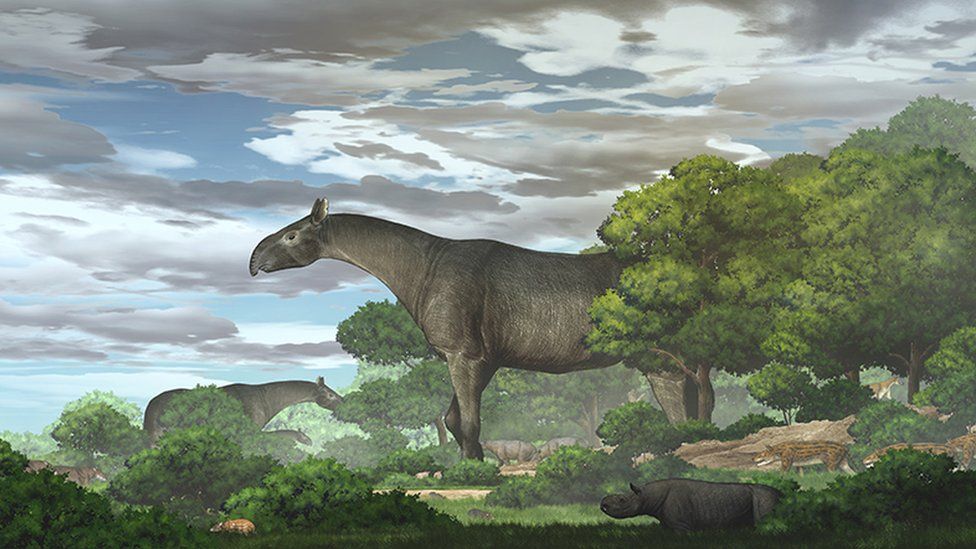

A new species of the ancient giant rhino – among the largest mammals to walk on land – has been discovered in north-western China, researchers say.








