Animal Life news stories

The eye is so complex that even Charles Darwin was at a loss to explain how it could have arisen. Now, it turns out that the evolution of the vertebrate eye got an unexpected boost—from bacteria, which contributed a key gene involved in the retina’s response to light.
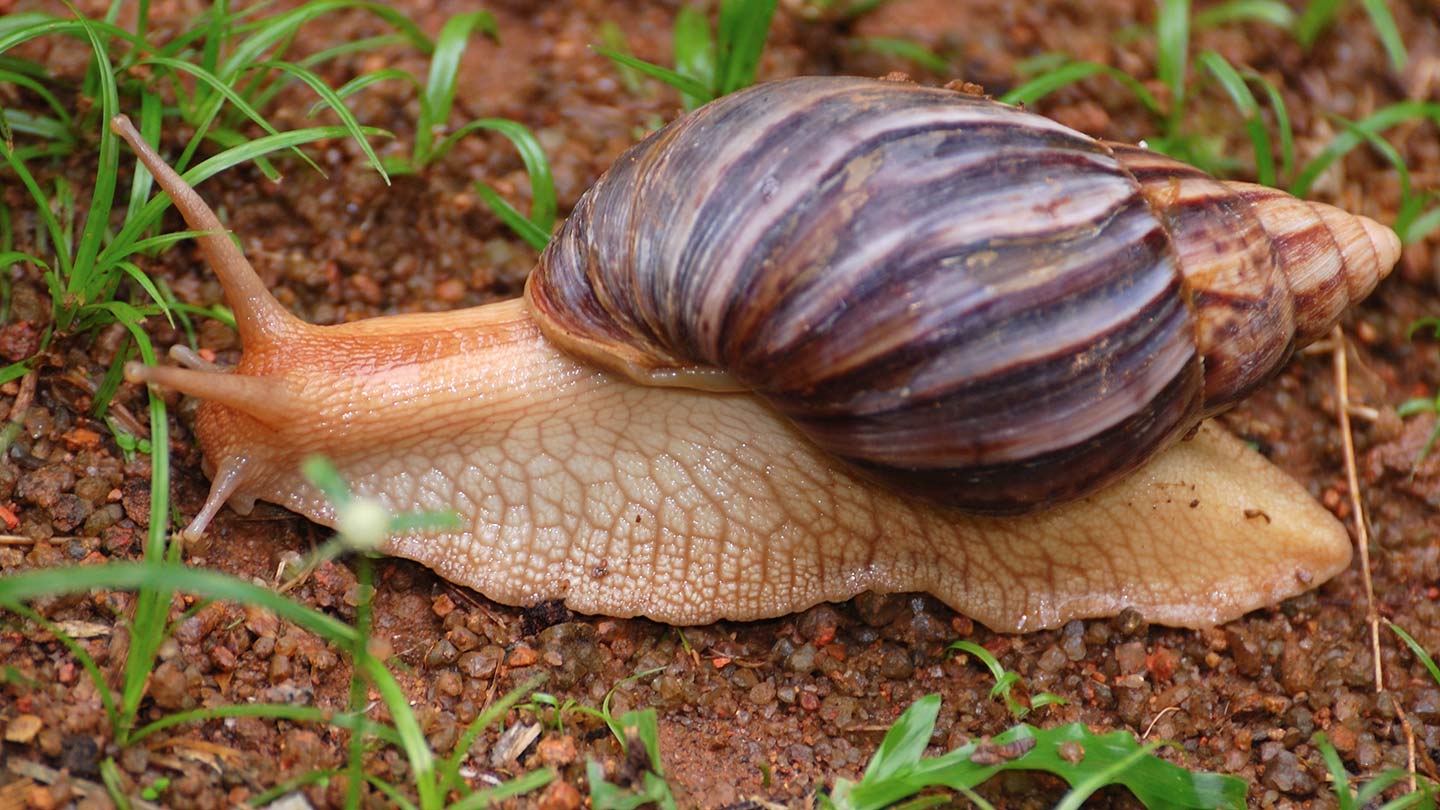

Until now, the oldest evidence of Homo sapiens eating land snails dated to roughly 49,000 years ago in Africa and 36,000 years ago in Europe. But tens of thousands of years earlier, people at a southern African rock shelter roasted these slimy, chewy — and nutritious — creepers that can grow as big as an adult’s hand, researchers report in the April 15 Quaternary Science Reviews.
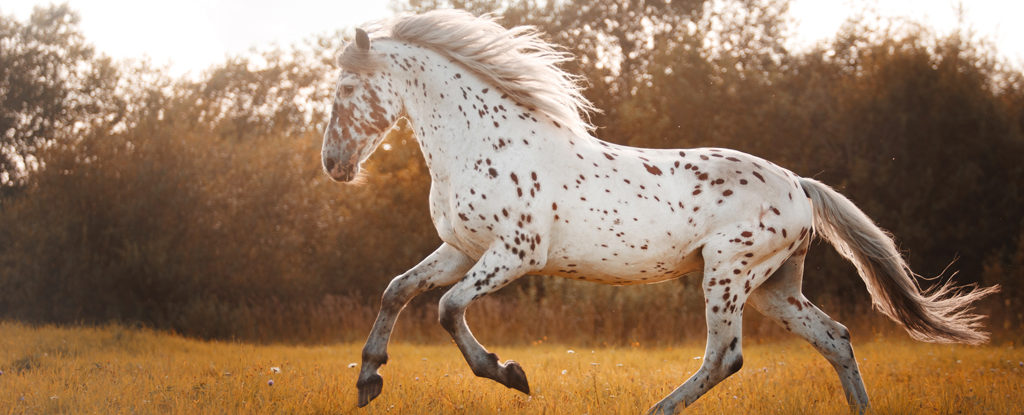

Native American people integrated horses into their communities much earlier than European colonial records suggest, according to an innovative study that combined archaeological and genetic analysis with Indigenous oral traditions.
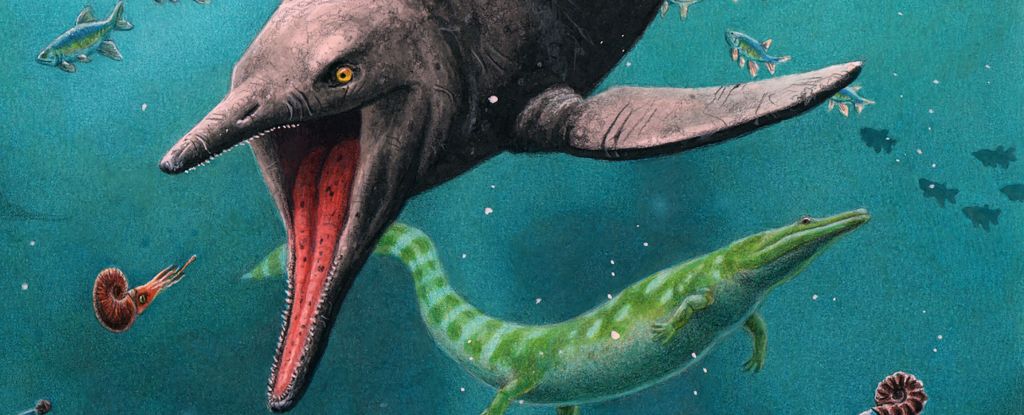

Bones found on the remote Arctic island of Spitsbergen suggest the ancient marine reptiles known as ichthyosaurs roamed Earth’s oceans for much longer than we thought.

It’s easy to see why most folks think of mushrooms as some type of weird plant, popping out from under the soil when it rains and found in the vegetable aisle of the grocery store…
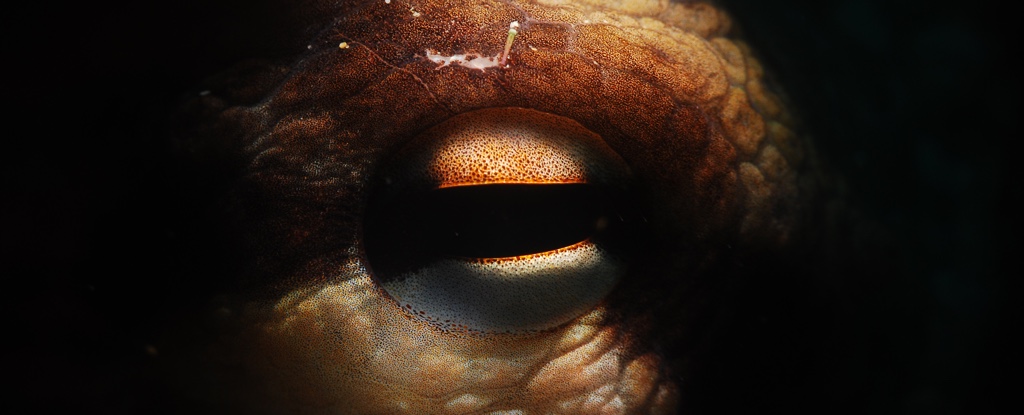
Scientists at Dartmouth College in the US have studied how octopuses experience reality in a specialist lab…They question the appropriateness of this for a species that has a sophisticated capacity for processing information, rudimentary tool use, complex visual pathways and, not least, the capacity for pain.
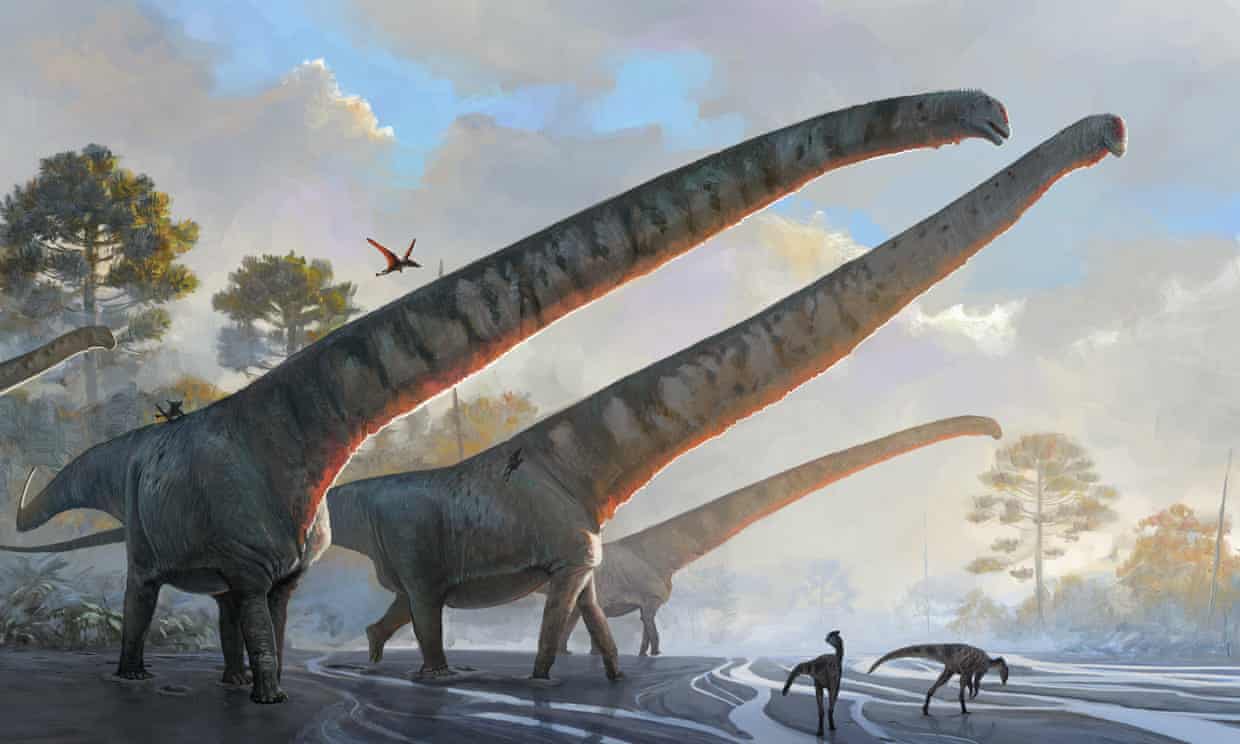

A dinosaur that roamed east Asia more than 160m years ago has been named a contender for the animal with the longest neck ever known.
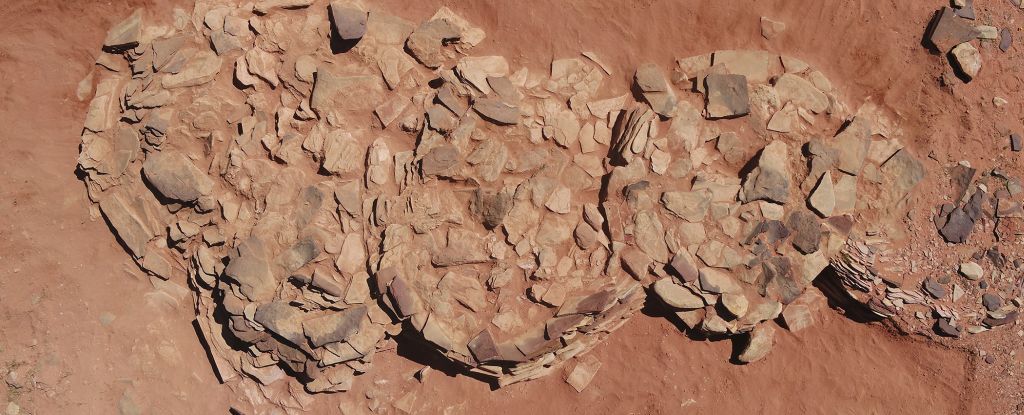

According to an in-depth new analysis, the mysterious, rectangular enclosures were used by Neolithic people for unknown rituals, depositing animal offerings, perhaps as votives to an unknown deity or deities.
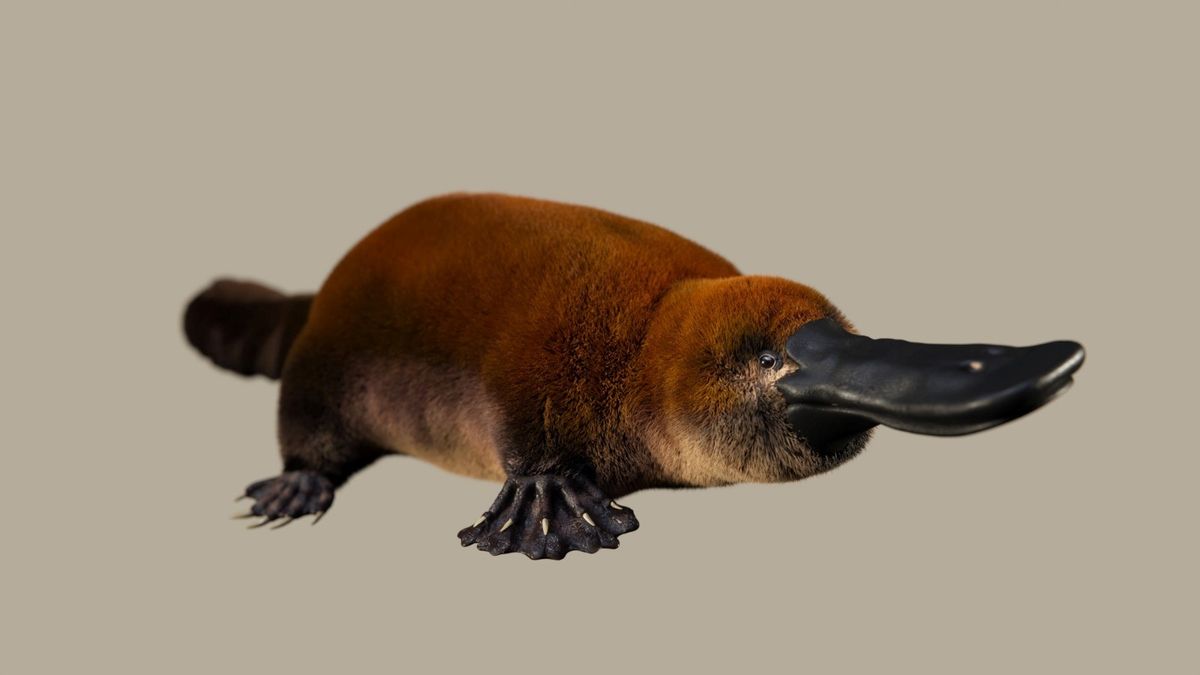

Fossils of a 70 million-year-old platypus relative called Patagorhynchus pascuali found in South America show that egg-laying mammals evolved on more than one continent.
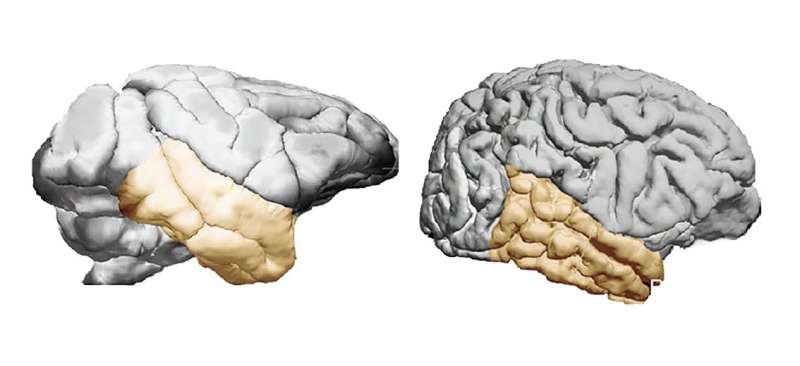
It had been thought to date that the species Homo sapiens has disproportionately large temporal lobes compared to other anthropoid primates, the group including anthropomorphic monkeys and apes. A new study, one of whose authors is Emiliano Bruner, a paleoneurologist at the Centro Nacional de Investigación sobre la Evolución Humana (CENIEH), contradicts that hypothesis.
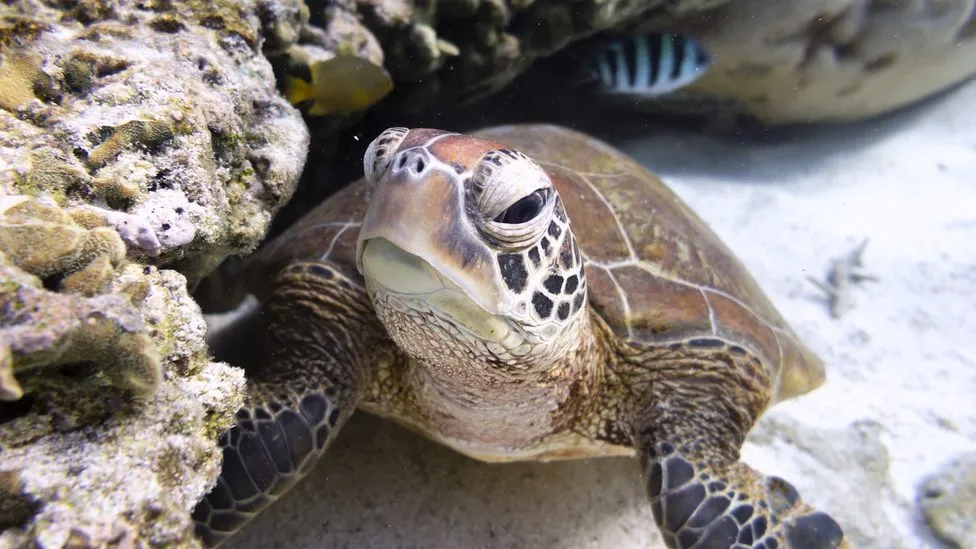

Nations have reached a historic agreement to protect the world’s oceans following 10 years of negotiations. The High Seas Treaty aims to place 30% of the seas into protected areas by 2030, to safeguard and recuperate marine nature.

Together, amino acids form proteins that play many vital roles in organisms. This new study was designed to help establish why a specific group of 20 ‘canonical’ amino acids is used again and again to build proteins when there are so many more of these amino acids to pick from.
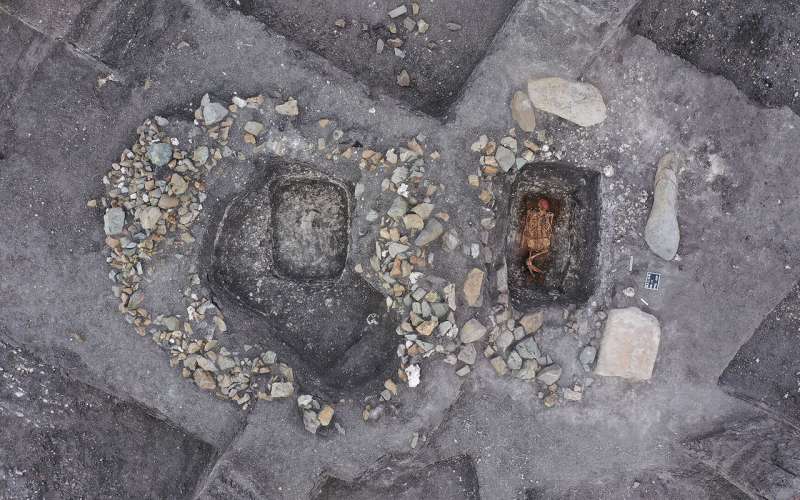

Researchers have discovered evidence of horse riding by studying the remains of human skeletons found in burial mounds called kurgans, which were between 4,500 and 5,000 years old.
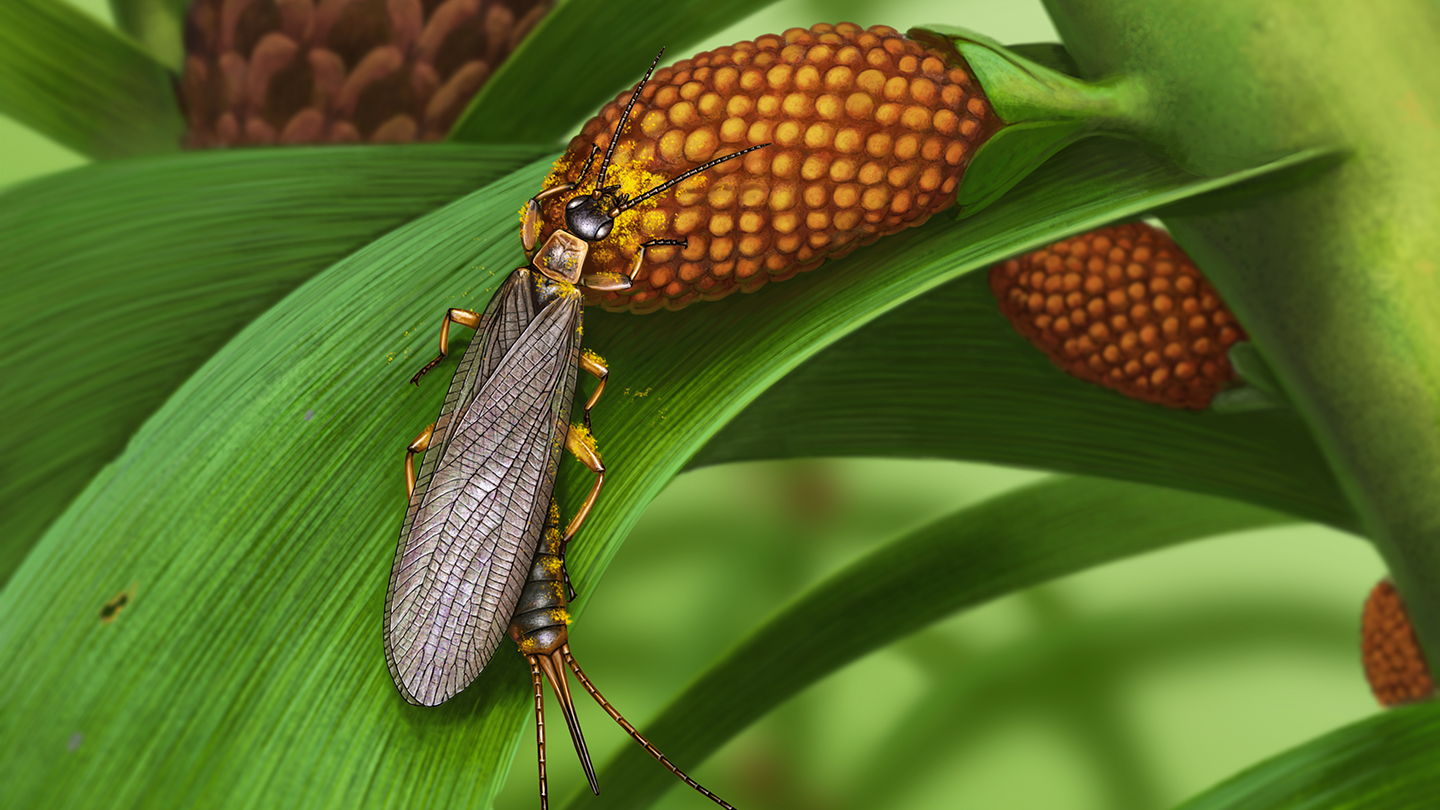

The oldest known fossils of pollen-laden insects are of earwig-like ground-dwellers that lived in what is now Russia about 280 million years ago, researchers report. Their finding pushes back the fossil record of insects transporting pollen from one plant to another, a key aspect of modern-day pollination, by about 120 million years.
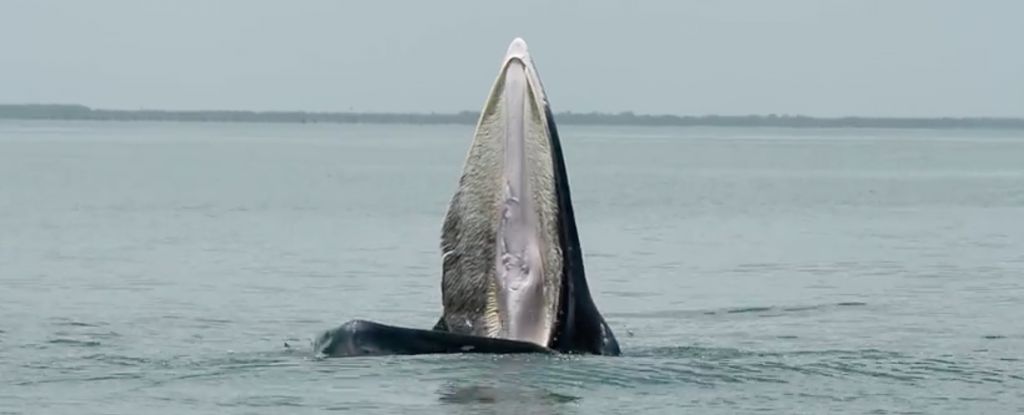

An unusual whale feeding technique only recorded for the first time in 2011 may have been around for at least two thousand years, according to researchers from Flinders University in Australia.
The study was published in Marine Mammal Science.
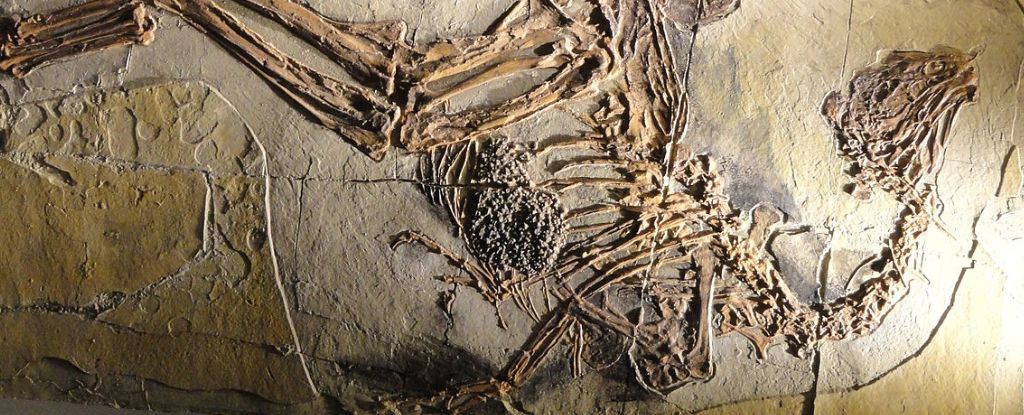

Dinosaur fossils featuring arms with a suspect bend at the elbow and wrist could hint at the presence of an unpreserved tendon that underpins all modern avian flight.
The study was published in Zoological Letters.








