Animal Life news stories
A team of researchers has just uncovered another striking connection between math and nature: between one of the purest forms of mathematics, number theory, and the mechanisms governing the evolution of life on molecular scales, genetics. See the study here.
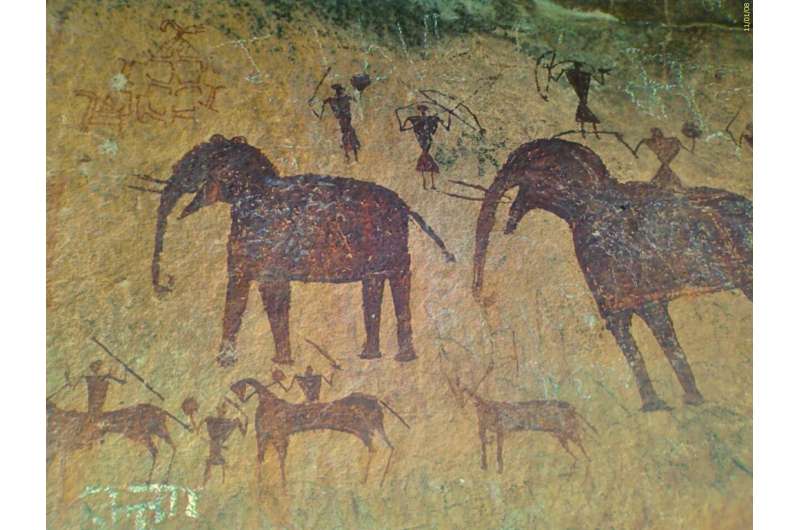

Research led by Complutense University, Madrid, has discovered an array of ancient cave paintings hidden among previously described cave art. In a paper, “Animals hidden in plain sight: stereoscopic recording of Paleolithic rock art at La Pasiega cave, Cantabria,” published in Antiquity, the team fills in details missing from previous photographic images.
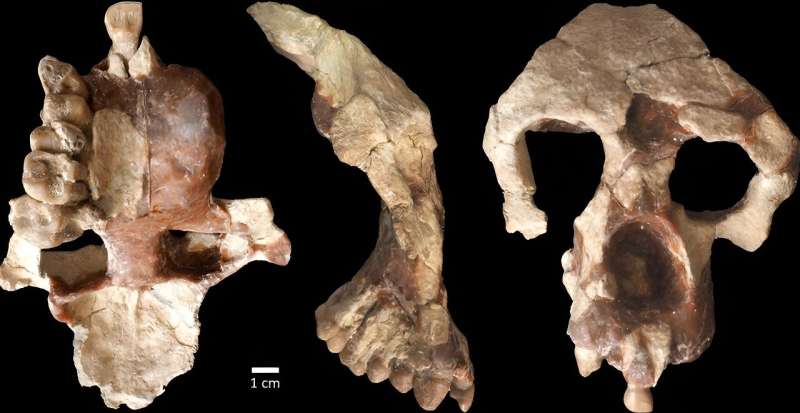
A new fossil ape from an 8.7-million-year-old site in Türkiye is challenging long-accepted ideas of human origins and adding weight to the theory that the ancestors of African apes and humans evolved in Europe before migrating to Africa between nine and seven million years ago. See the study here.
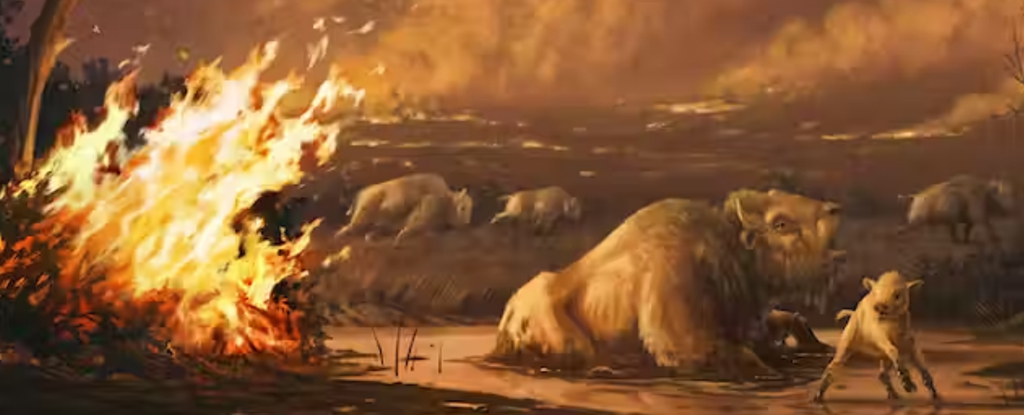

In a new study, published in August 2023, we sought to understand changes that were happening in California during the last major extinction event at the end of the Pleistocene, a time period known as the Ice Age.
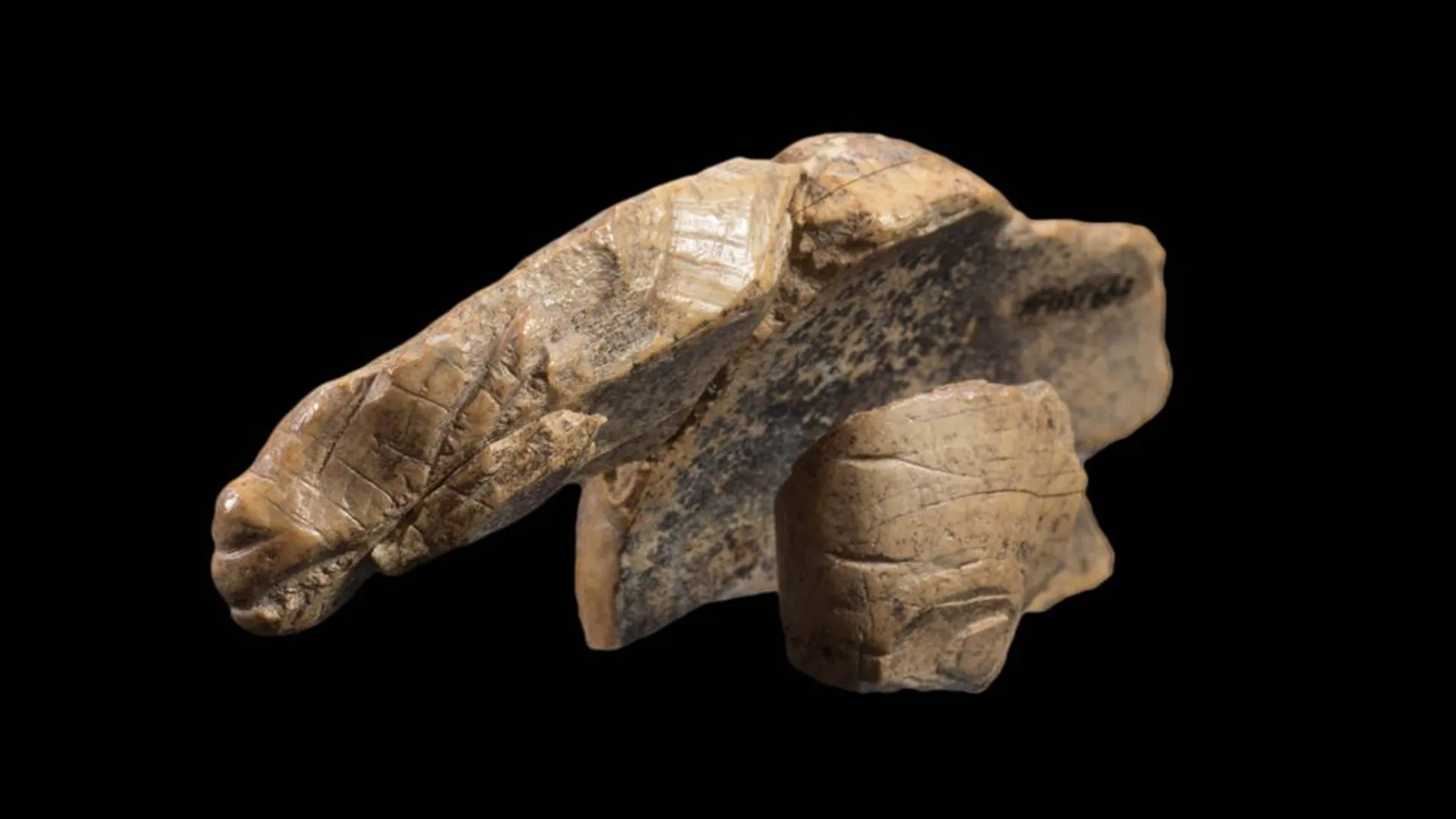

Archaeologists in Germany have discovered the missing piece of an ice age carving deep in a cave. But the new addition of the ivory carving, originally thought to depict a horse, has actually complicated matters: Now, researchers aren’t sure if it portrays a cave lion or a cave bear.
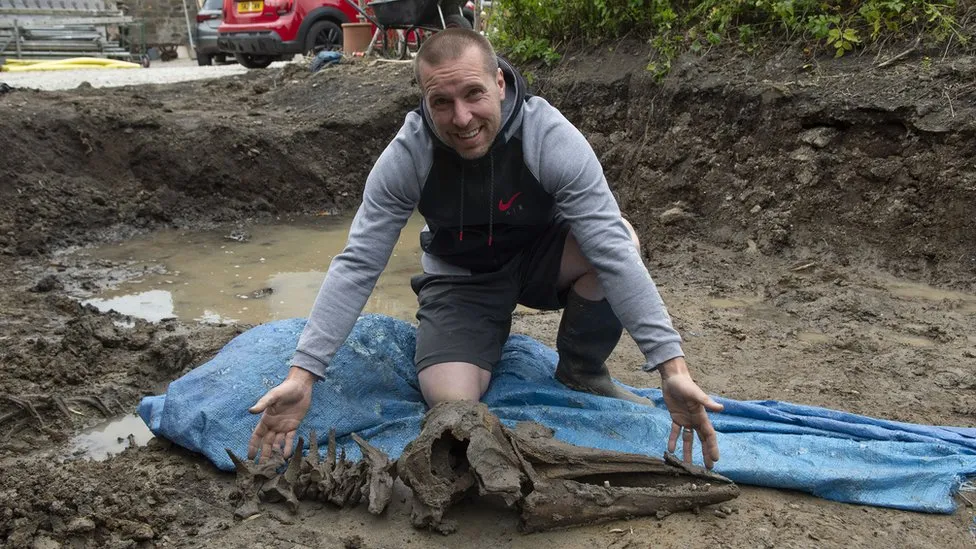

The bottlenose dolphin is thought to have washed up on an ancient shoreline after the last Ice Age. Archaeologists have described the prehistoric discovery in Causewayhead, Stirling, as “the find of a lifetime”.
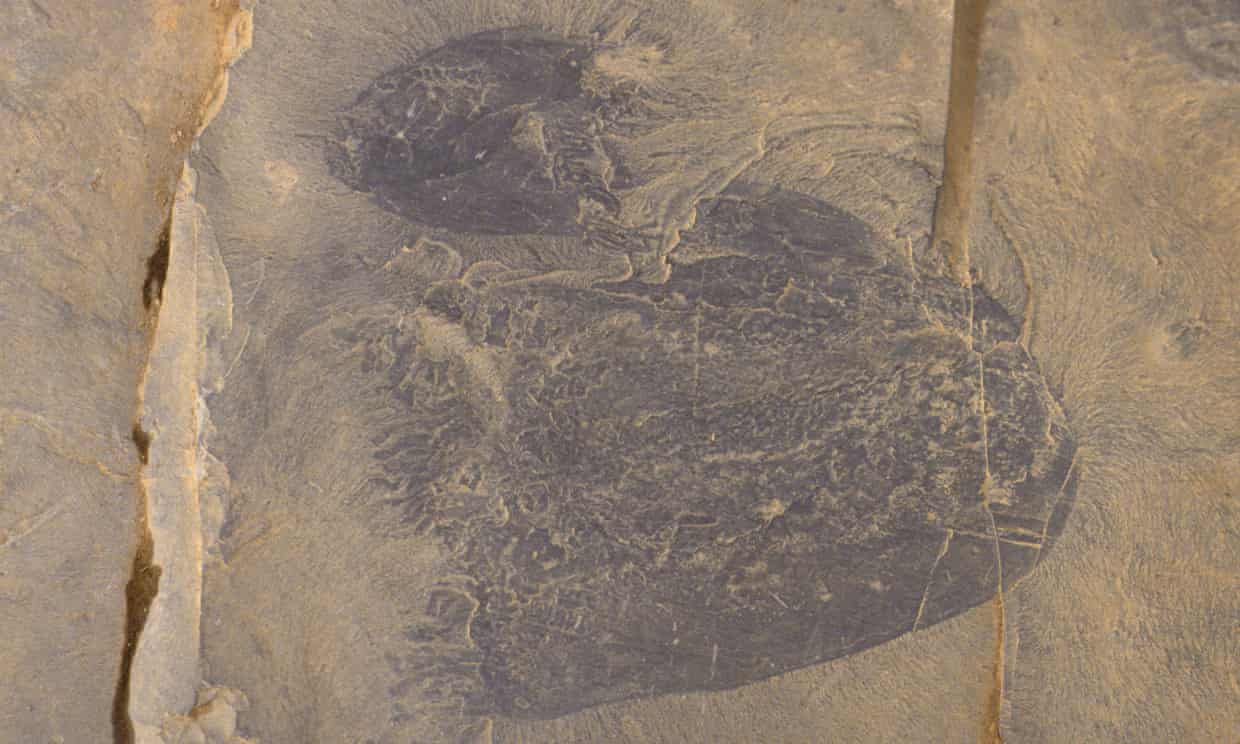

The new species, which has been named Burgessomedusa phasmiformis,resembles a large, swimming jellyfish with a saucer or bell-shaped body up to 20cm high. Its roughly 90 short tentacles would have allowed it to capture sizeable prey.
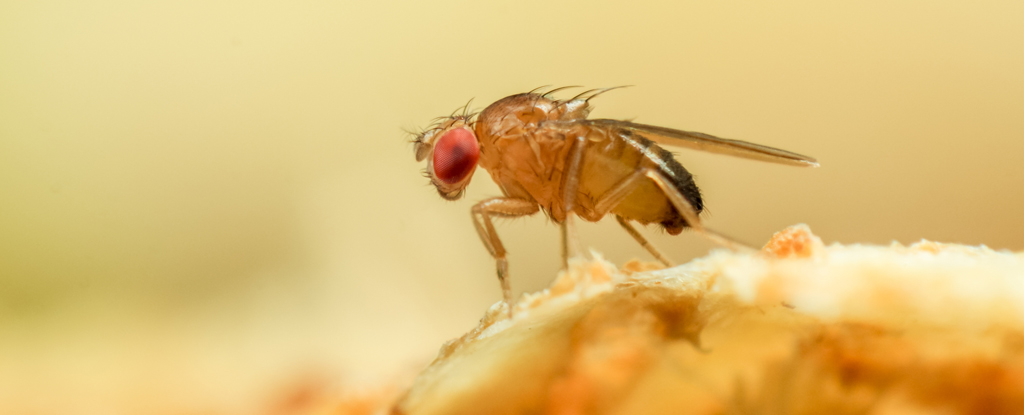

Scientists said on Friday they have genetically engineered female fruit flies that can have offspring without needing a male, marking the first time ‘virgin birth” has been induced in an animal. See the study here.
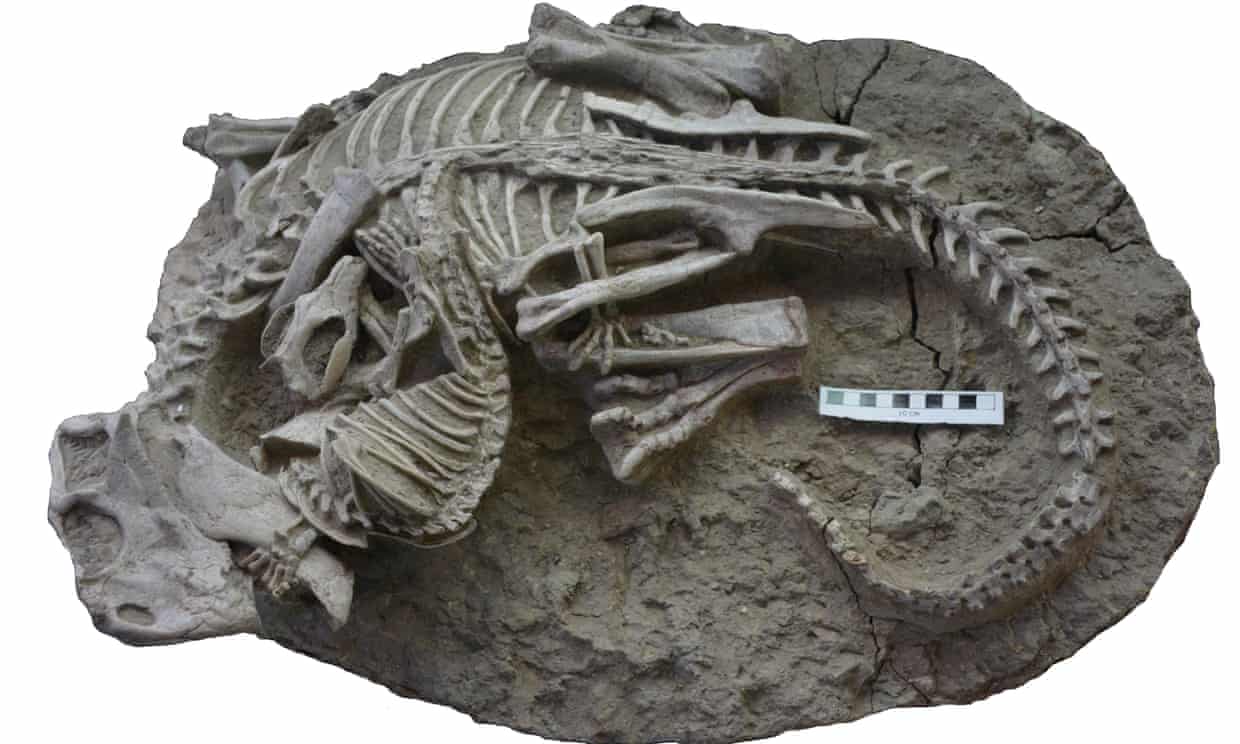

Experts revealed the 125m-year-old fossil that froze in time after being taken on by a small mammal a third of its size. They are tangled together, the mammal’s teeth sunk into the beaked dinosaur’s ribs, its left paw clasping the beast’s lower jaw. See research here.

New research suggests humans lived in South America at the same time as now extinct giant sloths, bolstering evidence that people arrived in the Americas earlier than once thought.
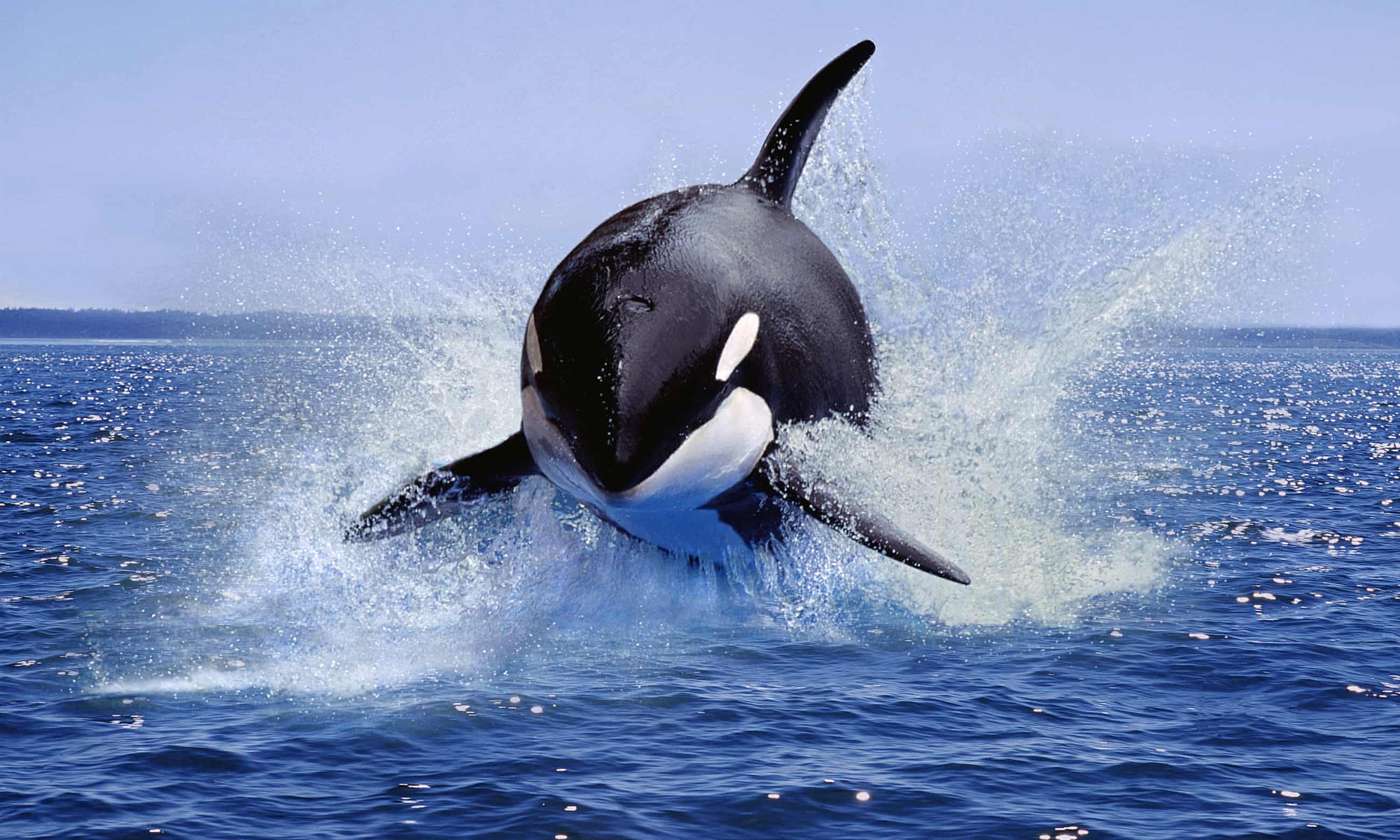

A pod in the strait of Gibraltar has sunk three boats and damaged dozens of others, and their story has captivated the world. What explains this unprecedented behaviour?
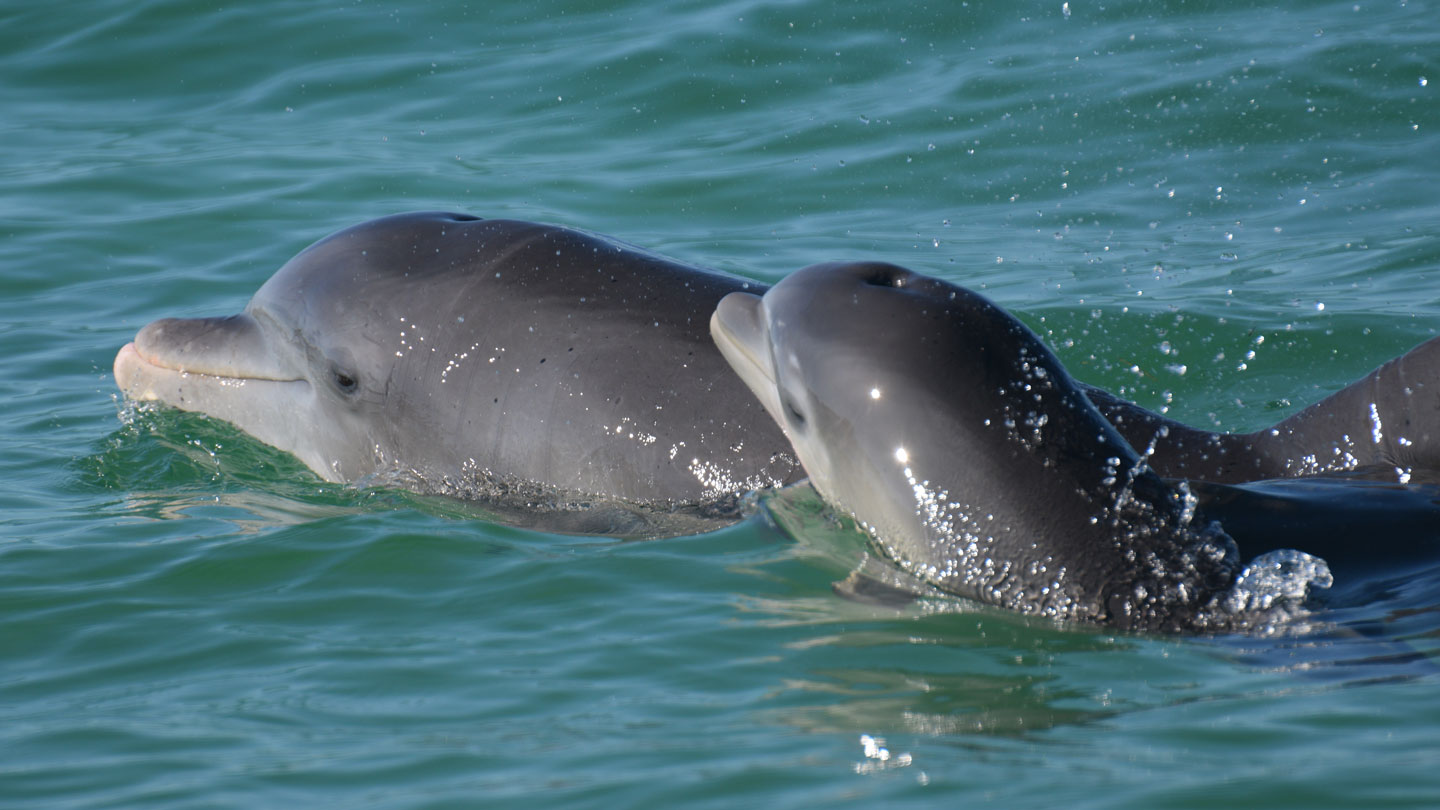

Bottlenose dolphin moms modify their individually distinctive whistles when their babies are nearby, researchers report June 26 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. This “parentese” might enhance attention, bonding and vocal learning in calves, as it seems to do in humans.
Researchers studying the sites have determined that the Yanliao Biota date back to between 164 million and 157 million years ago. Their results are published in the journal Earth and Planetary Science Letters.
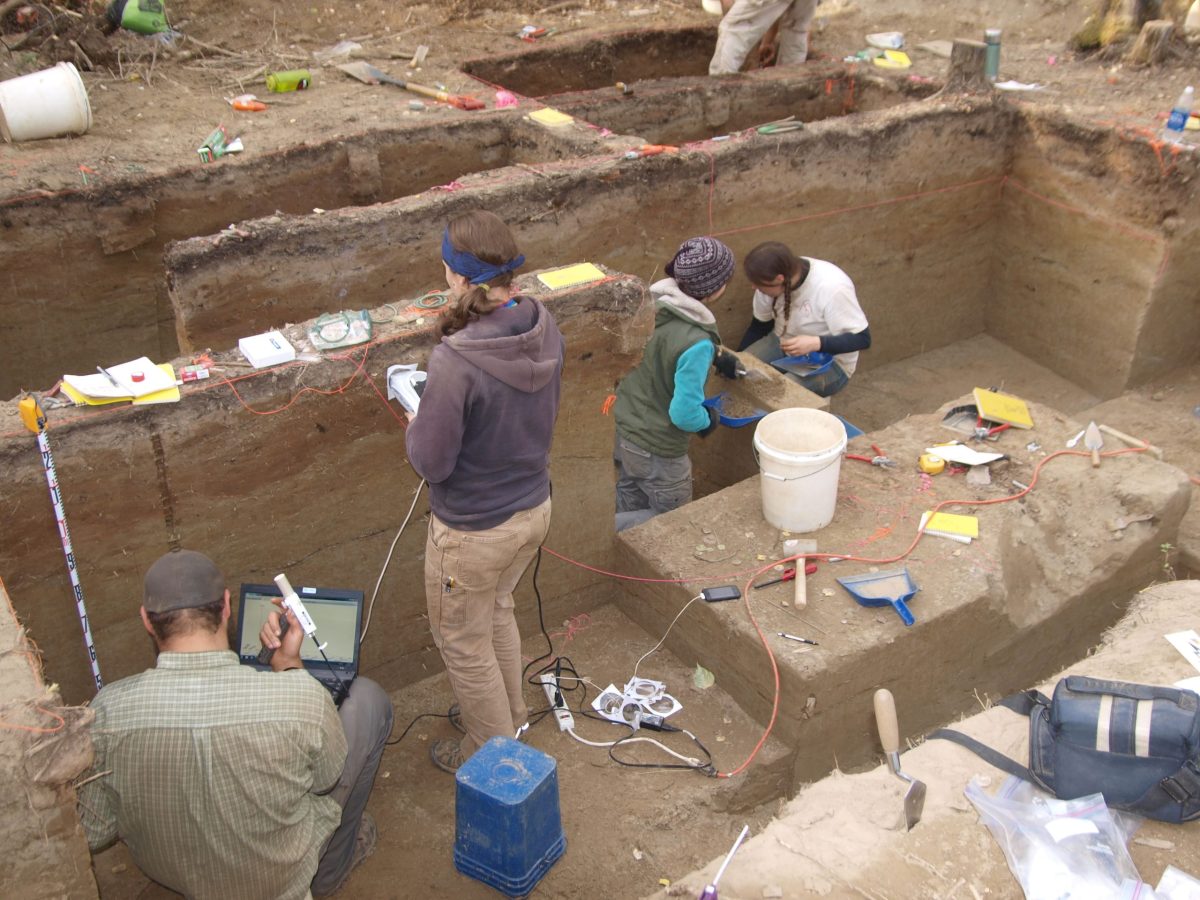

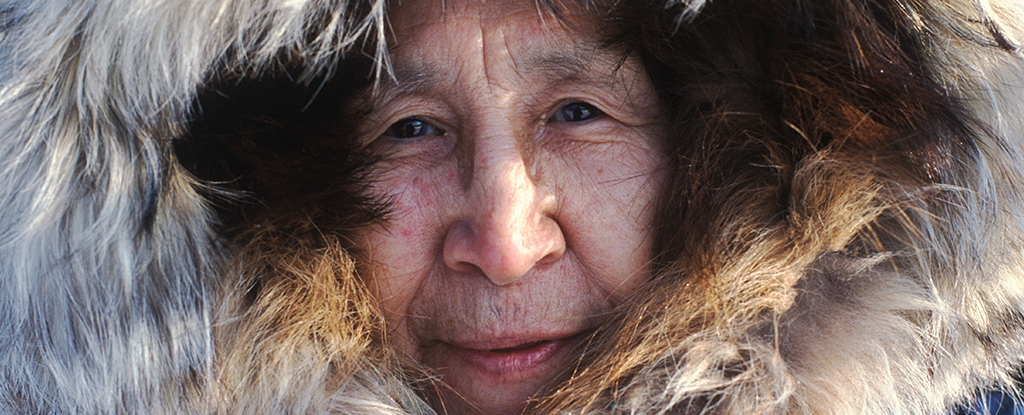
A team led by the University of Alaska Fairbanks researchers has discovered the earliest known evidence that Native Americans living in present-day central Alaska may have begun freshwater fishing around 13,000 years ago during the last ice age. See the study here.
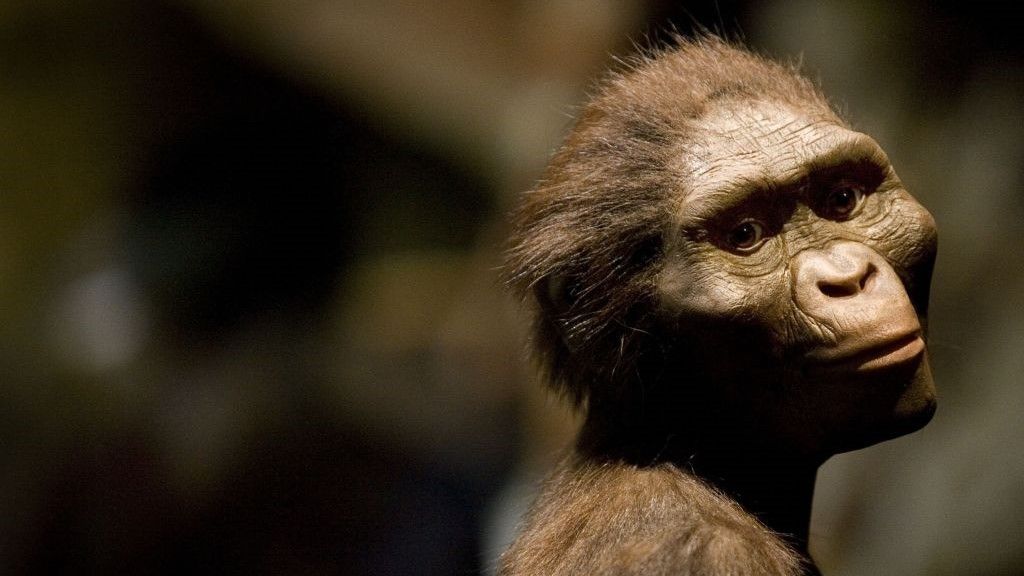

Our 3.2 million-year-old ancestor “Lucy” could stand and walk upright just like modern humans do, new 3D muscle modeling reveals. The study was published Wednesday (June 14) in the journal Royal Society Open Science.









