Ancient news stories
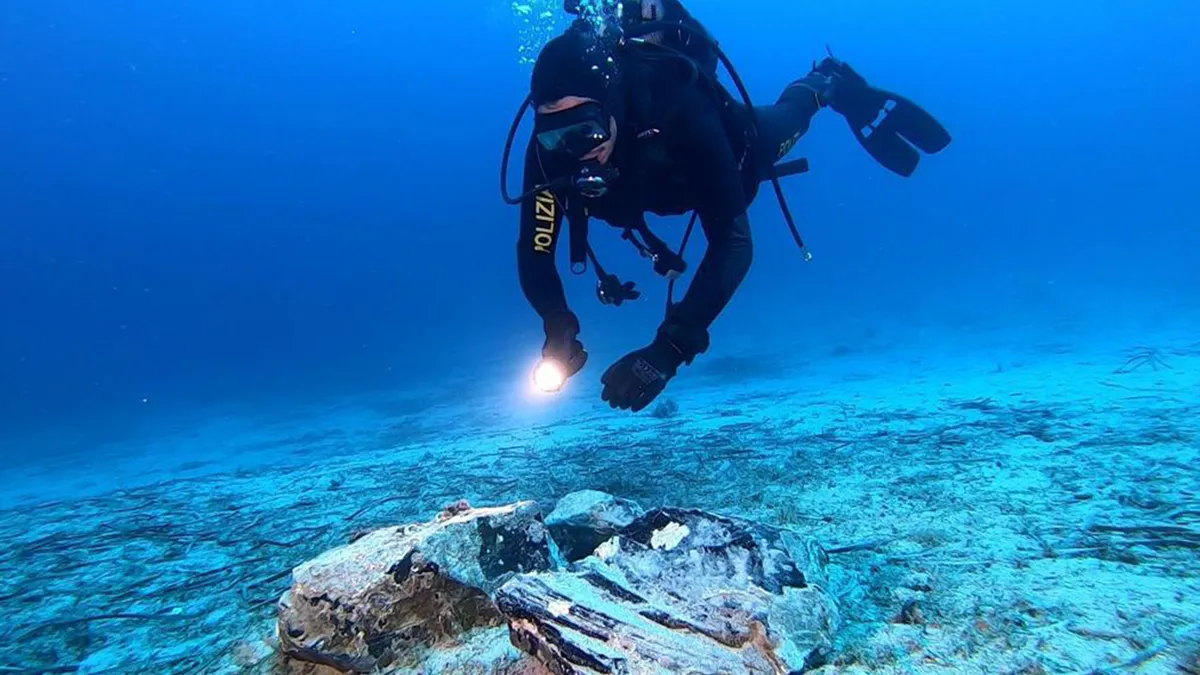

Divers off the coast of Naples, Italy have recovered a large chunk of chiseled obsidian that likely went down in a Stone Age shipwreck more than 5,000 years ago.
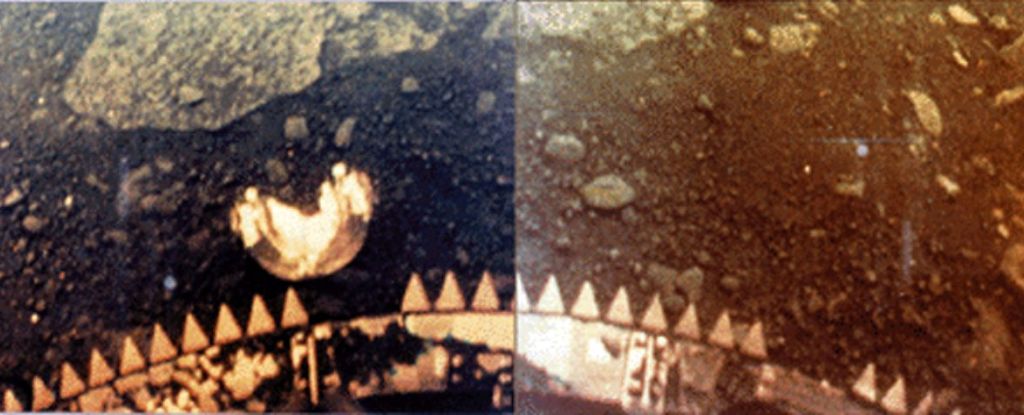
Venus is so tantalizingly close to being a twin of Earth. Its size, composition, and density are so similar to the properties of our homeworld… but when it comes to habitability, Venus couldn’t be more different.

Hunter-gatherers from Mexico migrated into California more than 5,000 years ago, potentially spreading distinctive languages from the south into the region nearly 1,000 years earlier than previously thought, a new genetic study details. See the study here.

Archaeological sites with evidence of major animal sacrifices are rarely known from the Iron Age of the Mediterranean region, and there is a gap between information offered by written sources and by the archaeological record. This makes it difficult to establish a clear understanding of the patterns and protocols of this practice. See the study here.
Recent research has shown that engravings in a cave in La Roche-Cotard (France), which has been sealed for thousands of years, were actually made by Neanderthals. This research was performed by Basel archaeologist Dorota Wojtczak together with a team of researchers from France and Denmark, whose findings reveal that the Neanderthals were in fact the first humans with an appreciation of art. See the research here.
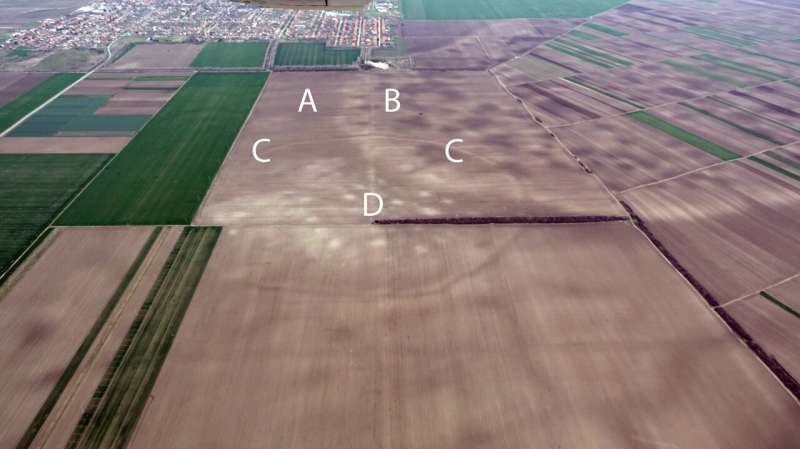

Archaeologists from University College Dublin, working with colleagues from Serbia and Slovenia, have uncovered a previously unknown network of massive sites in the heart of Europe that could explain the emergence of the continent’s Bronze Age megaforts—the largest prehistoric constructions seen prior to the Iron Age. See the research here.
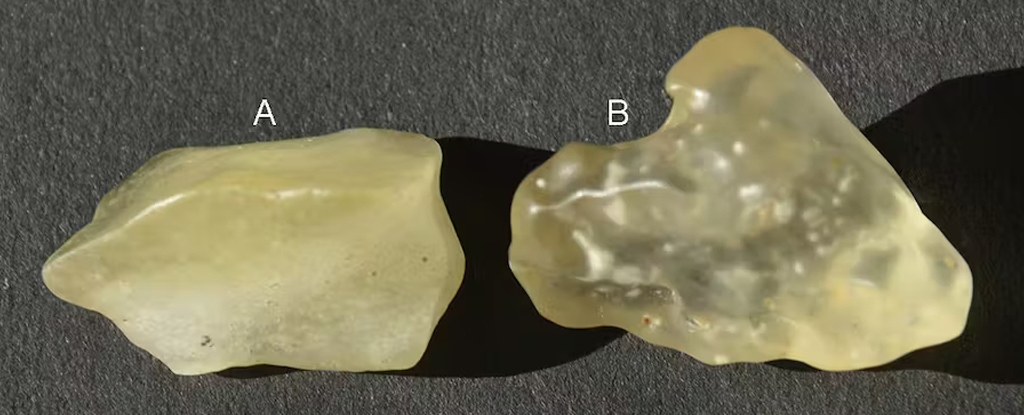
The Great Sand Sea Desert stretches over an area of 72,000km² linking Egypt and Libya. If you find yourself in a particular part of the desert in south-east Libya and south-western parts of Egypt, you’ll spot pieces of yellow glass scattered across the sandy landscape.

The excavation, taking place in the 3000-year-old funerary complex of Las Capellanías, in Cañaveral de León, Spain, uncovered a stela depicting a human figure with detailed face, hands and feet, a headdress, necklace, two swords and male genitals.
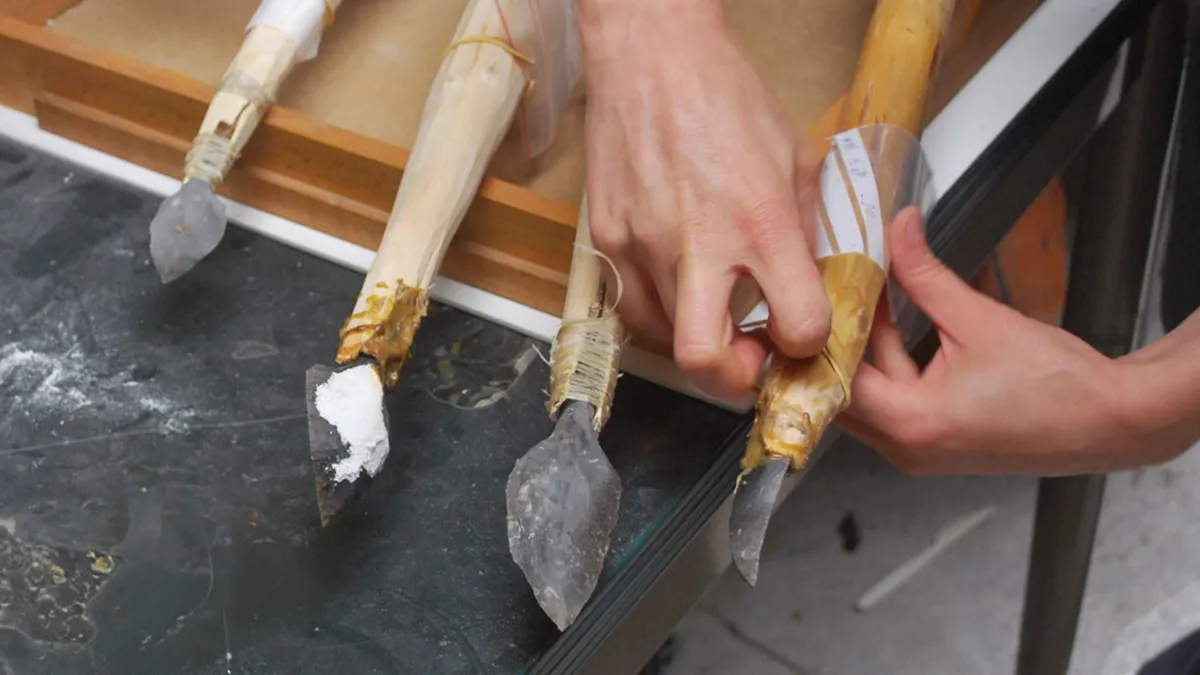

Stone Age people in Belgium were hunting with spear-throwers more than 30,000 years ago — the earliest known evidence of such a weapon in Europe, a new study suggests.
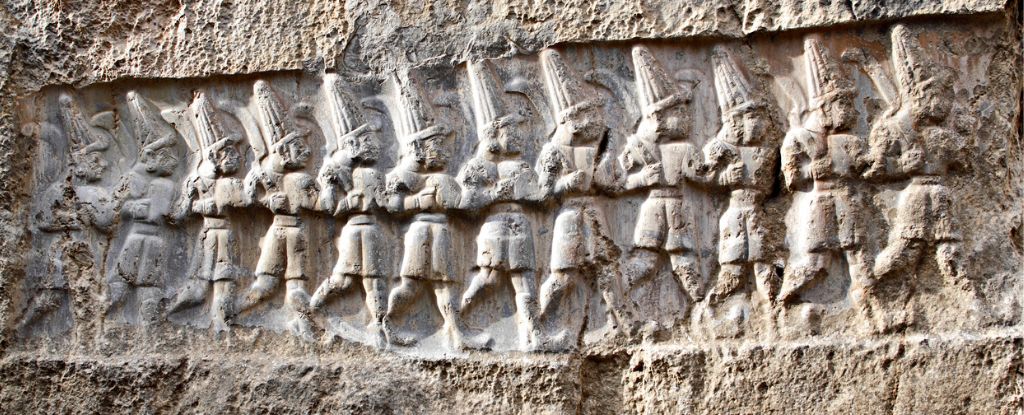

A secret text has been discovered in Türkiye, scattered among tens of thousands of ancient clay tablets, which were written in the time of the Hittite Empire during the second millennium BCE.
Using the James Webb Space Telescope, an international team…has discovered the most distant barred spiral galaxy similar to the Milky Way that has been observed to date. The research, published in Nature, was led by scientists at the Centro de Astrobiología in Spain.
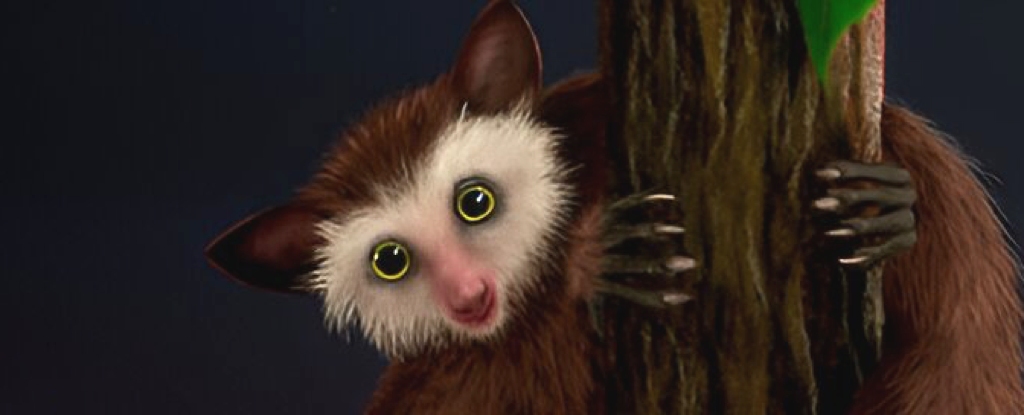

A mysterious primate appeared in North America 30 million years ago, long after the continent’s native primates had died out and even longer before the next big influx of primates – humans – would arrive. The study was published in the Journal of Human Evolution.
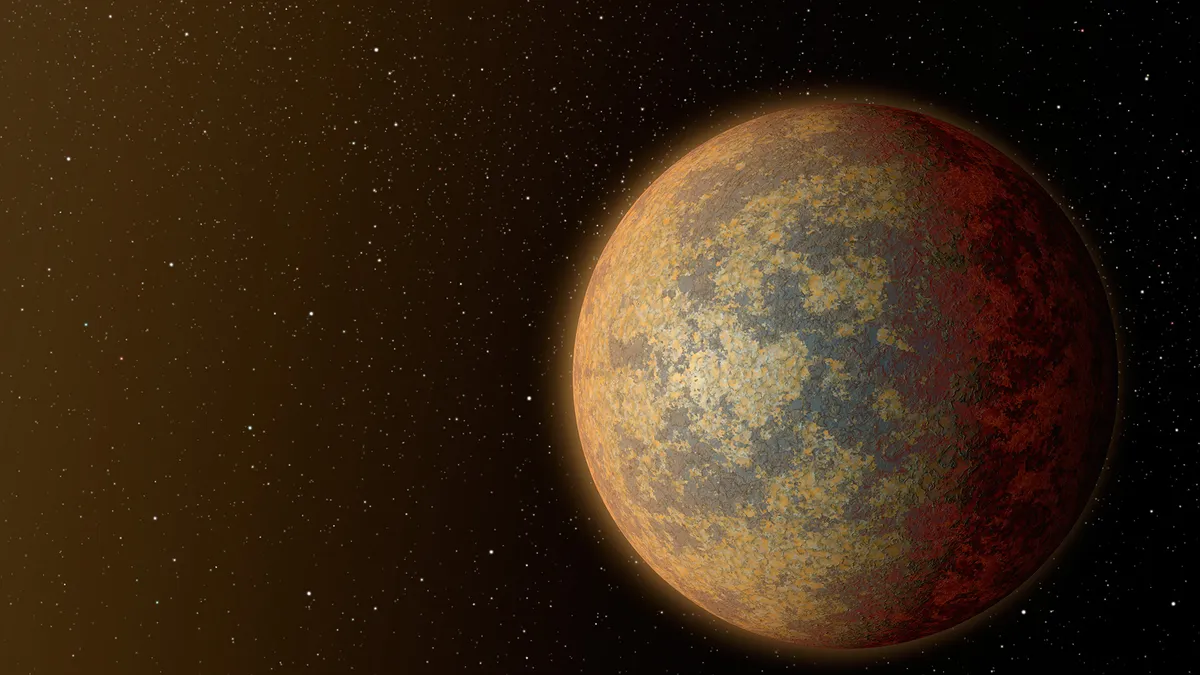
Several exoplanets at the edge of our galaxy could have formed continents — and advanced life — 5 billion years earlier than Earth, new research suggests.
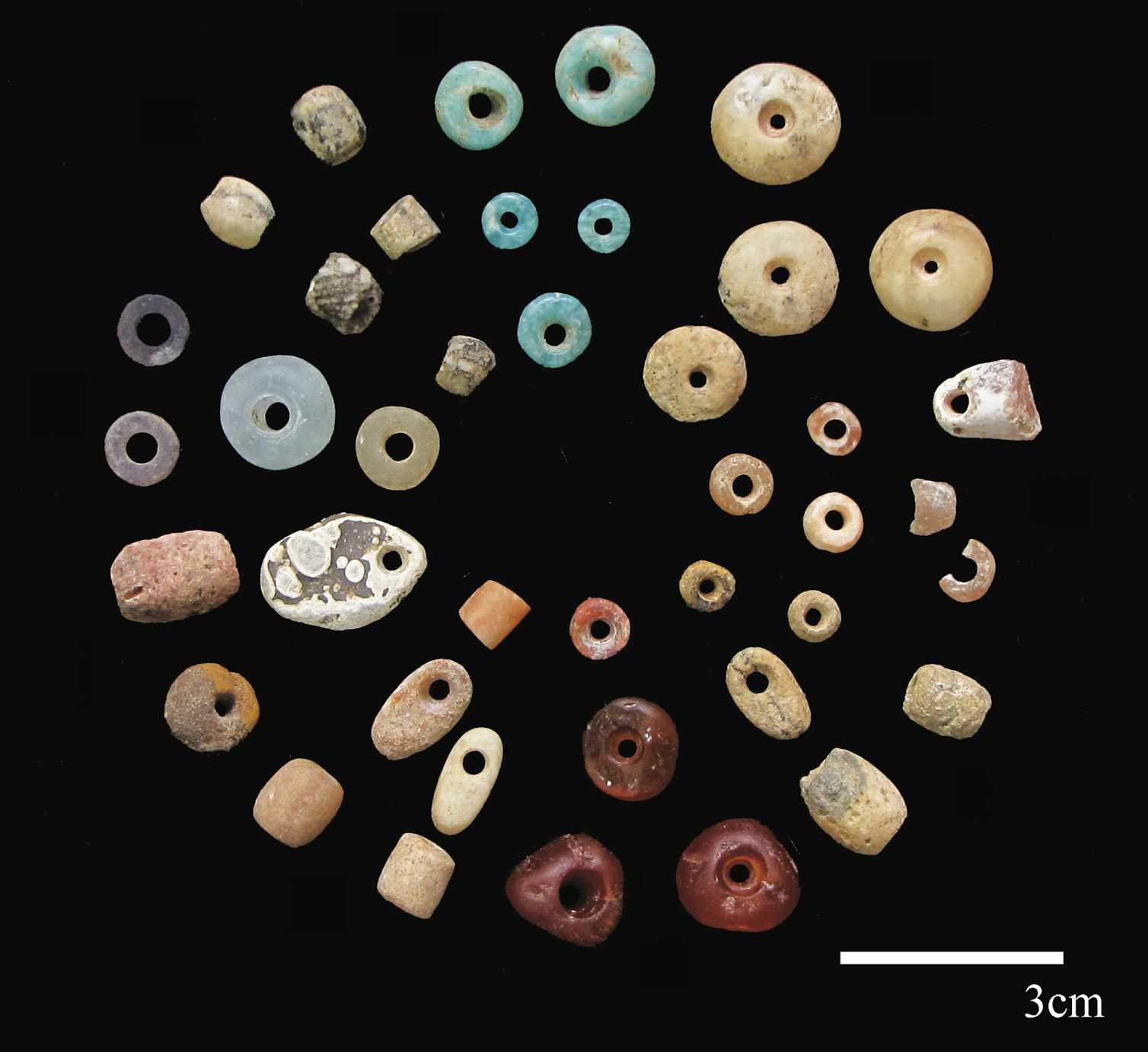

On the shores of Lake Turkana in East Africa, about 5,000 to 4,000 years ago, pastoralists buried their dead in communal cemeteries that were marked by stone circles and pillars.
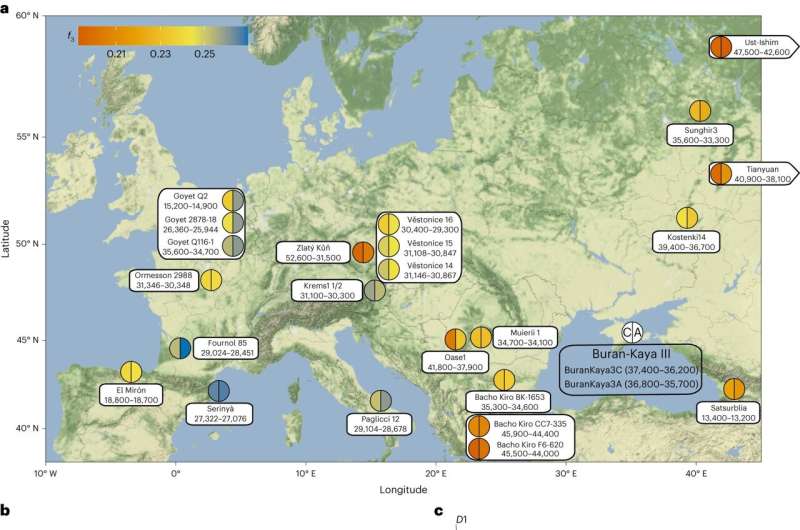
Published in Nature Ecology & Evolution, the new study analyzes two skull fragments dating back between 37,000 and 36,000 years to conclude that our ancestors came from Eastern Europe and migrated westwards.
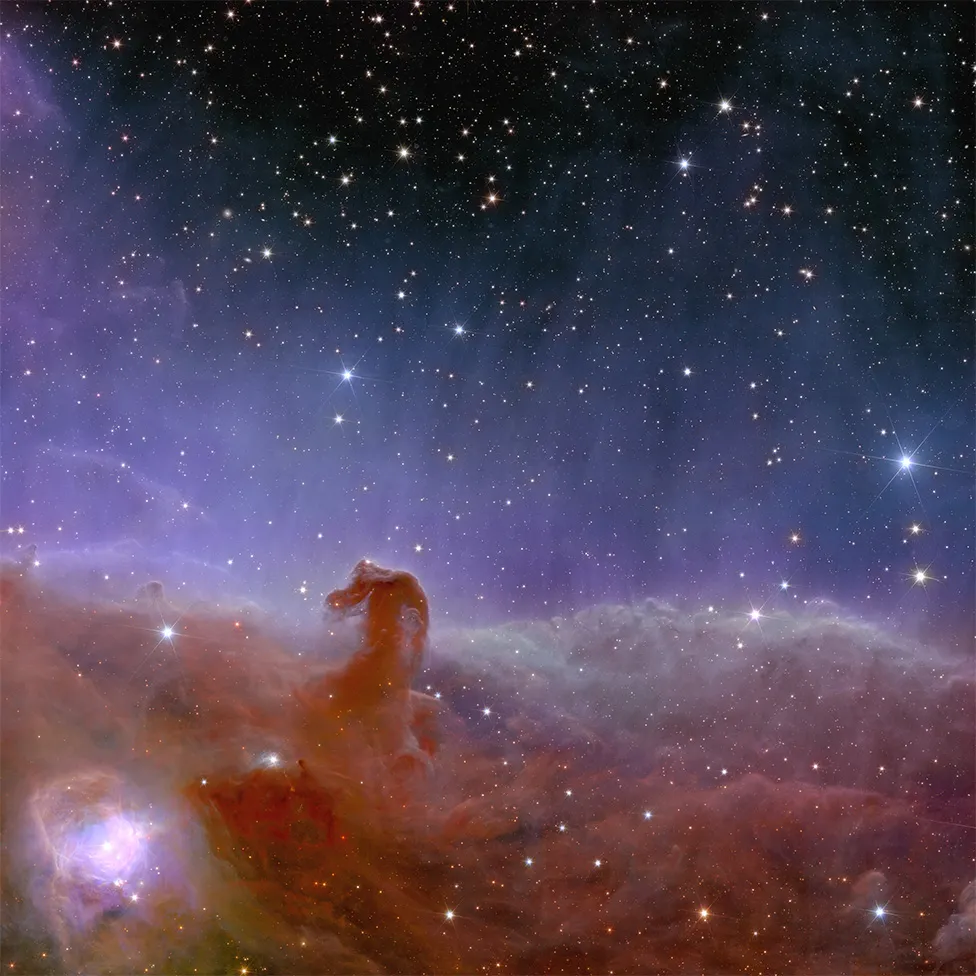

Over the next six years, Euclid will survey a third of the heavens to get some clues about the nature of so-called dark matter and dark energy.








