News Desk
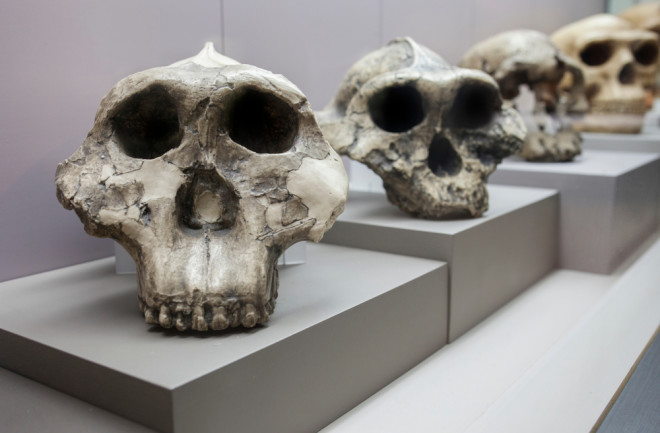

Two-million-year-old teeth (four sets, in fact) tell new stories in a newly posted preprint paper that strips them of enamel and analyzes what the proteins have to say. This “proteomic” approach, which relied on the more rugged protein molecules instead of fragile DNA, revealed their relationship to the wider family tree of early humans.
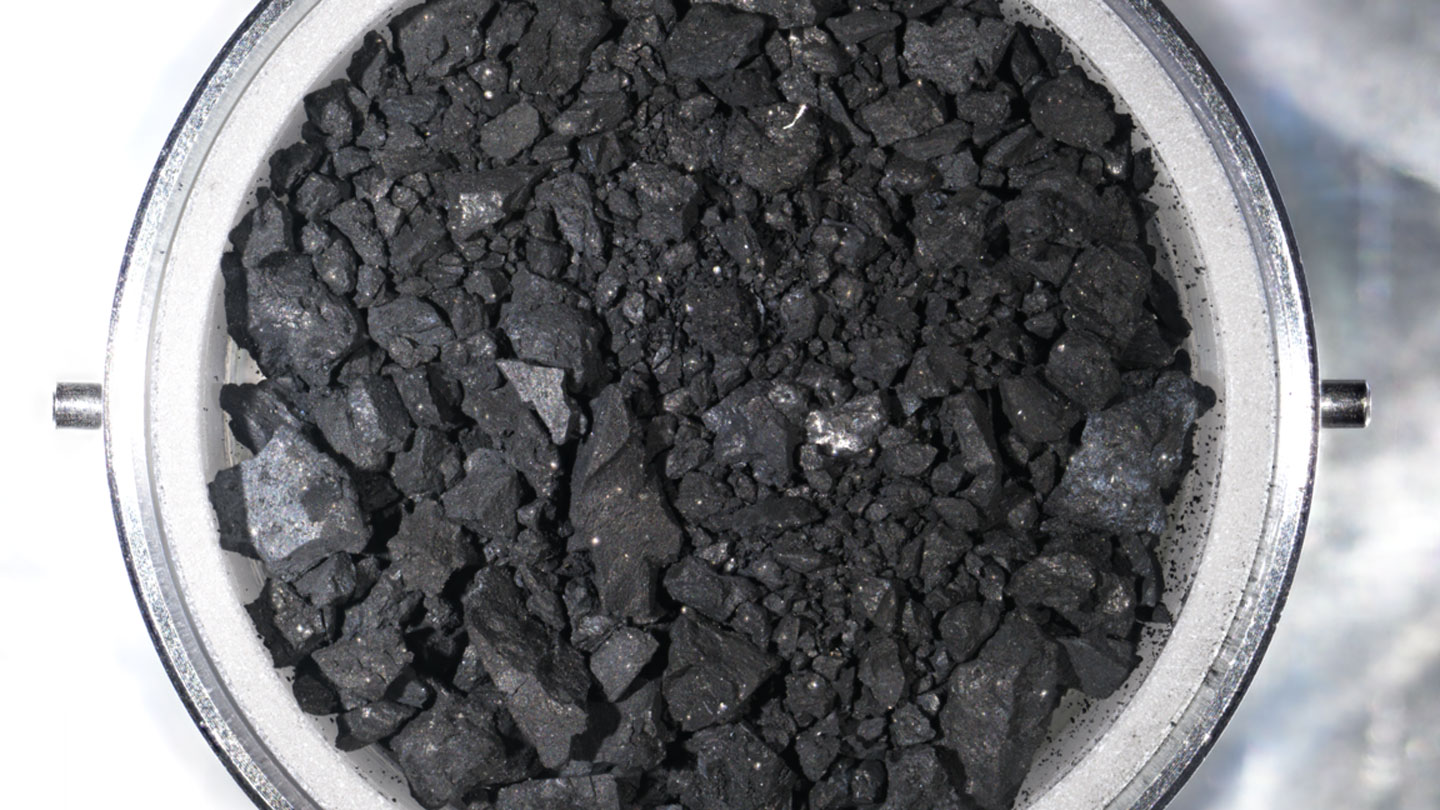

Slivers of Ryugu material, snagged by the Japanese Hayabusa2 spacecraft, appear to come from the solar system’s frozen fringes rather than from the asteroid itself, scientists report July 14 in Science Advances. These foreign fragments could illuminate details of the solar system’s history.

Ancient human skulls, oil lamps and parts of weapons hidden in a cave near Jerusalem are signs the site was used in the Roman era for attempts to speak to the dead — a practice known as necromancy, or “death magic” — according to a new study.
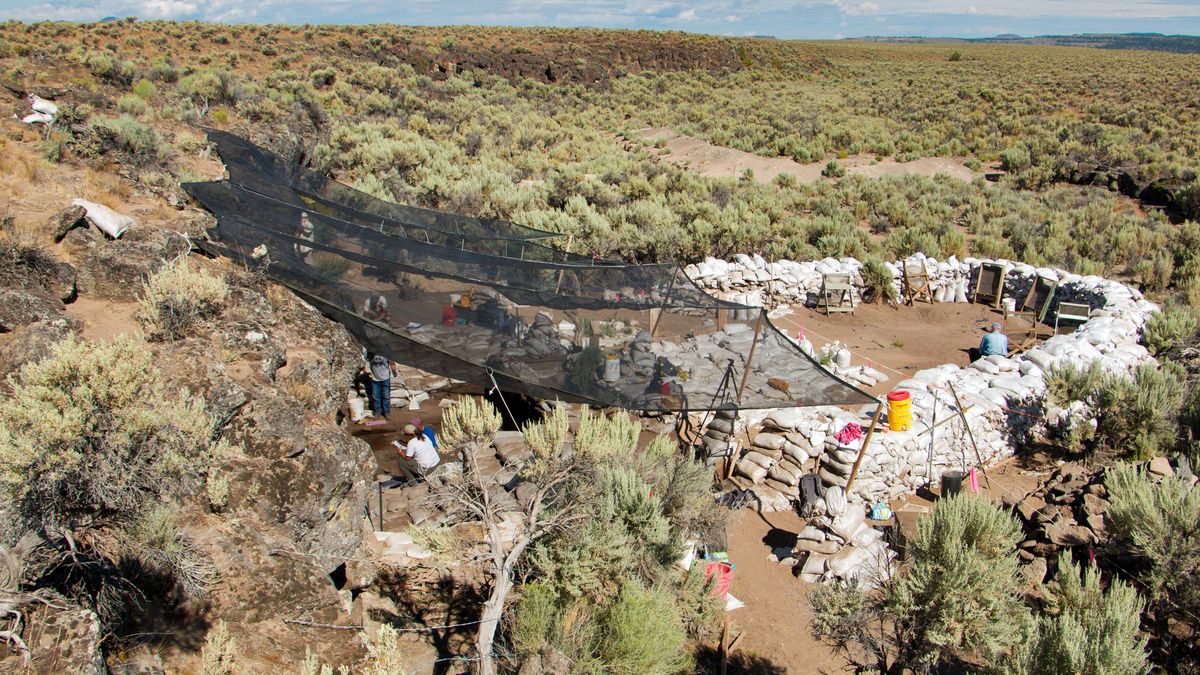

Although this is not the earliest date for human occupation of the Americas that has been proposed, the finding, which is not yet published in a peer-reviewed study, appears to be thousands of years older than any other archaeological site in Oregon.
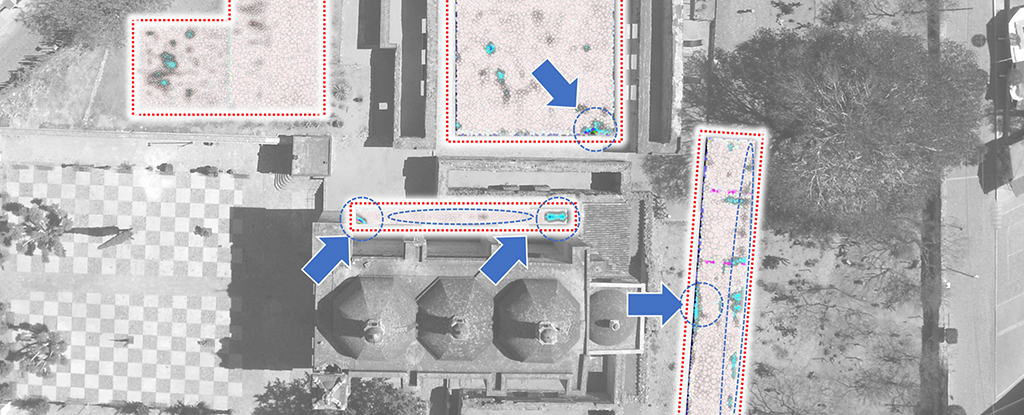
Publishing in the international journal Antiquity, a team of archaeologists from seven countries led by Kiel University has presented the “Big Exchange” project, which uses AI to better understand the networks and interactions of prehistoric and early historic people.
Archaeologists working at the Mitla site in southern Mexico have come across a discovery worthy of an Indiana Jones movie: a labyrinth of chambers and passageways hidden below a church, representing an ‘entrance’ to the underworld.
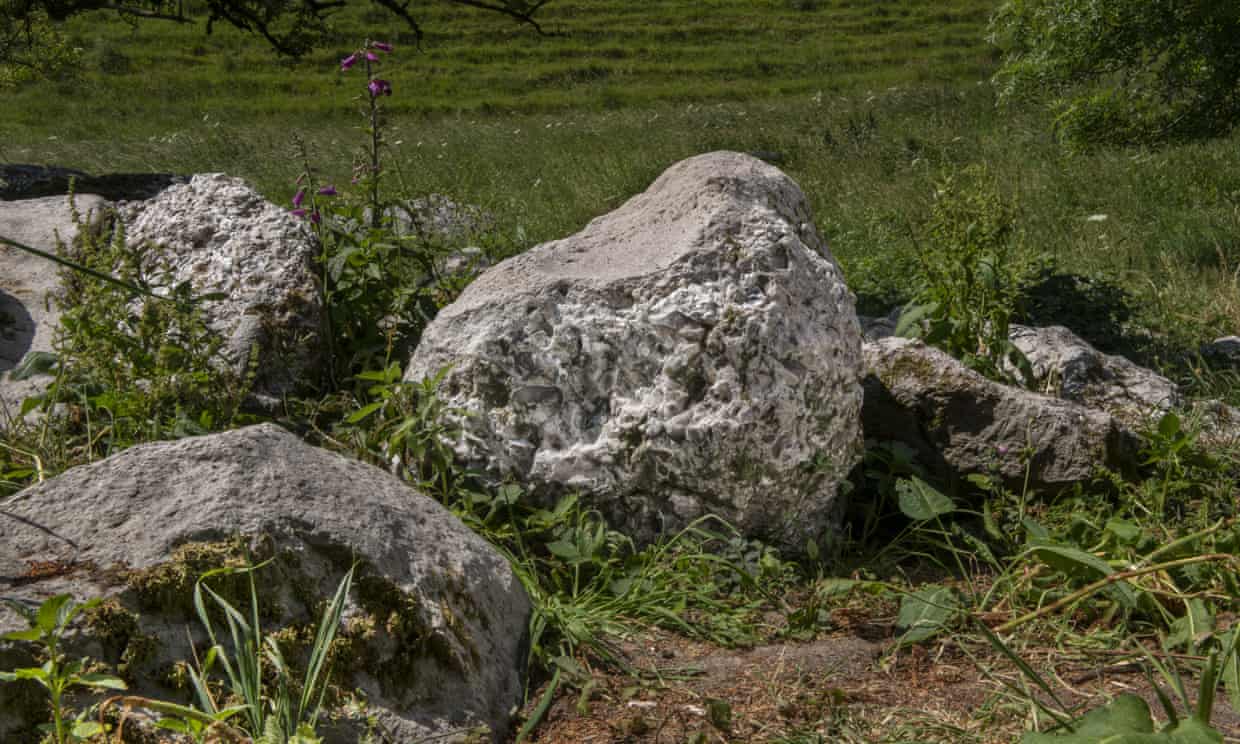

‘Polissoir’, discovered in Valley of Stones nature reserve, was used about 5,000 years ago to hone tools such as axes.

The findings, published in the Journal of Affective Disorders, highlight the importance of experiential avoidance as a potential mechanism underlying the positive effects of psilocybin therapy.
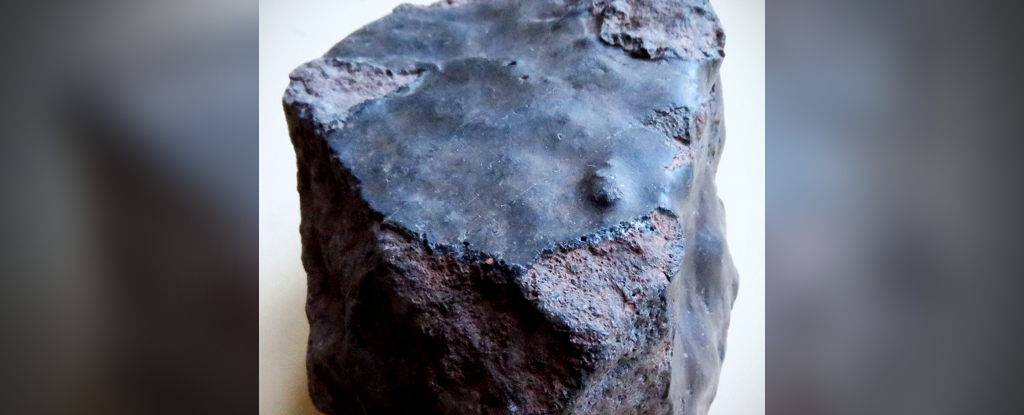

They say what goes around comes around, but it’s unlikely the saying was supposed to ever refer to meteorites. And yet here we are. Scientists are seeking to confirm that a black rock discovered in Morocco in 2018 departed Earth’s pull for outer space, only to return to it like a prodigal child.

New research suggests humans lived in South America at the same time as now extinct giant sloths, bolstering evidence that people arrived in the Americas earlier than once thought.
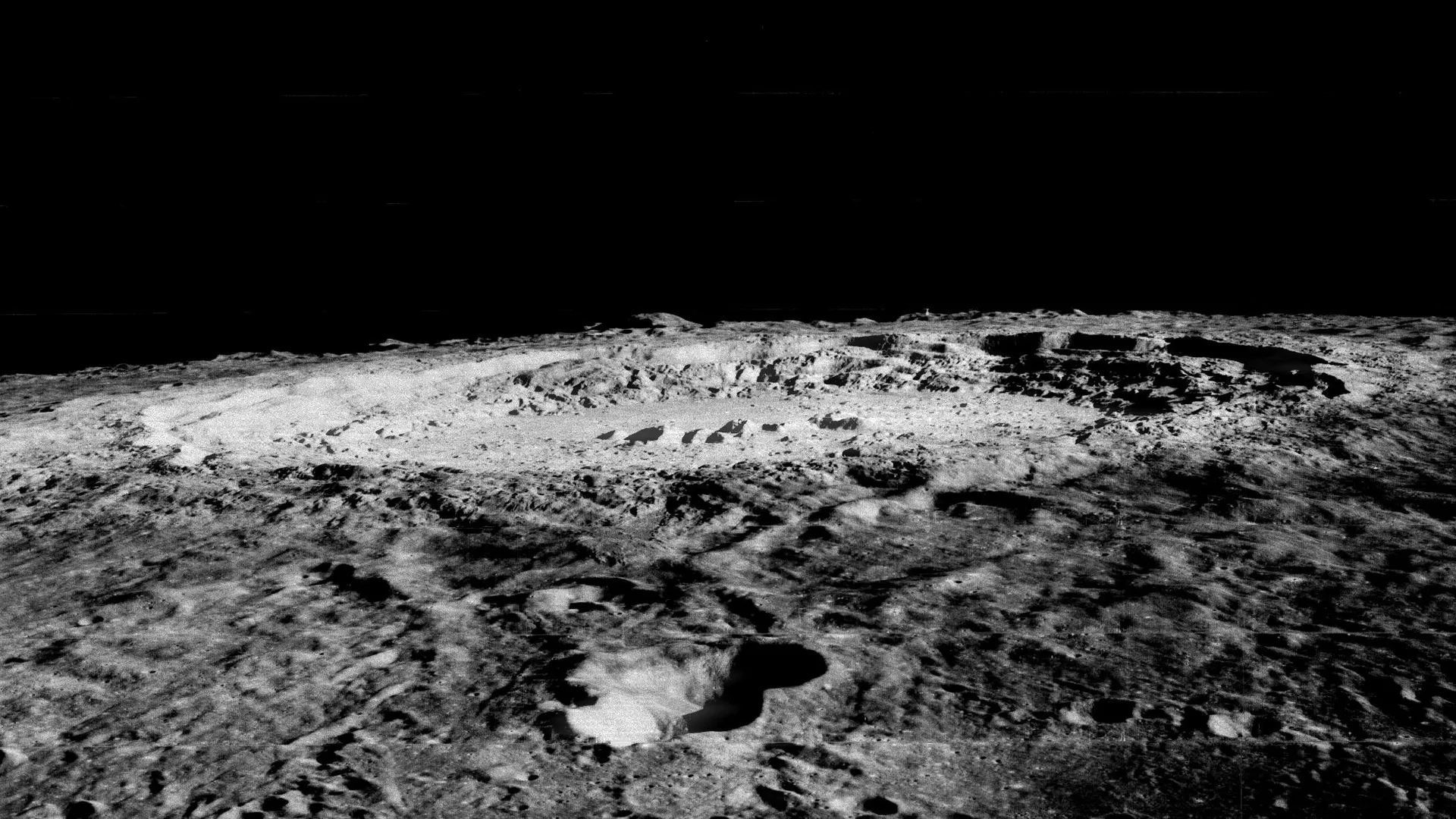

Much of the moon’s surface is 200 million years older than previously estimated, a new analysis suggests.

By marrying the existing expanding Universe theory with a fringe explanation called the tired light hypothesis, Gupta has found the Big Bang could have taken place an astonishing 26.7 billion years ago. That’s twice as old as current models predict. This research was published in the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
The launch of ever-capable large language models (LLMs) such as GPT-3.5 has sparked much interest over the past six months. However, trust in these models has waned as users have discovered they can make mistakes – and that, just like us, they aren’t perfect.
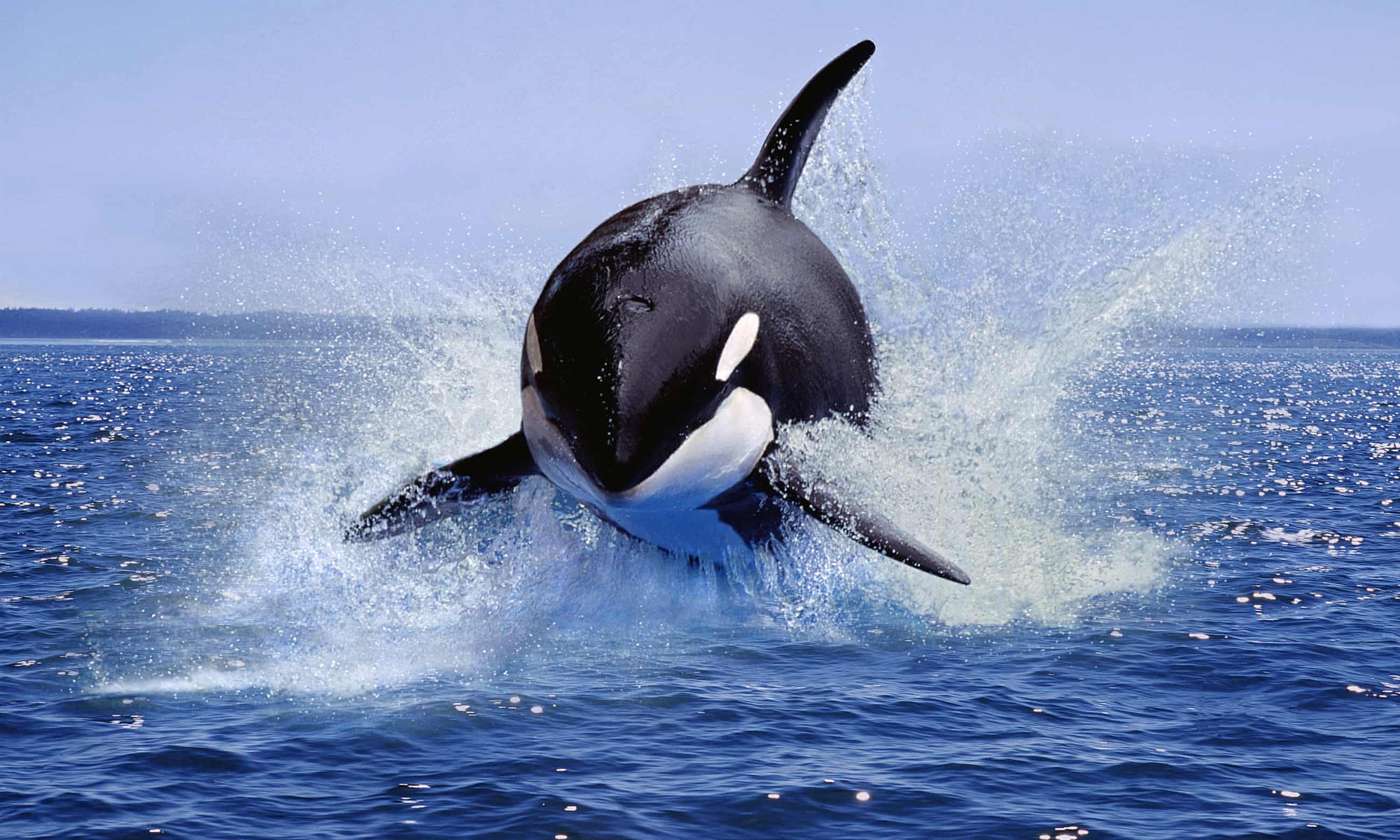

A pod in the strait of Gibraltar has sunk three boats and damaged dozens of others, and their story has captivated the world. What explains this unprecedented behaviour?
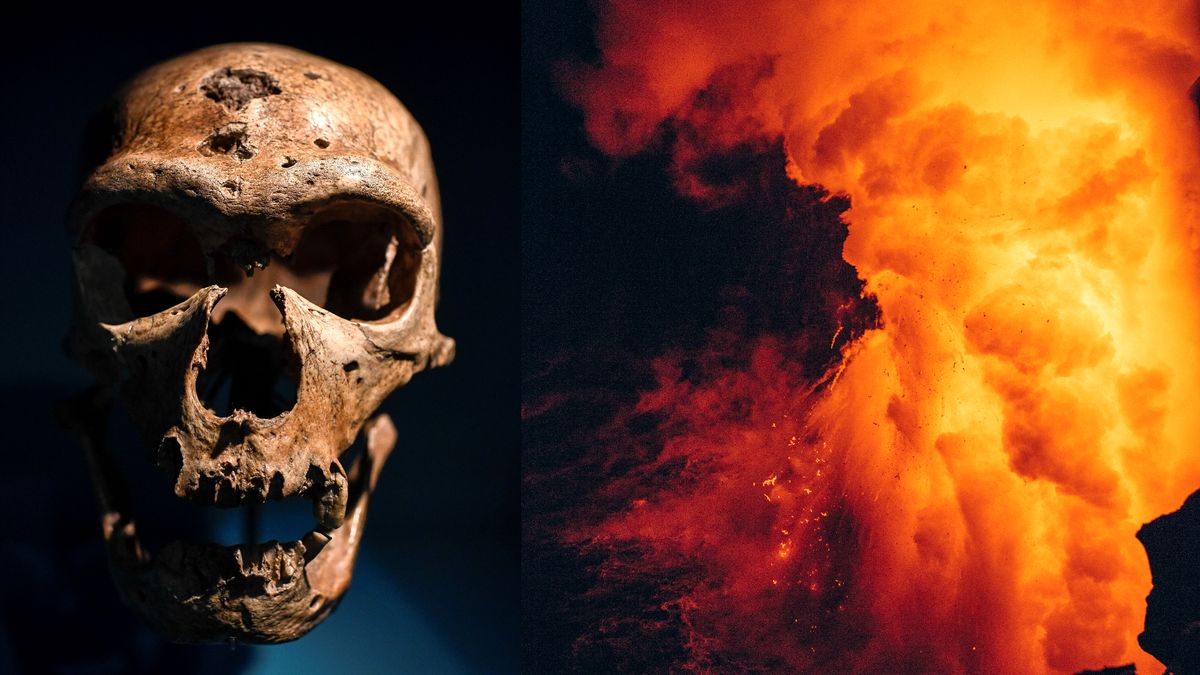
The volcano beneath Italy erupted 40,000 years ago and had catastrophic impact on Earth’s climate — around the same time that the Neanderthals began their slow march to extinction.
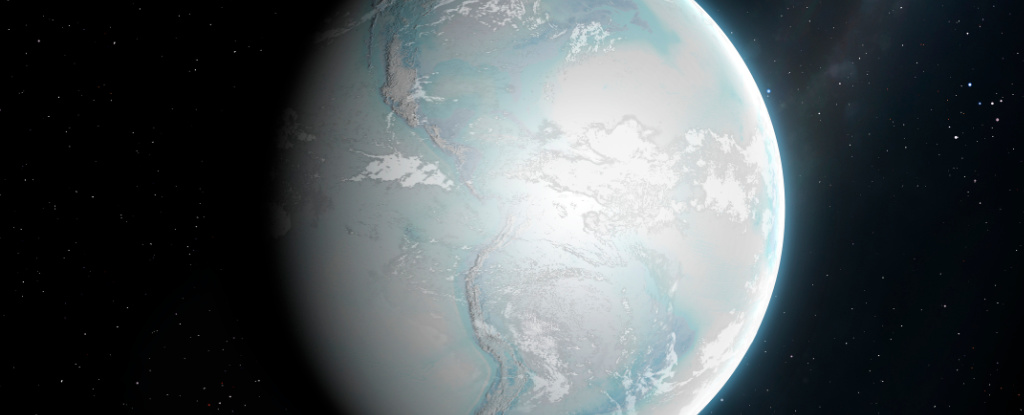

Scientists think they’ve uncovered evidence of the oldest glaciers ever found, in ancient rocks speckled with oxygen isotopes lying beneath the world’s largest gold deposits in South Africa. The study was published in Geochemical Perspectives Letters, with further results presented at the European Association of Geochemistry and the Geochemical Society’s Goldschmidt Conference.








