News Desk
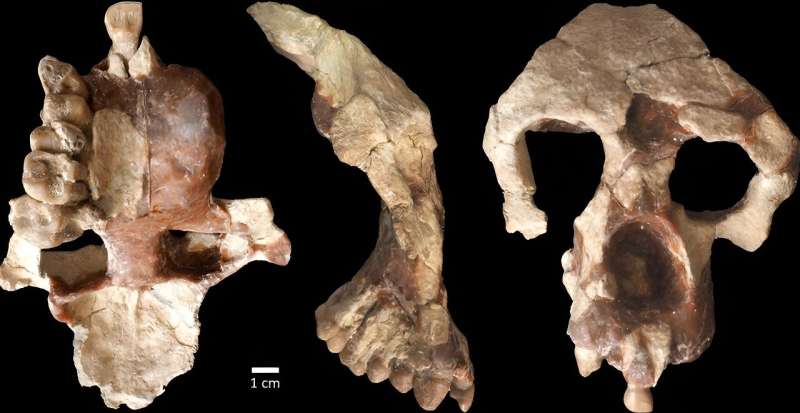
A new fossil ape from an 8.7-million-year-old site in Türkiye is challenging long-accepted ideas of human origins and adding weight to the theory that the ancestors of African apes and humans evolved in Europe before migrating to Africa between nine and seven million years ago. See the study here.

The team extracted DNA from the samples by adapting a protocol previously used for other porous materials, such as bone. The results are published in Scientific Reports.

A recent case study published in Frontiers in Psychology sought to compare the experiences of a near-death experience (NDE) and an experience induced by the psychedelic drug 5-MeO-DMT.
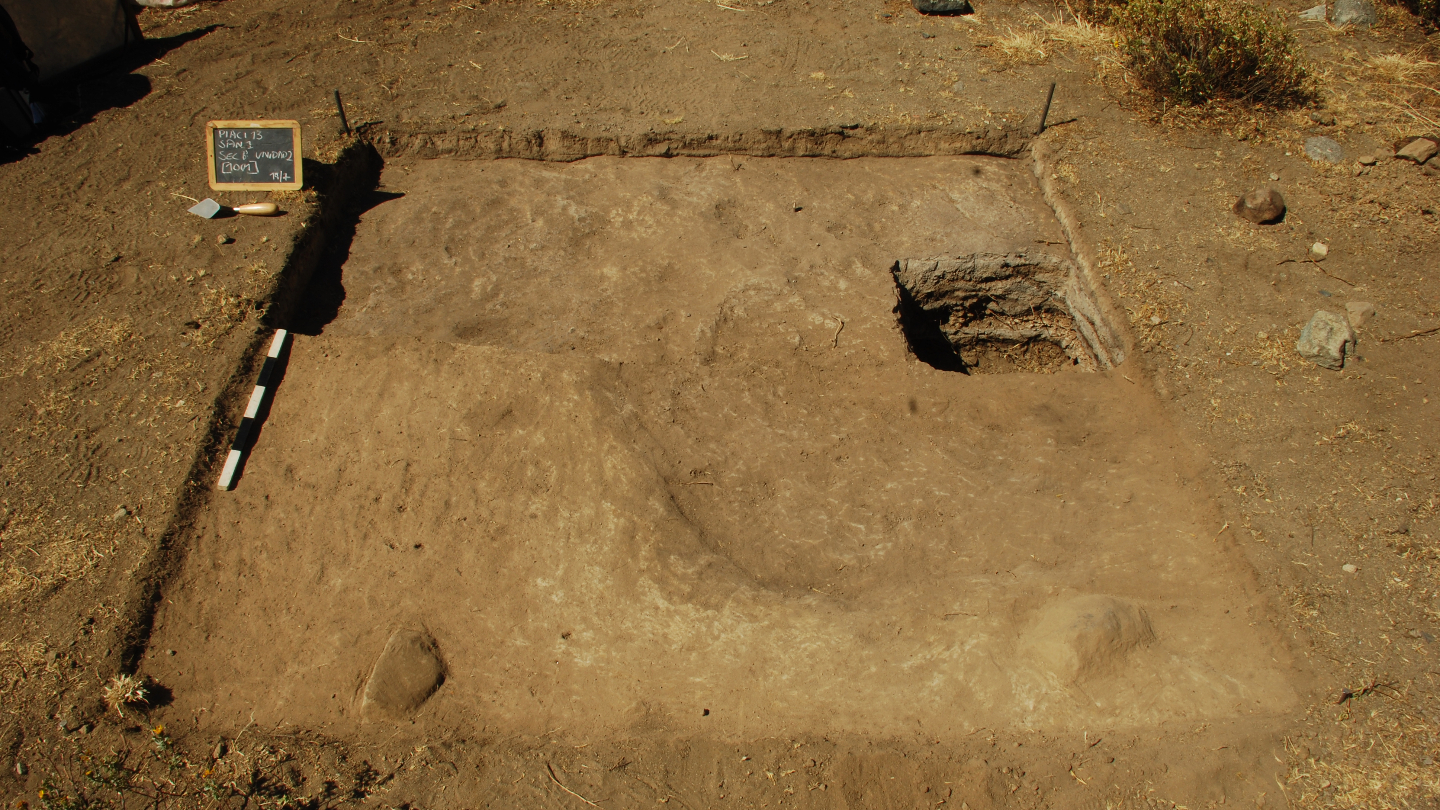

The find provides a rare glimpse into the role played by sound and dance in ancient societies. See the research here.

When archaeologists recently carried out an excavation at Vinjeøra in southern Trøndelag County, they made a surprising discovery that they had only dreamed of finding.
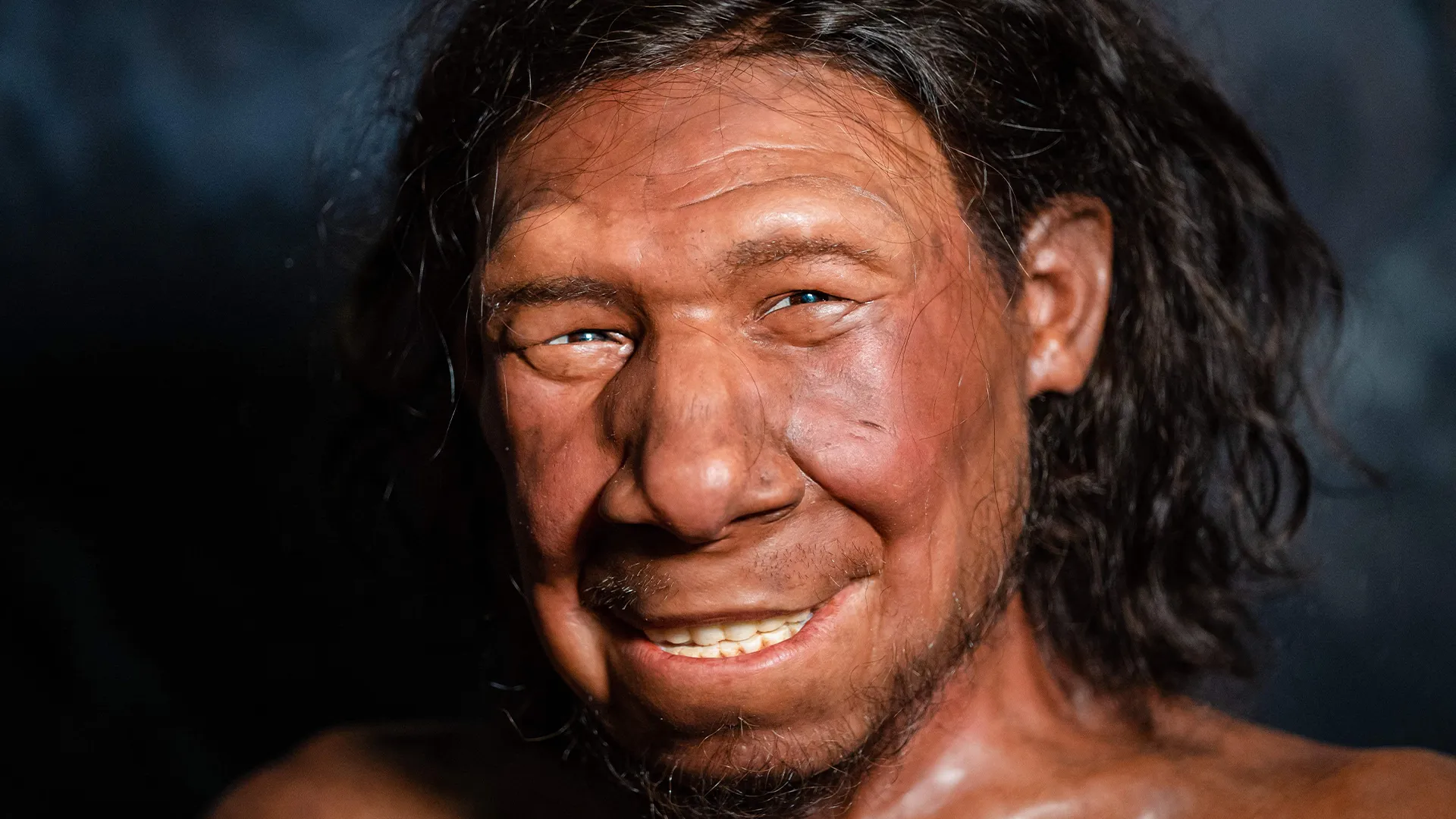

Studies suggest that H. sapiens last shared a common ancestor with Neanderthals somewhere between 600,000 and 800,000 years ago, though the exact date of the split is debated. Neanderthals arose as a distinct population between 400,000 and 350,000 years ago and went extinct around 40,000 years ago, though exactly why isn’t clear.
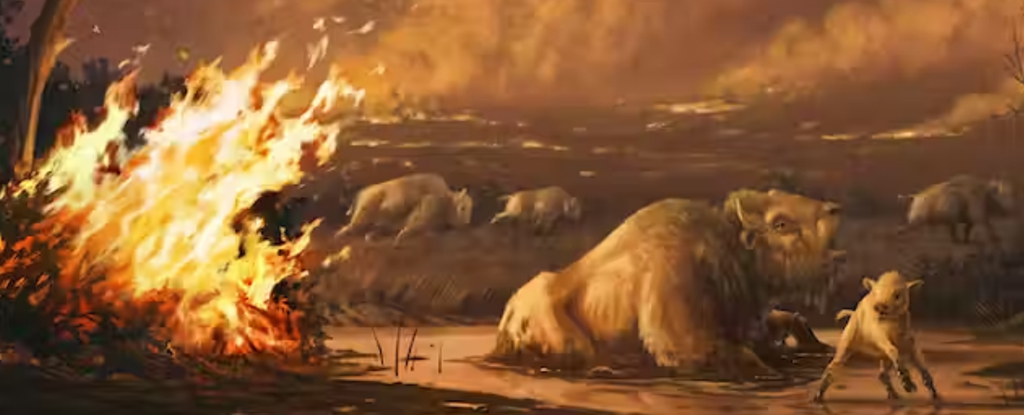

In a new study, published in August 2023, we sought to understand changes that were happening in California during the last major extinction event at the end of the Pleistocene, a time period known as the Ice Age.

A new study found that giving mice 5-MeO-DMT, a short-acting psychedelic, leads to a long-lasting increase of dendritic spine density in the medial frontal cortex region of their brains… The study was published in Neuropsychopharmacology.
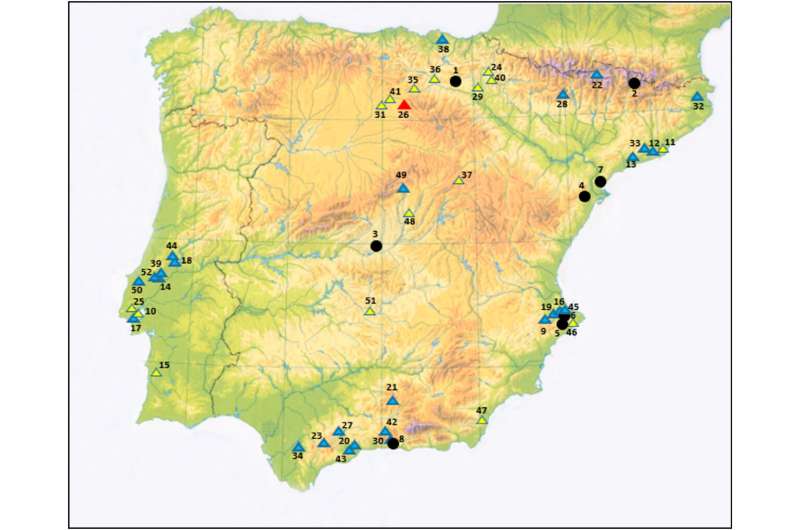
Research led by the Universidad de Alcala, Spain, has revisited Early Neolithic human remains found within the Galería del Sílex cave in Spain’s Sierra de Atapuerca cave system. See the paper here.
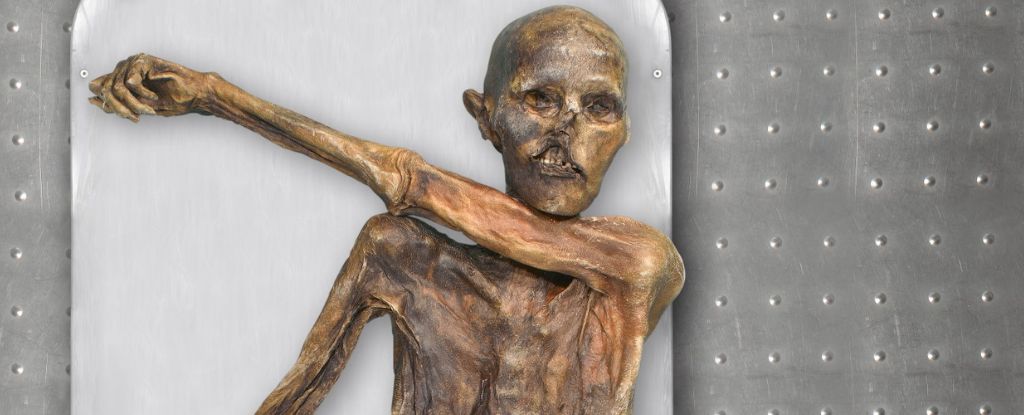

A new and improved DNA analysis of the famous ‘Iceman’ mummy suggests this ancient individual is not who we thought he was. The study was published in Cell Genomics.
A team of Australian and Indonesian researchers have found that reflective shell beads, sewn onto clothing and other items, was a common trend across the islands of Alor, Timor, and Kisar. This means there were shared ornament traditions across the region 12,000 years ago. See the research here.

A new study has shown that arithmetic has biological roots and is a natural consequence of how our perception of the world around us is organised. The results explain why arithmetic is true and suggest that mathematics is a realisation in symbols of the fundamental nature and creativity of the mind.
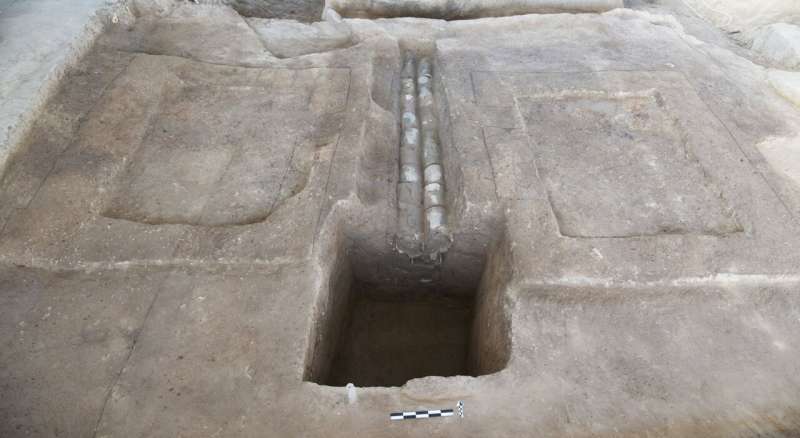

In a study published in Nature Water, the archaeological team describe a network of ceramic water pipes and drainage ditches at the Chinese walled site of Pingliangtai dating back 4,000 years to a time known as the Longshan period.
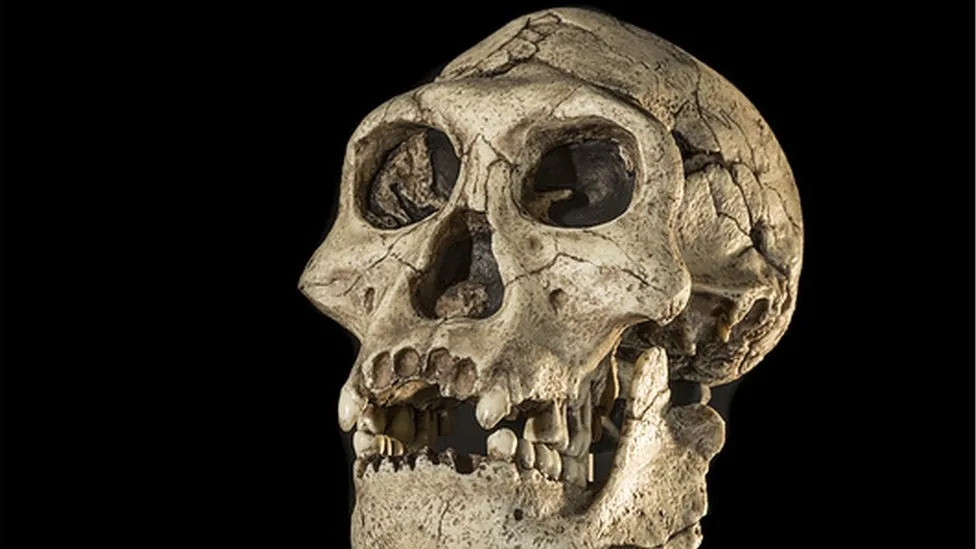

A big freeze previously unknown to science drove early humans from Europe for 200,000 years, but they adapted and returned, new research shows.
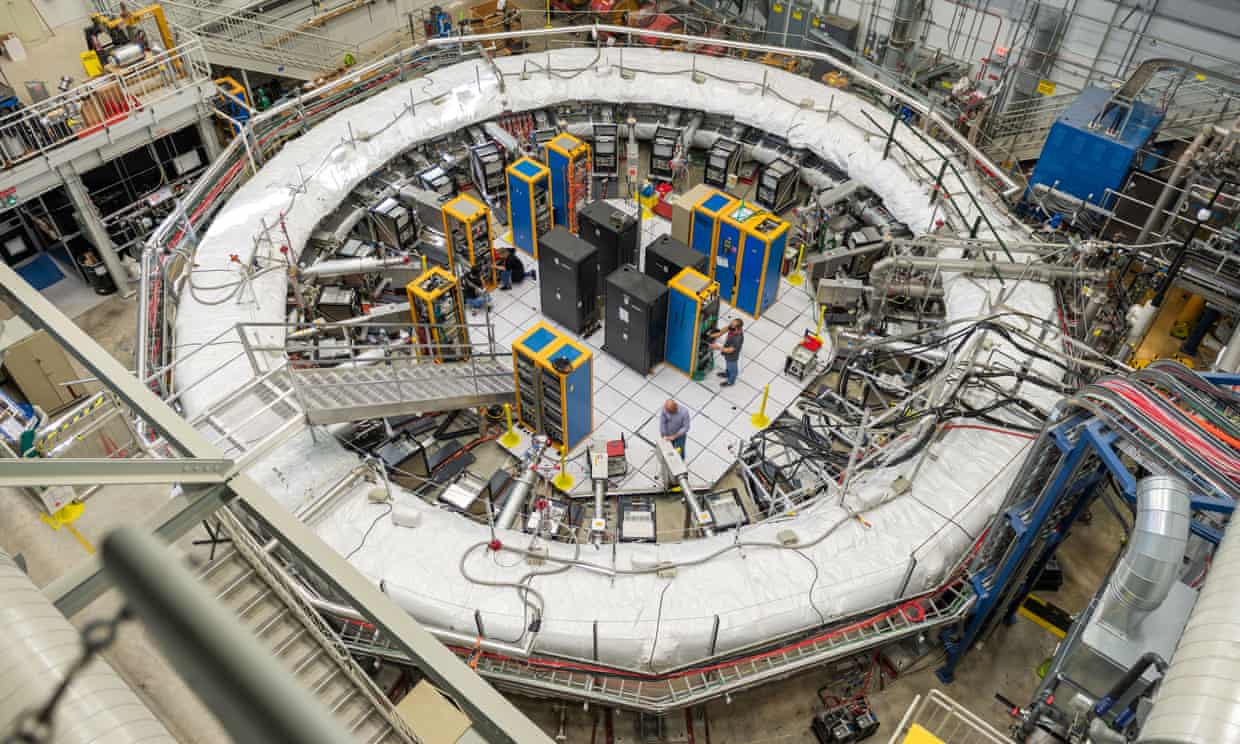

The tantalising theory that a fifth force of nature could exist has been given a boost thanks to unexpected wobbling by a subatomic particle, physicists have revealed.
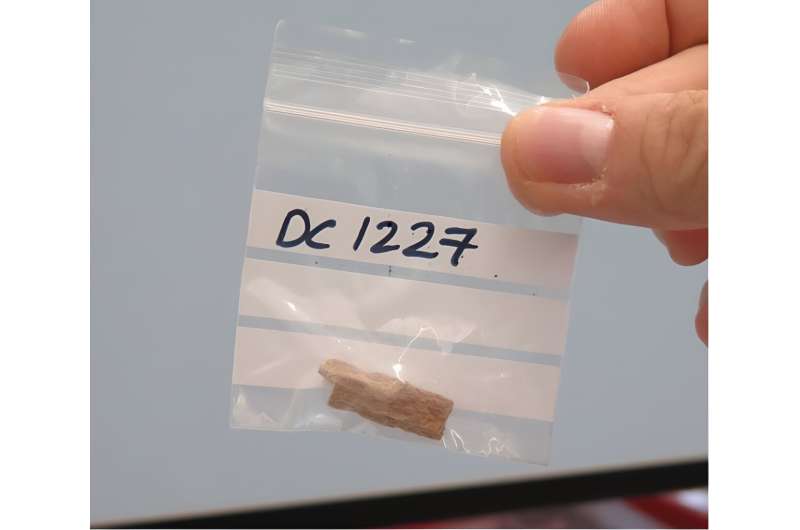

A new study published in the journal Science by an international team finds that past changes in atmospheric CO2 and corresponding shifts in climate and vegetation played a key role in determining when and where early human species interbred.








