News Desk
Some 9,700 years ago, on an autumn day, a group of people were camping on the west coast of Scandinavia. They were hunter-gatherers that had been fishing, hunting and collecting resources in the area. Analysis of DNA left in the chewed resin has been published in Scientific Reports.

A new study offers preliminary evidence that small, regular doses of psilocybin could potentially offer therapeutic benefits, particularly in reducing stress-induced anhedonia (the inability to feel pleasure) and compulsive behaviors.

Researchers have been able to prove, in the first archaeobotanical study of burnt food residues on the surface of ceramic vessels, how varied the meals prepared in Eastern Holstein 5,000 years ago were.

About 8,200 years ago, an underwater landslide known as the Storegga slide near Norway triggered a tsunami that engulfed parts of northern Europe. Around the same time, there was a massive dip in Britain’s population. See the research here.

In a groundbreaking study, researchers at the University of Chicago have discovered that low doses of LSD may have potential antidepressant effects. The findings have been published in the journal Neuropsychopharmacology.
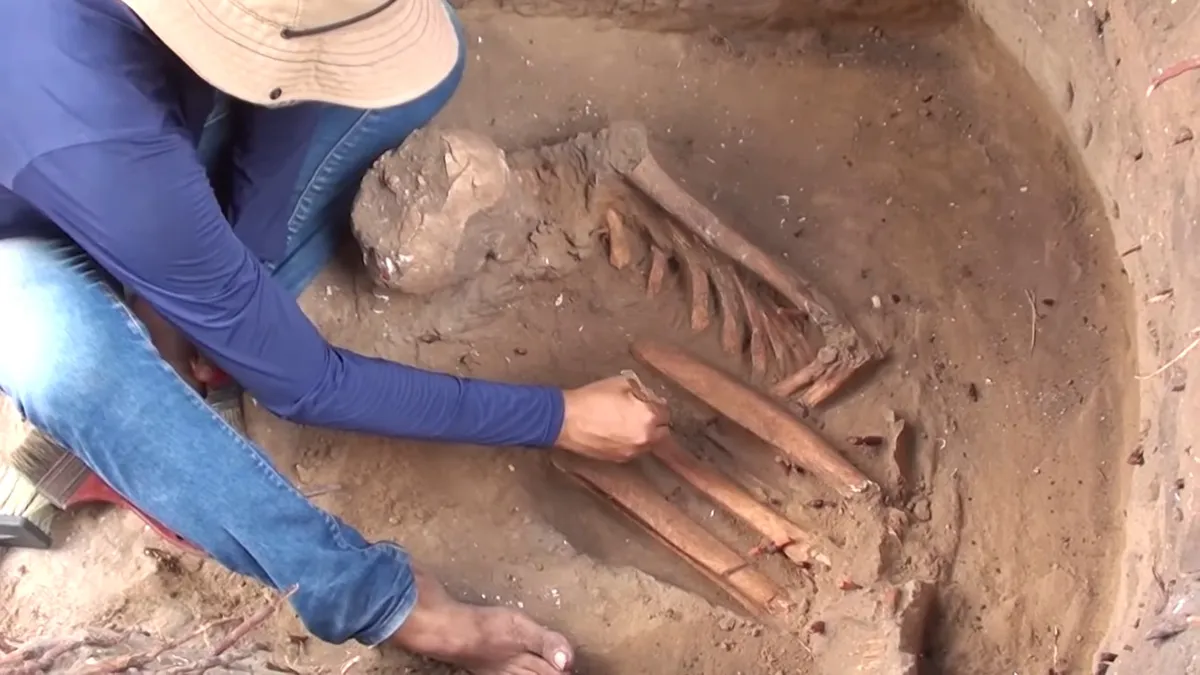

Evidence of at least four populations from different times in Brazil’s history was found at the same archaeological site.

Windswept piles of dust, or layers of ice? ESA’s Mars Express has revisited one of Mars’s most mysterious features to clarify its composition. Its findings suggest layers of water ice stretching several kilometers below ground—the most water ever found in this part of the planet.

The random nature of genetic mutation implies evolution is largely unpredictable. But recent research suggests this may not be entirely so, with interactions between genes playing a bigger role than expected in determining how a genome changes.
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/73062155/stsci_01gqqfcdz3j7arc9f8qdxe0f7z__1_.0.jpg)
Monsters lurk in the background of James Webb Space Telescope images. Scientists are scrambling to make sense of them.
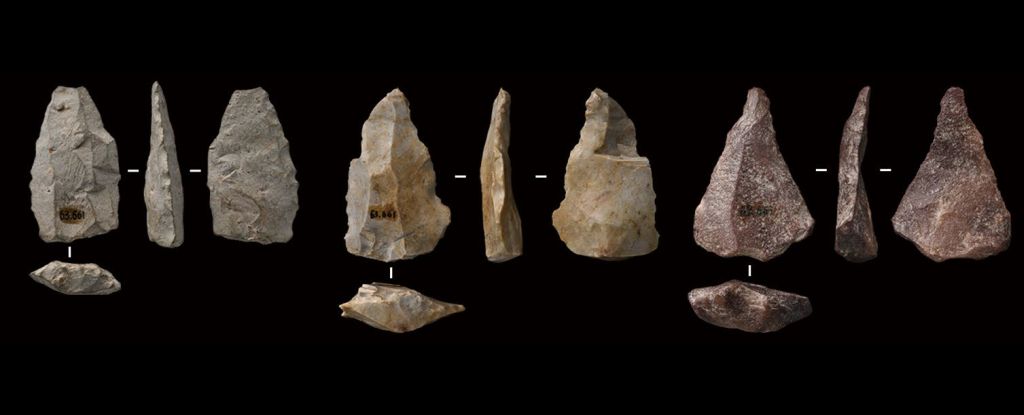

Fragments of ancient rock and bone in Eastern Asia are changing our understanding of the history of human migration. They’re artifacts found in the Shiyu site of northeastern China, and new analysis has revealed that they were created by Homo sapiens some 45,000 years ago. See the research here.

The tale of one female woolly mammoth, written in the layers of her tusk, has shown researchers how the extinct megafauna species moved across Alaska with humans right on their heels…Her life and its connection to human activity have been described in a recent paper published in Science Advances.

In a recent Scientific Reports study, researchers examined the brain’s reaction to Cannabis Sativa, the plant responsible for giving pot smokers the munchies after firing up a joint.
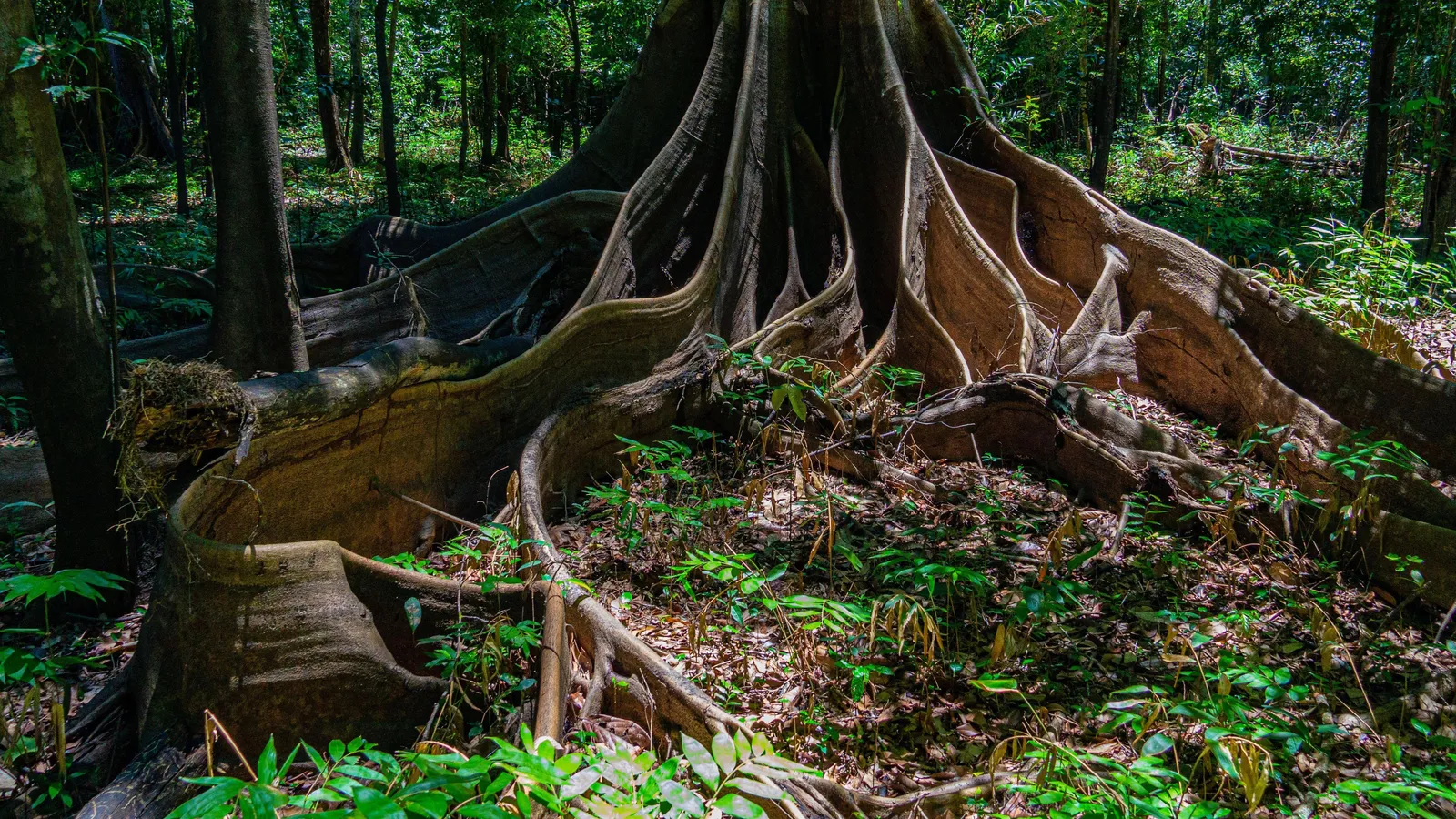

Amid the discovery of a lost city in the Amazon rainforest, scientists are uncovering a different kind of relic underground – one that’s still being used today.

Crocodile-like skin belonging to an early species of reptile is the oldest fossilized skin ever discovered, dating back almost 290 million years — 130 million years older than the previous record holder.

As analytical methods get more sophisticated, existing scientific models are constantly reexamined. The latest to come under scrutiny is the way molecules are organized at the surface of a volume of salt water. See the research here.
Complex, multicellular life emerged on Earth 600-700 million years ago. For the first time, scientists have accurately dated some of the oldest examples of complex life. See the research here.








