News Desk

A 1,800-year-old silver amulet discovered in a burial in Germany is the oldest evidence of Christianity north of the Alps, according to a new study.

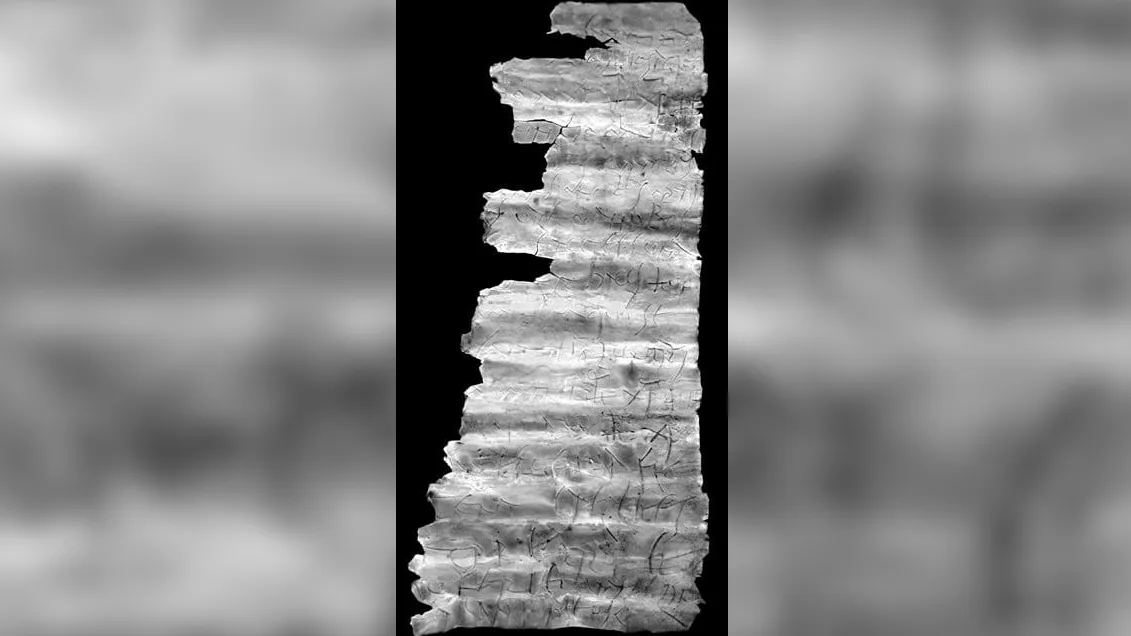
A team of archaeologists from across Georgia has confirmed the impressions represent samples of a script that has never been documented, raising questions on the spread and preservation of writing across the transcontinental region.This research was published in the Journal of Ancient History and Archaeology.
A new study, not yet peer reviewed but published on the biological sciences repository bioRxiv, suggests an ancestor of P. cubensis could have come from Africa before spreading far and wide.
The remains of at least 37 people unearthed from the Early Bronze Age site of Charterhouse Warren in England have revealed the darker side of human prehistory…the findings have been published in the journal Antiquity.

A granite boulder carved more than 35,000 years ago deep in a cave in Israel may be the oldest evidence of ritual practices in the Holy Land, a new study suggests.

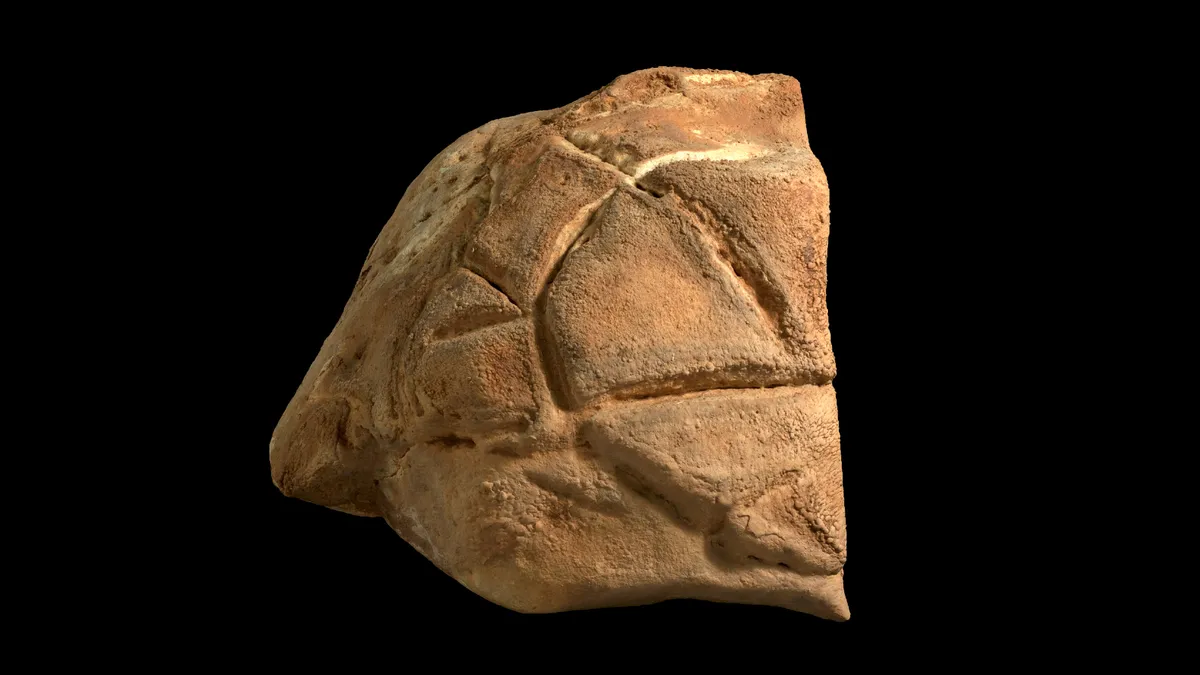
Archaeologists Dr. Wim van Neer, Dr. Bea De Cupere, and Dr. Renée Friedman have published a study on the earliest evidence of horn modification in livestock in the Journal of Archaeological Science.
A new study published in the Journal of Psychoactive Drugs has uncovered significant associations between naturalistic ayahuasca use and improved mental health.

The people associated with the Neolithic Cucuteni-Trypilla culture lived across Eastern Europe from approximately 5500 to 2750 BCE. With up to 15,000 inhabitants, some of their mega-sites are among the earliest and largest city-like settlements in prehistoric Europe.

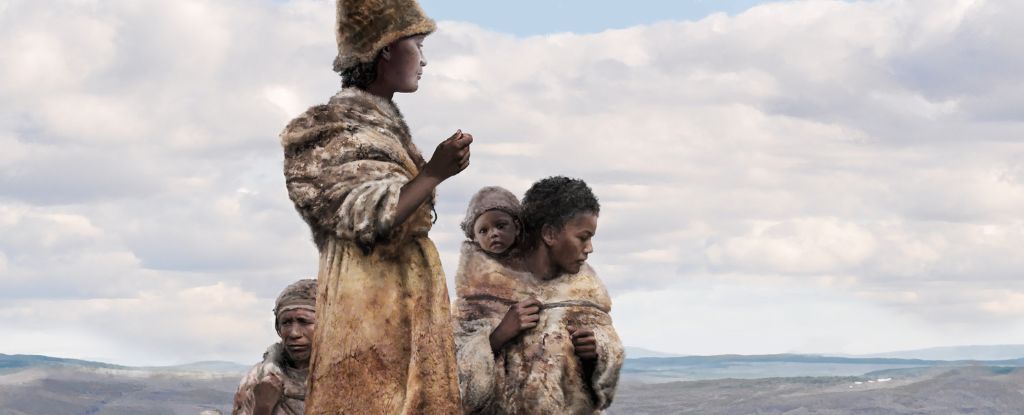
The Bering land bridge that spanned between Siberia and Alaska during the Ice Age was more of a Bering land bog, new research finds.
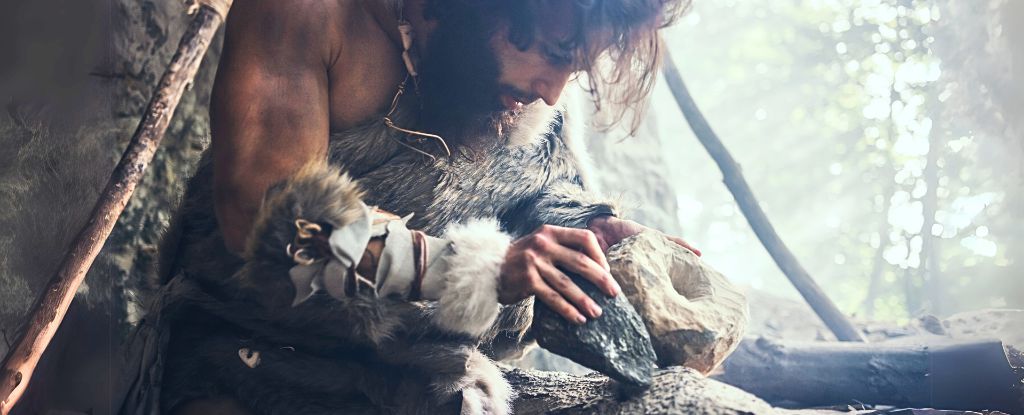

Around 900,000 years ago stone tech 2.0 was released into Spain. University of Santiago de Compostela anthropologist Diego Lombao and colleagues found the earliest known European example of advanced stone tool techniques. This research was published in the Journal of Paleolithic Archaeology.

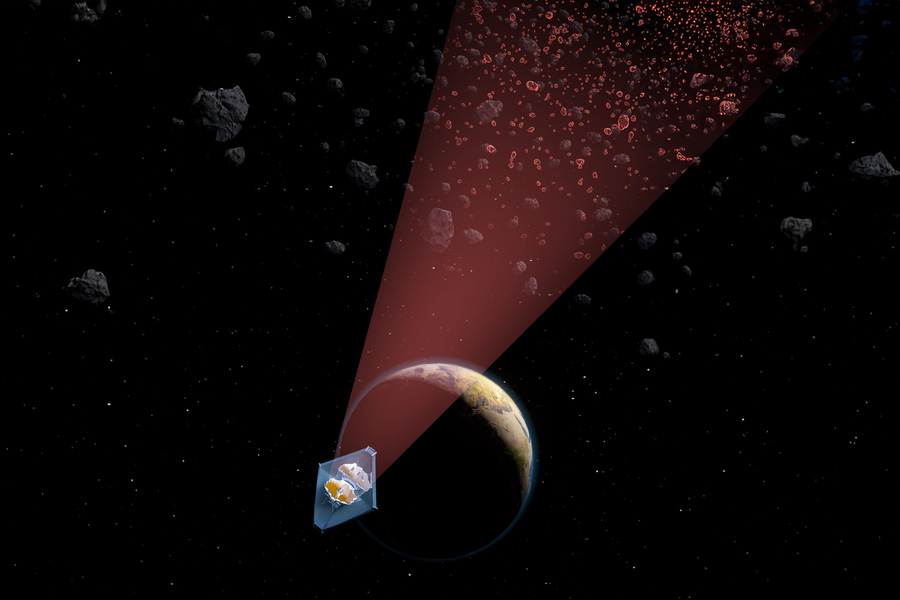
The team’s detection method, which identified 138 space rocks ranging from bus- to stadium-sized, could aid in tracking potential asteroid impactors. In a paper appearing in the journal Nature, the researchers report that they have used their approach to detect more than 100 new decameter asteroids in the main asteroid belt.

Homo sapiens groups assembled at the cave to hold torchlit ceremonies, probably inspired by mythological or religious beliefs, as early as around 37,000 years ago, researchers report December 9 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.

A fertile stretch of the Nile River, flanked by arid deserts to the east and west, has supported human life for over a million years. The Middle Nile Valley has a history of diverse subsistence strategies, including pastoralism, hunting, fishing, and plant foraging, made possible by unique features underground.

Our earliest studies of Neanderthals were fundamentally flawed.









